点击左上方蓝色“一口Linux”,选择“设为星标”
第一时间看干货文章 ☞【干货】嵌入式驱动工程师学习路线 ☞【干货】Linux嵌入式知识点-思维导图-免费获取 ☞【就业】一个可以写到简历的基于Linux物联网综合项目 ☞【就业】找工作简历模版
蓝牙在我们生活中非常普遍,小到手表,大到电视洗衣机等都有蓝牙的身影。
那么,你对蓝牙协议了解多少?
蓝牙技术起源于爱立信在1994年提出的方案,旨在解决移动电话和其他配件之间进行低功耗、低成本的无线通信连接的方法。

下面的分析都是基于V4.1版本,方便入门,可以理解很多核心协议的设计思想
蓝牙技术包含蓝牙发展过程中的两套技术,但是这两套原理和实现都不一样,也无法实现互通
Basic Rate(BR)/AMP
最初的蓝牙技术,包括可选的EDR(Enhanced Data Rate)技术和交替使用的MAC层和PHY层扩展 AMP(Alternate MAC and PHY layer extension)【优化传输速度的过程】
解释:蓝牙诞生之初使用的BR技术,传输速率很低,随着发展而变得无法支持,所以引入了EDR,这时还没有修改软硬件架构,但是之后又落伍了,所以直接引入了WiFi的底层协议,也就是MAC/PHY扩展,但这部分的实现就无法直接更替,所以BR/EDR只能与AMP交替使用
Low Energy(LE)
蓝牙低功耗,则不关心传输速率,而是从降低功耗的角度实现的另一套技术,跟前面的协议没有丝毫关系
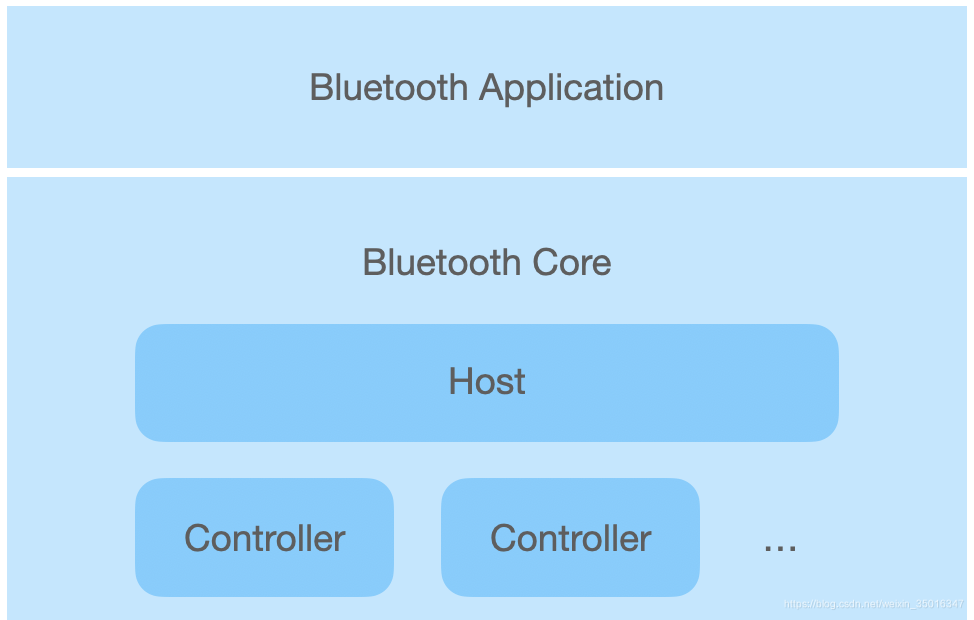
蓝牙协议将蓝牙整体分成了两层架构,底层是核心协议,描述了蓝牙核心技术的基础和规范,应用层协议则基于具体需求,使用核心协议提供的机制,实现不同的功能策略
