微信公众号:OpenCV学堂
关注获取更多计算机视觉与深度学习知识
测试与发现
https://github.com/doleron/yolov5-opencv-cpp-python/blob/main/python/yolo-tiny.pycv2.dnn.blobFromImage(input_image , 1/255.0, (640, 640), swapRB=True)indexes = cv2.dnn.NMSBoxes(boxes, confidences, 0.25, 0.45)修改输入转换
cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(input_image , 1/255.0, (640, 640), swapRB=True)可以通过下面的代码等价替换:
rgb = cv.cvtColor(image, cv.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
input_image = cv.resize(src=rgb, dsize=(INPUT_WIDTH, INPUT_HEIGHT))
blob_img = np.float32(input_image) / 255.0
input_x = blob_img.transpose((2, 0, 1))
input_blob = np.expand_dims(input_x, 0)修改之后测试发现该替代降低了执行时间,说明替代有效!
修改非最大抑制
indexes = cv2.dnn.NMSBoxes(boxes, confidences, 0.25, 0.45)输入的box格式x, y,w,h,我参考了网上的代码,修改实现一个基于并交比最简单的NMS抑制算法,基于矩阵计算,保证不会因为对象变得多了,增加计算耗时,然后把它们封装成一个单独的方法,导入该方法直接替换之前的代码行为:
class_ids, boxes = non_max_suppression_fast(np.asarray(class_ids), np.asarray(boxes), 0.75)该函数完整的实现代码如下:
import numpy as np
def non_max_suppression_fast(class_ids, boxes, nms_threshold):
# if there are no boxes, return
if len(boxes) == 0:
