点击左上角“锂电联盟会长”,即可关注!


Highlights
•综述了基于液冷的电池热管理系统。
•讨论了基于冷板的液冷电池热管理系统优化技术的进展和影响。
•建立了冷板式液冷多目标优化方法和评价系统的框架。
Research gap
本文从结构设计、工作液类型、空间布置和系统等方面对液冷板BTMS优化技术进行了综述和讨论,探索和建立了一种多目标优化系统和统一的评价体系结合的框架来设计液冷板和评估液冷板BTMS的能力,以实现整个系统的性能提升。
Abstract
With the rapid progress of the new power automotive industry, the requirements for vehicle range and charging ratio have gradually increased. With the high-speed cycling of batteries, the heat content increases rapidly, and the thermal problem has become the main factor restricting its development. One of the key technologies to maintain the performance, longevity, and safety of lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) is the battery thermal management system (BTMS). Owing to its excellent conduction and high temperature stability, liquid cold plate (LCP) cooling technology is an effective BTMS solution. Currently, the maximum surface temperature (Tmax), the pressure drop loss of the LCP, and the maximum temperature variance (Tmax-v) of the battery are often applied to evaluate the cooling capacity of LCP cooling BTMS. These parameters are also used as design indicators to guide the optimization of new liquid cooling BTMS. However, objective factors such as system safety, cost, system simplification, and heating or cooling efficiency should also be considered in the design and evaluation process of BTMS. Therefore, it is necessary to explore a multi-objective optimization system to design liquid plate BTMS and use a unified evaluation system to assess the capability of LCP cooling BTMS to comprehensively analyze and achieve the whole system performance improvement. Four common BTMS cooling technologies are described in this paper, including their working principle, advantages, and disadvantages. Direct liquid cooling and indirect liquid cooling BTMS are compared and analyzed. The BTMS optimization technology of LCP is reviewed and discussed from the aspects of structure design, type of working liquid, space arrangement, and system. Finally, the challenges affecting the development of liquid-cooled BTMS are outlined and suggestions for future research are made.
Keywords
Battery Thermal Management System;
Liquid Cold Plate;
Optimization Techniques;
Maximum Temperature;
Temperature Variance;
Graphics
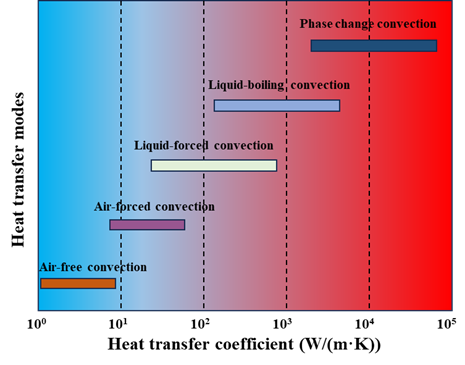
Fig. 2. The cooling capacity of various cooling techniques.
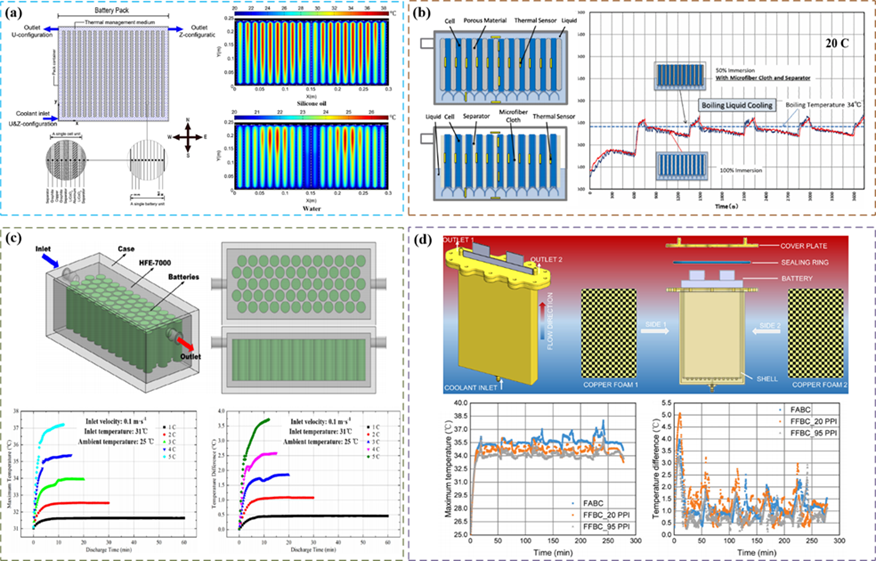
Fig. 4. Direct contact liquid cooled battery thermal management system.
