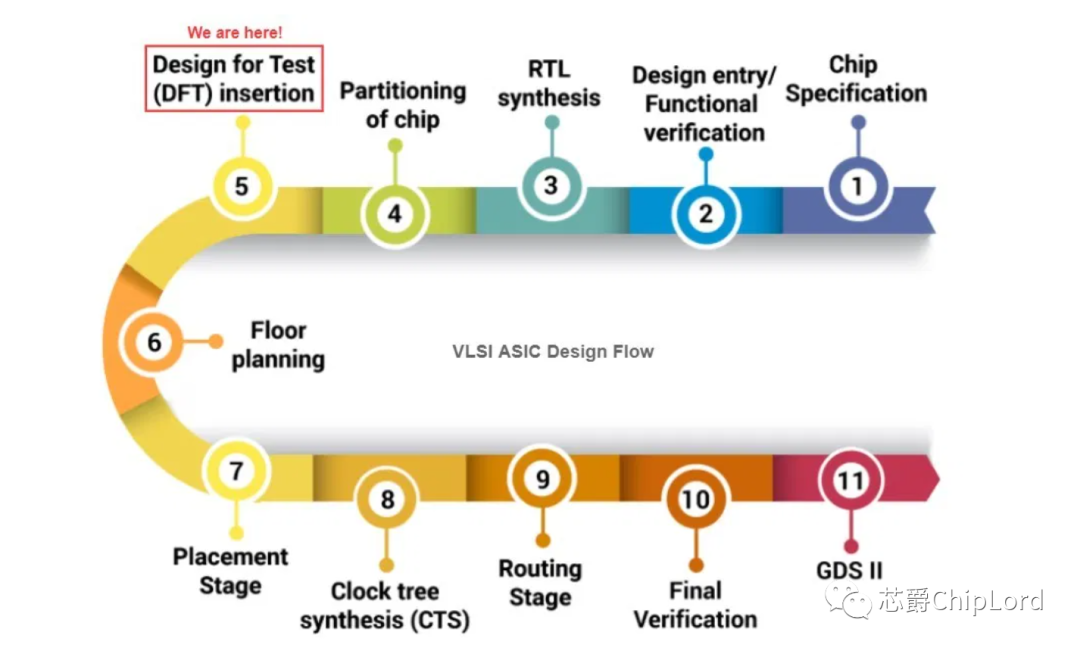
什么是Design for Tesability,我们为什么需要它?
芯片在制造过程中的问题
解决问题的办法:DFT
DFT的作用
测试时序电路
优化芯片制造过程
DFT可以永久的消除故障吗?
验证和测试的关系?
验证和测试的不同点
职业选择?验证 vs DFT
术语介绍
测试的分类
芯片失效的来源
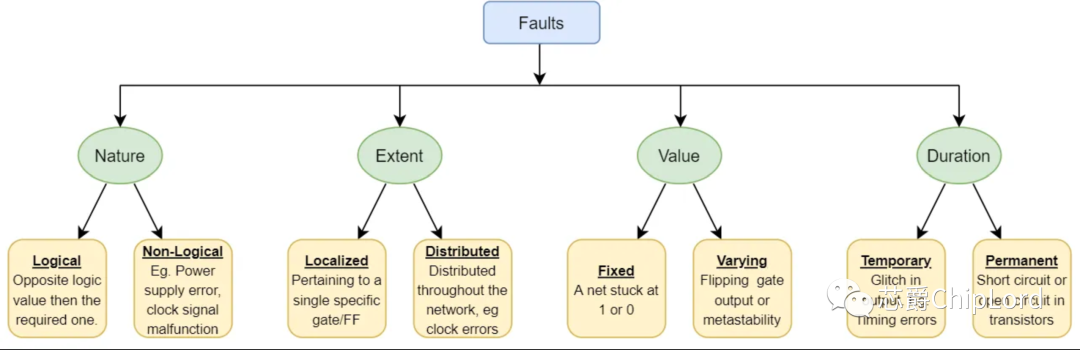
失效的分类
DFT技术详解
专用DFT技术
结构化DFT技术
总结
软件问题:此外,除了制造过程的defect,用于设计芯片的EDA软件的bug或者工程师的失误,也会造成芯片失效。
应用问题:在一些关键应用中,我们无法承受芯片的故障。例如,在医疗行业,设备控制器中的单个故障甚至会造成个人生命危险。对于使用低温燃料运行的火箭或航天飞机,其控制芯片需要在较宽的温度范围内工作。因此,这些芯片的测试条件应针对特定的环境且在极端条件上进行,以防止使用过程中发生任何故障。
| |
Testing: An experiment in which the system is put to work and its resulting response is analyzed to ascertain whether it behaved correctly
Diagnosis: Process for locating the cause of misbehavior in the circuit if it happened
Defect: Refers to a flaw in the actual hardware or eleectronic system
Fault: it is a model or representation of defect for analyzing in a computer program
Error: it is caused by a defect and happens when a fault in hardware causes line/gate output to have a wrong value
Failure: this occurs when a defect causes misbehavior in the circuit of functionality of a system and cannot be reversed or recovered
Fault Coverage: Percentage of the total number of logic faults that can be tested using a given test set T
Defect Level: Refers to the fraction of shipped parts that are defective. Or, the propotion of the faulty chip in which fault isn't detected and has been classified as good.
System-level