主要介绍下蓝牙协议栈(bluetooth stack) 串口协议(bluetooth SPP)Serial Port Profile 协议概念介绍。
本专栏文章我们会以连载的方式持续更新,本专栏计划更新内容如下:
第一篇:蓝牙综合介绍 ,主要介绍蓝牙的一些概念,产生背景,发展轨迹,市面蓝牙介绍,以及蓝牙开发板介绍。
第二篇:Transport层介绍,主要介绍蓝牙协议栈跟蓝牙芯片之前的硬件传输协议,比如基于UART的H4,H5,BCSP,基于USB的H2等
第三篇:传统蓝牙controller介绍,主要介绍传统蓝牙芯片的介绍,包括射频层(RF),基带层(baseband),链路管理层(LMP)等
第四篇:传统蓝牙host介绍,主要介绍传统蓝牙的协议栈,比如HCI,L2CAP,SDP,RFCOMM,HFP,SPP,HID,AVDTP,AVCTP,A2DP,AVRCP,OBEX,PBAP,MAP等等一系列的协议吧。
第五篇:低功耗蓝牙controller介绍,主要介绍低功耗蓝牙芯片,包括物理层(PHY),链路层(LL)
第六篇:低功耗蓝牙host介绍,低功耗蓝牙协议栈的介绍,包括HCI,L2CAP,ATT,GATT,SM等
第七篇:蓝牙芯片介绍,主要介绍一些蓝牙芯片的初始化流程,基于HCI vendor command的扩展
第八篇:附录,主要介绍以上常用名词的介绍以及一些特殊流程的介绍等。
另外,开发板如下所示,对于想学习蓝牙协议栈的最好人手一套。以便更好的学习蓝牙协议栈,相信我,学完这一套视频你将拥有修改任何协议栈的能力(比如Linux下的bluez,Android下的bluedroid)。

-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
CSDN学院链接(进入选择你想要学习的课程):
蓝牙交流扣扣群:970324688
Github代码:
入手开发板:
蓝牙学习目录:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
SPP是Serial Port Profile(串口协议)的缩写,其定义了使用蓝牙进行RS232(或类似)串行电缆仿真的设备应使用的协议和过程。简单来说就是在蓝牙设备之间建立虚拟的串口进行数据通信。说白了就是可以两个设备对端发送自定义数据,NOTED:苹果不支持SPP协议。
目前SIG最新的版本是V1.2,之前更早的版本在官网只有V1.1可以下载到,但是这两份文档没有功能上的差别,所以不做介绍

Device A (DevA) – This is the device that takes initiative to form a connection to another device
Device B (DevB) – This is the device that waits for another device to take initiative to connect.
说白了就是就是两台设备连接,谁发起的连接角色就是Device A,被连接的就是Device B,但是这个和其他协议不同,两台设备之前的code基本都是一样,角色只是区分两台设备。