核心协议包含两部分,Host和Controller,这两部分在不同的蓝牙协议版本中略有区别,但大致上是,Controller完成硬件侧的规范制订,包括信号调制解调,会抽象出用于通信的逻辑链路,可能存在一个或多个,如LE Controller、BR/EDR Controller;Host则在逻辑链路的基础上完成更友好的封装,屏蔽掉技术细节,方便应用层对数据的使用
蓝牙协议也采用层次结构,自下而上依次为物理层、逻辑层、L2CAP层和应用层
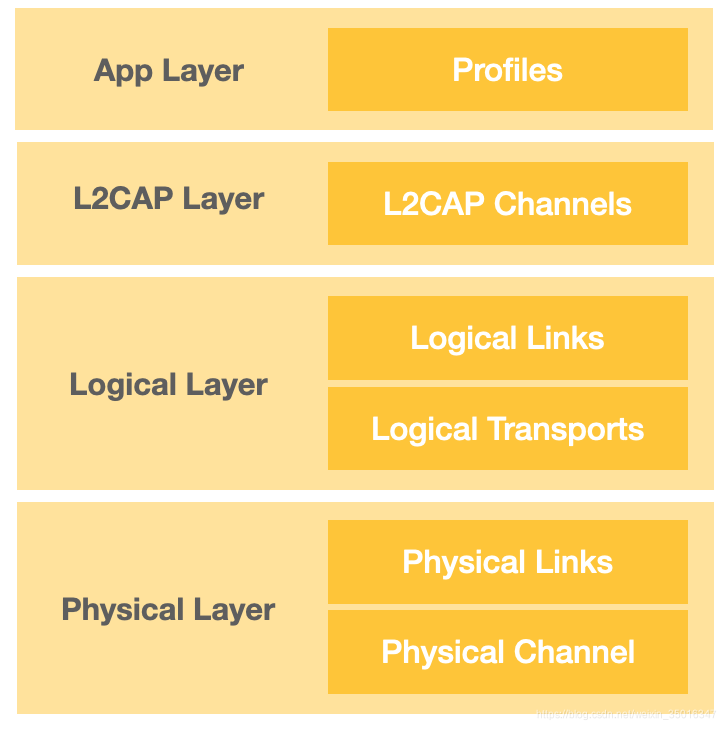
应用层(App Layer)为不同场景定义规范,提出Profile(一项服务)的概念,实现各种应用功能
L2CAP(Logical Link Control and Adaptation Protocol Layer)
逻辑层(Logical Layer)
物理层(Physical Layer)
实现一个BLE应用,需要一个支持BLE射频的芯片,然后基于一个与芯片配套的协议栈,开发蓝牙应用。
协议栈的作用就是软件和硬件之间的桥梁,对应用数据进行封包然后生成可以通过射频发送的空中数据包及其逆向过程。
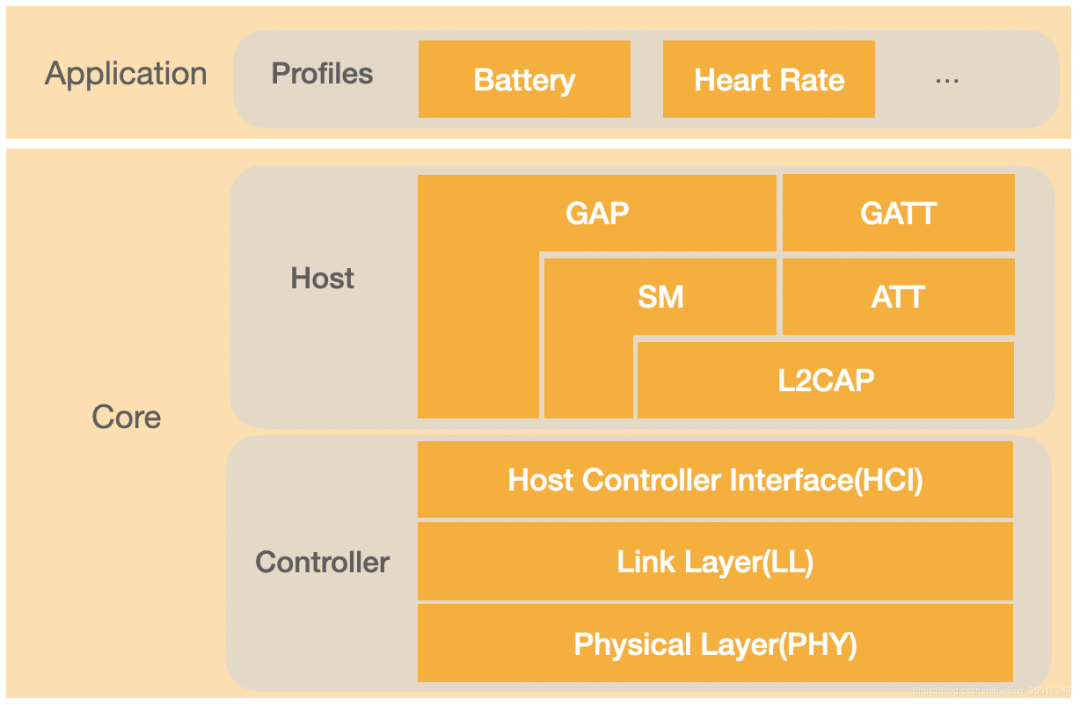
Physical Layer(PHY)
Link Layer(LL)
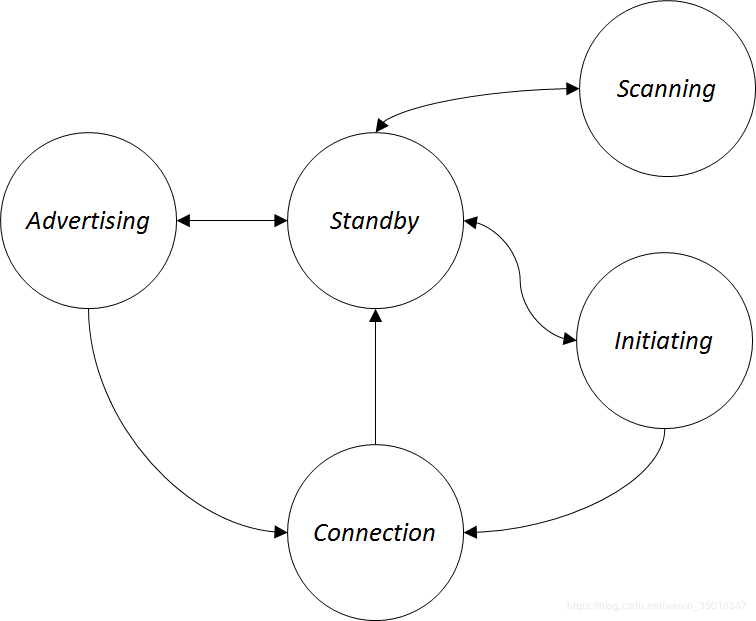
- Standby:初始状态,不收发数据,接受上层协议命令与其他状态切换
- Advertising:通过广播发送数据的状态,建立连接后可进入Connection
- Scanning:接收广播的数据的状态
- Initiating:特殊的接收状态,类似Scanning,接收Advertiser广播的连接数据,建立连接后进入Connection
- Connection:建立连接后拥有单独的通道
12345
Host Controller Interface(HCI)
L2CAP
Attribute Protocol(ATT)
0x0004Generic Attribute Profile(GATT)