return [], []
if boxes.dtype.kind == "i":
boxes = boxes.astype("float")
# initialize the list of picked indexes
pick = []
# grab the coordinates of the bounding boxes
x1 = boxes[:,0]
y1 = boxes[:,1]
x2 = boxes[:,2]
y2 = boxes[:,3]
# compute the area of the bounding boxes and sort the bounding
# boxes by the bottom-right y-coordinate of the bounding box
area = (x2 - x1 + 1) * (y2 - y1 + 1)
idxs = np.argsort(y2)
# keep looping while some indexes still remain in the indexes
# list
while len(idxs) > 0:
# grab the last index in the indexes list and add the
# index value to the list of picked indexes
last = len(idxs) - 1
i = idxs[last]
pick.append(i)
# find the largest (x, y) coordinates for the start of
# the bounding box and the smallest (x, y) coordinates
# for the end of the bounding box
xx1 = np.maximum(x1[i], x1[idxs[:last]])
yy1 = np.maximum(y1[i], y1[idxs[:last]])
xx2 = np.minimum(x2[i], x2[idxs[:last]])
yy2 = np.minimum(y2[i], y2[idxs[:last]])
# compute the width and height of the bounding box
w = np.maximum(0, xx2 - xx1 + 1)
h = np.maximum(0, yy2 - yy1 + 1)