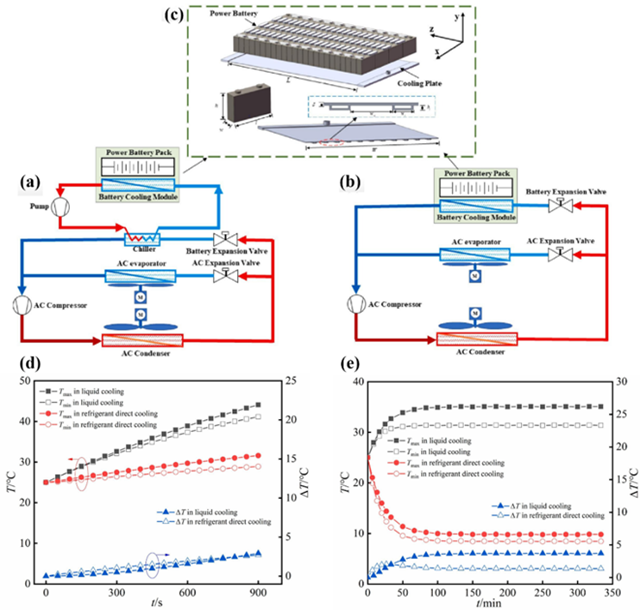
Fig. 12. Diagram of different systems.
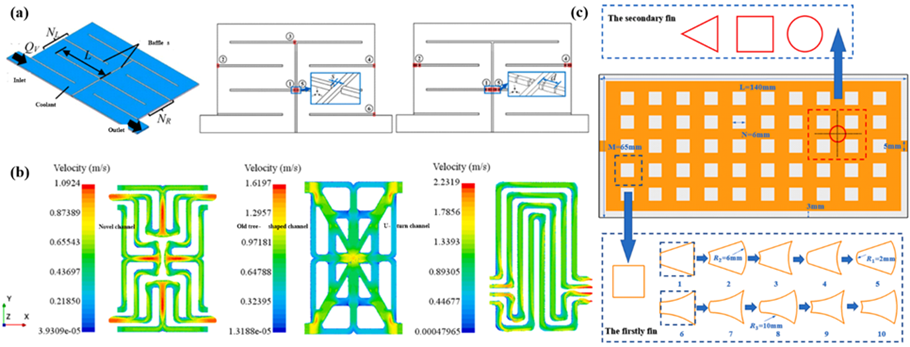
Fig. 14. Optimization design and simulation results of channel structure parameters.
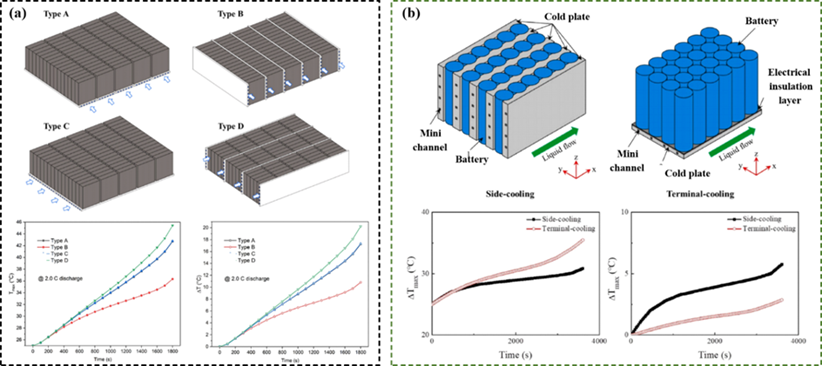
Fig. 17. Liquid-cooled plate space arrangement design and test results.