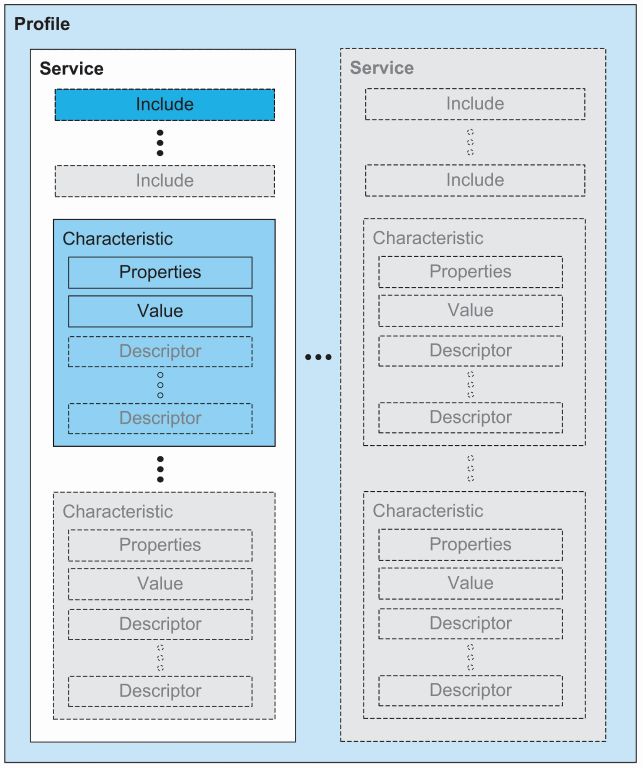
00000000-0000-1000-8000-00805F9B34FB0000xxxx-0000-1000-8000-00805F9B34FBxxxxxxxx-0000-1000-8000-00805F9B34FBSecurity Manager(SM)
Generic Access Profile(GAP)
使用场景
协议层次
LL
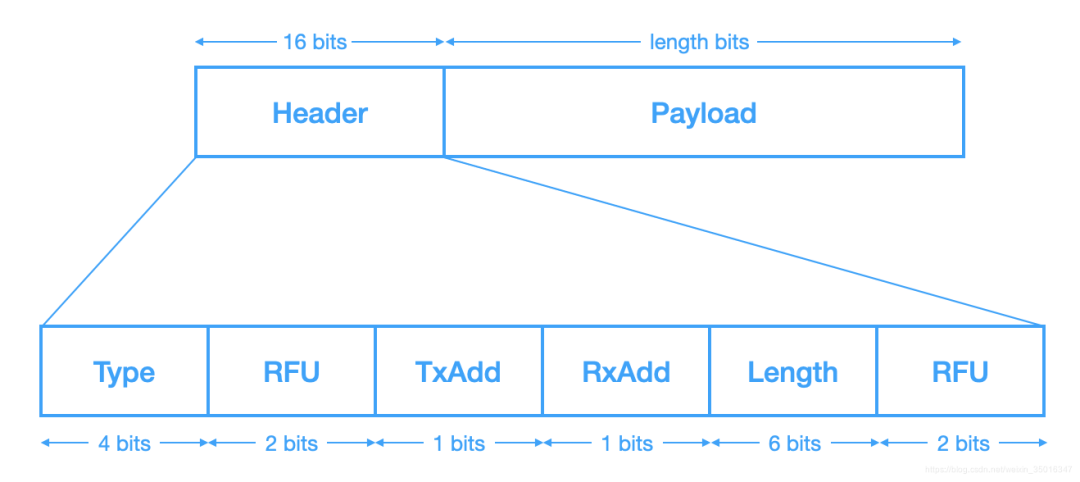
Type是指PDU的类型,如不同的状态下也有不同的消息类型,TxAdd和RxAdd都是地址类型flag,针对不同的type有不同的含义,RFU都是保留字段,Length标明payload的长度
Payload内容
| State | Type | Descriptions | Payload | length | Descriptions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Advertising | ADV_IND | 常规广播,可连接可扫描 | AdvA | 6 | address of broadcaster |
| 【后续建立点对点连接,监听CONNECT_REQ请求】 | AdvData | 0~31 | Broadcast data | ||
| ADV_NONCONN_IND | 同ADV_IND,不可连接不可扫描 | AdvA | 6 | address of broadcaster | |
| 【用于定时传输简单数据】 | AdvData | 0~31 | Broadcast data | ||
| ADV_SCAN_IND | 同ADV_IND,不可连接可扫描 | AdvA | 6 | address of broadcaster | |