# compute the ratio of overlap
overlap = (w * h) / area[idxs[:last]]
# delete all indexes from the index list that have
idxs = np.delete(idxs, np.concatenate(([last],
np.where(overlap > nms_threshold)[0])))
# return only the bounding boxes that were picked using the
# integer data type
return class_ids[pick], boxes[pick].astype("int")
if __name__ == "__main__":
boxes = []
boxes.append((163, 0, 27+163, 41))
boxes.append((164, 0, 28+164, 43))
boxes.append((165, 0, 29+165, 42))
res = non_max_suppression_fast(None, np.asarray(boxes), 0.25)
print(res)对比测试
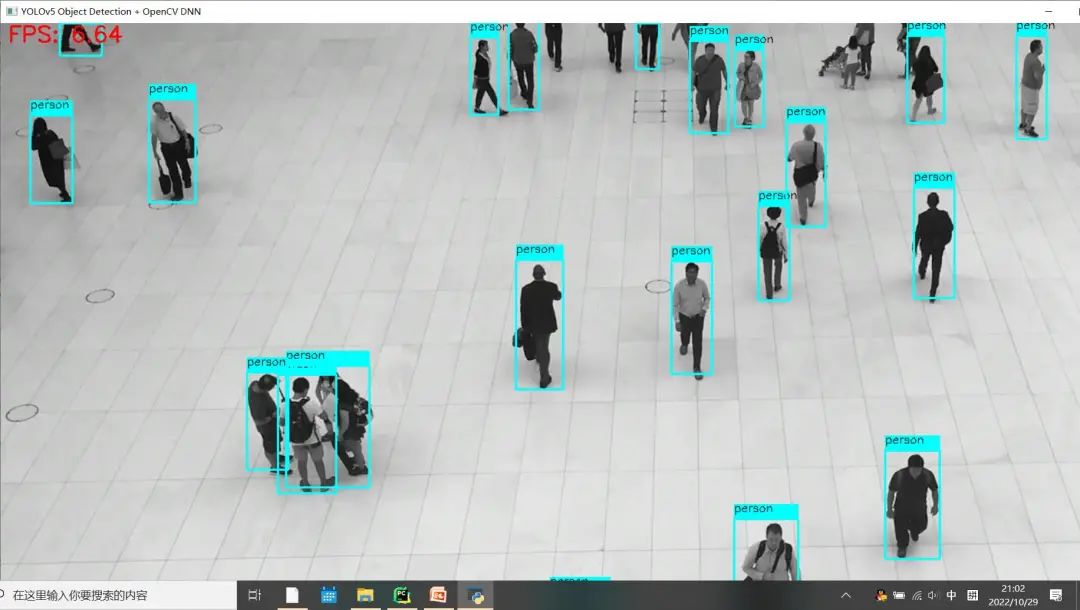
两处都修改完成之后,其它输入条件与代码不变,硬件相同条件下对比测试效果如下:修改之前 Python版本OpenCV与OpenVINO上推理速度:
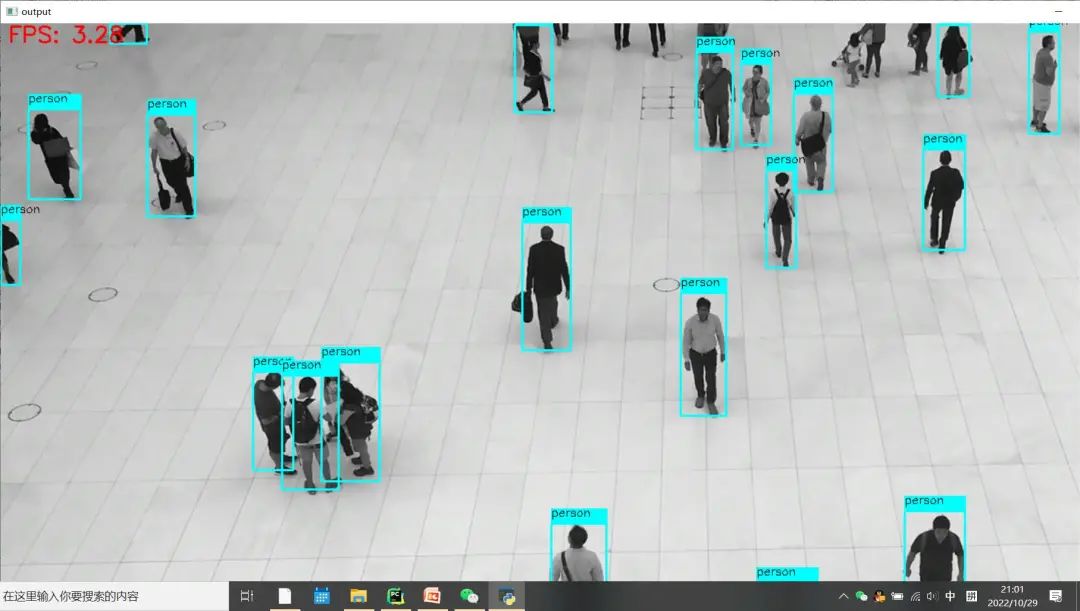
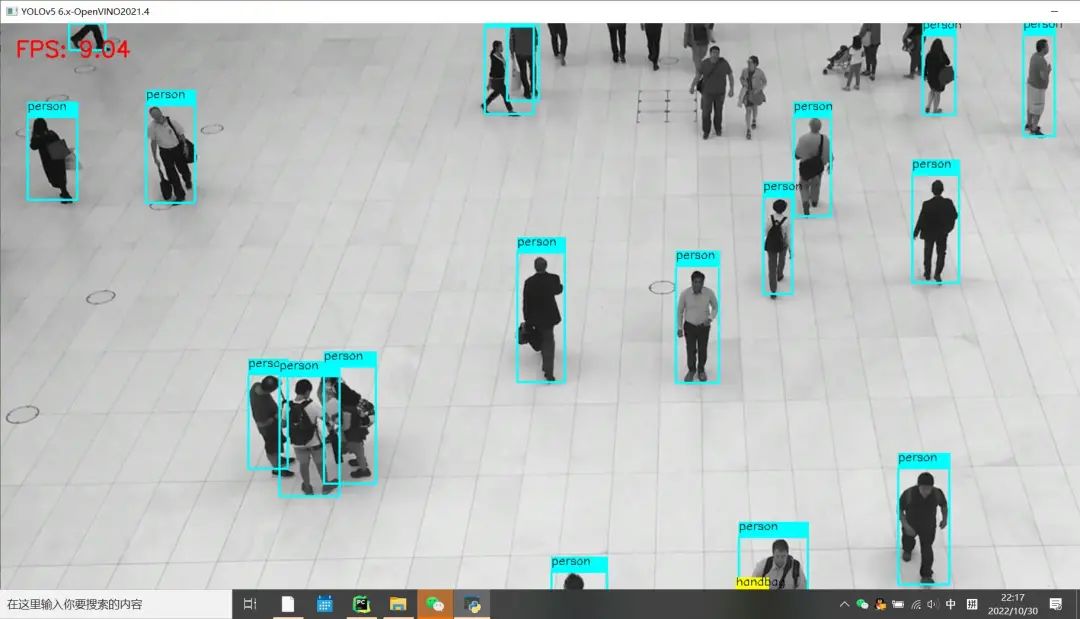
修改之后 Python版本OpenCV与OpenVINO上推理速度:
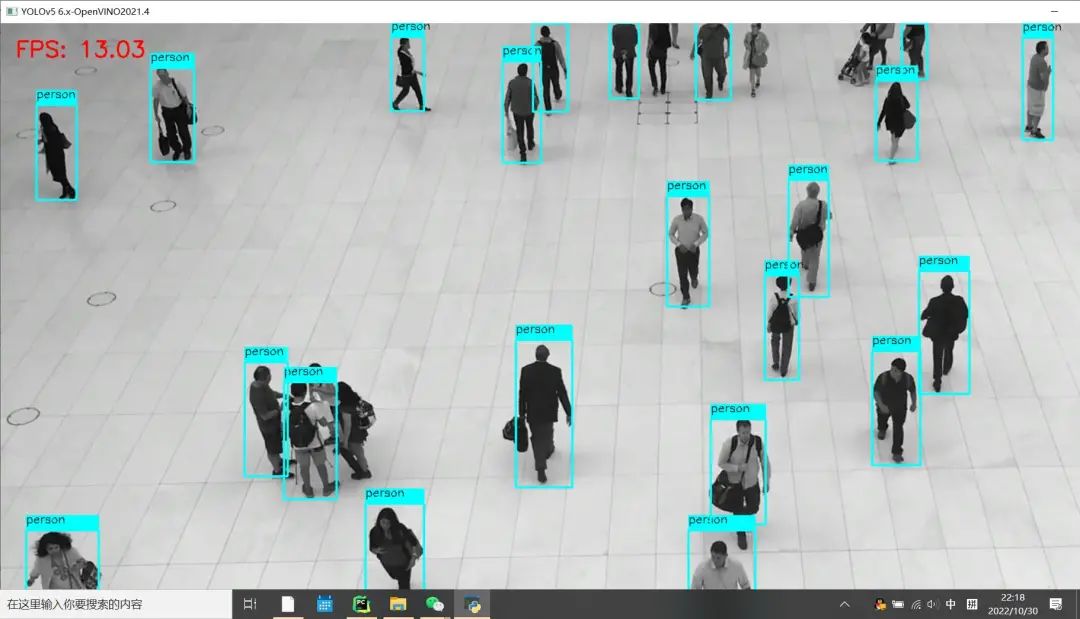
可以看到FPS较之前有明显的提升!

原价:398
折扣:299
推荐阅读
OpenCV4.8+YOLOv8对象检测C++推理演示
ZXING+OpenCV打造开源条码检测应用
总结 | OpenCV4 Mat操作全接触
三行代码实现 TensorRT8.6 C++ 深度学习模型部署
实战 | YOLOv8+OpenCV 实现DM码定位检测与解析
对象检测边界框损失 – 从IOU到ProbIOU
YOLOv8 OBB实现自定义旋转对象检测
初学者必看 | 学习深度学习的五个误区
YOLOv8自定义数据集训练实现安全帽检测