Device A是发起连接的主动房,所以Device A要至少支持Establish link and set up virtual serial connection.,Device B是被连接的乙方,所以要至少支持Accept link and establish virtual serial connection和Register Service record for application in local SDP database.以便Device A查询服务并且连接,但是此协议漏掉最主要的两个功能,发送数据,接收数据,或者SIG是觉得rfcomm做到了这个功能,所以不写在SPP协议中吧,但是我还是决定要在SPP介绍收发功能。
This procedure refers to performing the steps necessary to establish a connection to an emulated serial port (or equivalent) in a remote device. The steps in this procedure are:
1)Submit a query using SDP to find out the RFCOMM Server channel number of the desired application in the remote device. This might include a browsing capability to let the user select among available ports (or services) in the peer device. Alternatively, if it is known exactly which service to contact, it is sufficient look up the necessary parameters using the Service Class ID associated with the desired service.
2)Optionally, require authentication of the remote device to be performed. Also optionally, require encryption to be turned on.
3) Request a new L2CAP channel to the remote RFCOMM entity.
4) Initiate an RFCOMM session on the L2CAP channel.
5) Start a new data link connection on the RFCOMM session, using the aforementioned server channel number.After step 5, the virtual serial cable connection is ready to be used for communication between applications on both sides.
This procedure refers to taking part in the following steps:
1)If requested by the remote device, take part in authentication procedure and, upon
further request, turn on encryption.
2) Accept a new channel establishment indication from L2CAP.
3) Accept an RFCOMM session establishment on that channel.
4) Accept a new data link connection on the RFCOMM session. This may trigger a local request to authenticate the remote device and turn on encryption, if the user has required that for the emulated serial port being connected to (and authentication/encryption procedures have not already been carried out).
This procedure refers to registration of a service record for an emulated serial port (or equivalent) in the SDP database. This implies the existence of a Service Database, and the ability to respond to SDP queries.
NOTED:SPP只有安卓手机支持,并且部分安卓手机必须有SPP APP才可以连接,iphone手机不能直接SPP,但是又一个替代协议IAP,此协议需要买MFI chip才能用
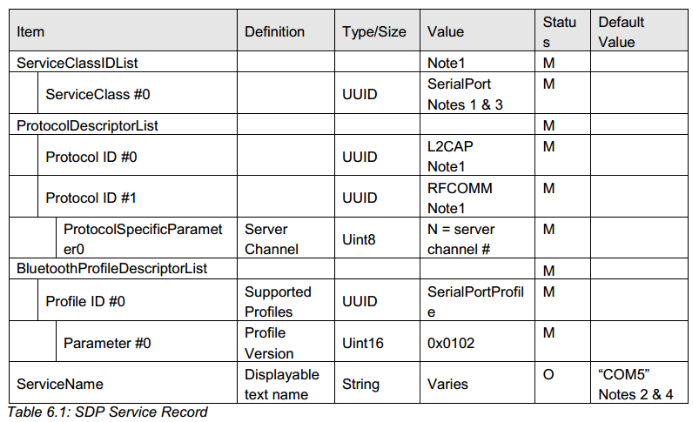
我看下我们的SDP注册:
static const uint8_t spp_service_record[] =
{
/* 1.ServiceClassIDList */
SDP_DES_SIZE8, 0x8,
SDP_UINT16, BT_ATTRIBUTE_SERVICE_CLASS_ID_LIST>>8&0xff, BT_ATTRIBUTE_SERVICE_CLASS_ID_LIST&0xff, /* Service class ID list attribute */
SDP_DES_SIZE8, 3,
SDP_UUID16, BT_SERVICE_CLASS_SERIAL_PORT>>8&0xff, BT_SERVICE_CLASS_SERIAL_PORT&0xff,
/* 2.ProtocolDescriptorList */
SDP_DES_SIZE8, 0x11,
SDP_UINT16, BT_ATTRIBUTE_PROTOCOL_DESCRIPTOR_LIST>>8&0xff, BT_ATTRIBUTE_PROTOCOL_DESCRIPTOR_LIST&0xff,/* Protocol descriptor list attribute */
SDP_DES_SIZE8, 0xc,
SDP_DES_SIZE8, 0x3,
SDP_UUID16, BT_PROTOCOL_L2CAP>>8&0xff, BT_PROTOCOL_L2CAP&0xff, /*L2CAP*/
SDP_DES_SIZE8, 0x5,
SDP_UUID16, BT_PROTOCOL_RFCOMM>>8&0xff, BT_PROTOCOL_RFCOMM&0xff, /*RFCOMM*/
SDP_UINT8, RFCOMM_SPP_SERVER_CHNL, /*RFCOMM channel*/
/* BluetoothProfileDescriptorList */
SDP_DES_SIZE8, 0xd,
SDP_UINT16, BT_ATTRIBUTE_BLUETOOTH_PROFILE_DESCRIPTOR_LIST>>8&0xff, BT_ATTRIBUTE_BLUETOOTH_PROFILE_DESCRIPTOR_LIST&0xff, /* profile descriptor List */
SDP_DES_SIZE8, 0x8,
SDP_DES_SIZE8,0x06,
SDP_UUID16,BT_SERVICE_CLASS_SERIAL_PORT>>8&0xff, BT_SERVICE_CLASS_SERIAL_PORT&0xff,
SDP_UINT16,0x01,0x02, /* V1.2 */
};