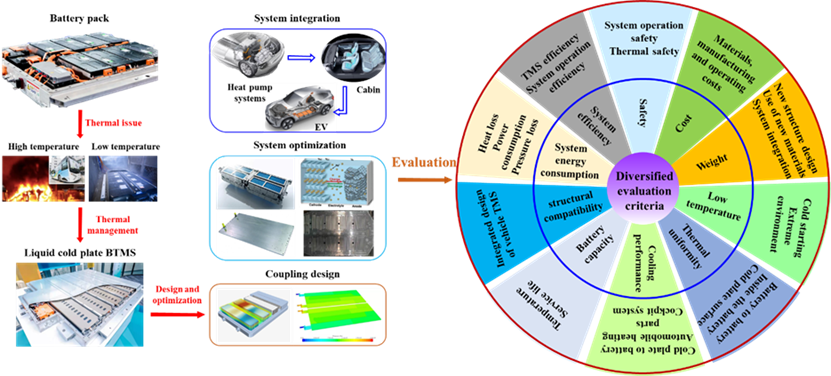
Fig. 21. LCP cooling BTMS synthesized design architectur.
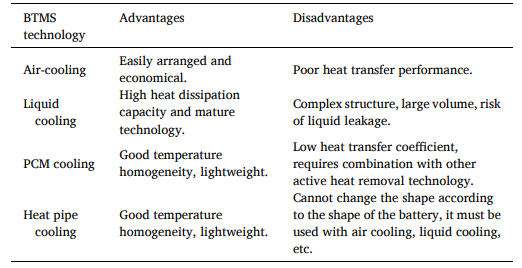
Table 2. Summary of thermal management technology for LIBs.
团队简介
本研究由华南理工大学、深圳大学以及郑州大学的研究人员共同完成。
通讯作者简介:
汤勇,博士,深圳大学特聘教授,华南理工大学教授,博士生导师,国务院政府特殊津贴专家,现任“半导体显示与光通信器件研发”国家地方联合工程研究中心主任。长期从事表面光/热功能结构制造理论以及半导体器件热控与封装。主持了国家自然科学基金重点项目(5项)、973计划、国防科技173计划、财政部重大专项等一批国家、省部级科研项目,相关成果发表在《Applied Energy》《International Journal of Machine Tools & Manufacture》《Journal of Materials Processing Technology》《机械工程学报》等国内外重要刊物上(其中,SCI索引论文300余篇,入选ESI高被引论文8篇,1篇获评2010年中国百篇最具影响国际学术论文)。同时,获授权国家发明专利100余项,PCT专利4项。一系列专利技术形成产品并得到广泛应用,经济效益显著。相关技术成果以第一完成人获国家科学技术进步奖二等奖1项(2016年)、中国专利优秀奖2项(2013年、2018年)、广东省科学技术奖一等奖2项(2010年、2018年)。
唐恒,博士,深圳大学长聘副教授,深圳市“鹏城孔雀计划”特聘岗位,硕士生导师。一直从事相变传热器件设计与制造研究工作,先后主持国家自然科学基金青年项目和重点项目(合作单位负责人)、广东省自然科学基金面上项目、深圳市基础研究面上项目、深圳市优秀科技创新人才培养项目等多项国家、省部级科研项目。相关成果以第一/通讯作者发表SCI/EI检索论文29篇,其中ESI高被引论文1篇(Applied Energy, 2018, 223: 383-400. 被《Science》等期刊引用,总引用320次),《机械工程学报》6篇(1篇封面论文及本期最受关注论文),SCI检索论文22篇(TOP期刊19篇,Editor's Pick论文1篇),并入选《机械工程学报》《中国表面工程》《机械科学与技术》等期刊青年编委。同时,授权国家发明专利10余项,获科学技术研究成果1项、深圳市科技进步二等奖1项。
朱立宽,博士,深圳大学长聘副教授,深圳市“孔雀计划C类”人才,硕士生导师。一直从事强对流多相传质、相变换热仿真与实验研究工作,先后主持广东省基础与应用基础研究项目、深圳市稳定支持B类项目等多项省部级科研项目。相关成果以第一/通讯作者发表SCI检索论文21篇,其中包括中科院一区5篇、二区2篇。同时,授权国家发明专利10余项,获得广东省机械工业科学技术一等奖1项。
第一作者简介:
伍春霞,华南理工大学博士生,研究方向为微纳功能结构制造、相变传热器件设计和制造。在Applied Energy、Applied Thermal Engineering、Physics of Fluids、机械工程学报等期刊发表一作论文4篇。