| 【用于传输额外数据,监听SCAN_REQ请求】 | AdvData | 0~31 | Broadcast data | ||
| ADV_DIRECT_IND | 点对点连接,已知双方蓝牙地址,无广播数据,可被指定设备连接不可扫描 | AdvA | 6 | address of broadcaster | |
| 【快速建立连接,不关心广播数据,监听CONNECT_REQ请求】 | InitA | 6 | address of receiver/initiater | ||
| Scanning | SCAN_REQ | 接收ADV_IND/ADV_SCAN_IND后,请求更多信息 | ScanA | 6 | address of scanne r |
| 【接收广播数据后请求更多信息】 | AdvA | 6 | address of broadcaster | ||
| SCAN_RSP | SCAN_REQ的响应,返回更多信息 | AdvA | 6 | address of broadcaster | |
| ScanRspData | 0~31 | response data | |||
| Initiating | CONNECT_REQ | 接收ADV_IND/ADV_DIRECT_IND后,请求建立连接 | InitA | 6 | address of receiver/initiater |
| 【请求建立连接】 | AdvA | 6 | address of broadcaster | ||
| LLData | 22 | parameters of connection |
BLE设备地址类型
HCI
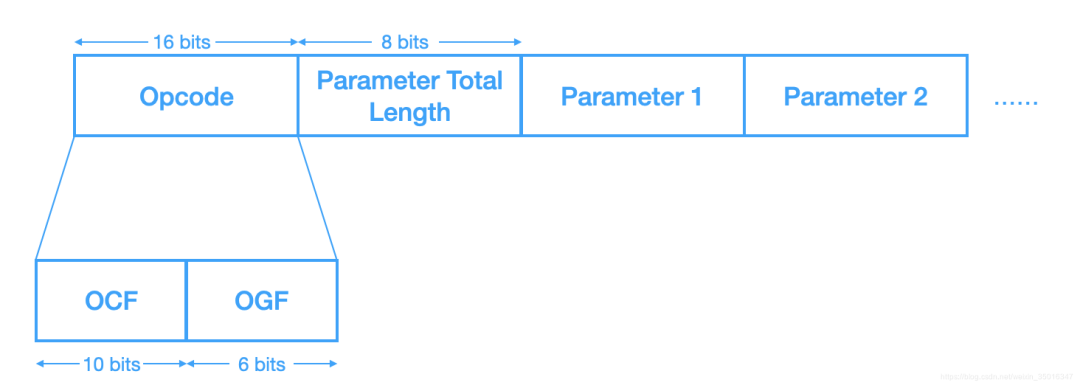
OCF(Opcode Command Field)表示特定的HCI命令,OGF(Opcode Group Field)表示该HCI命令所属组别,他们共同组成16位操作码;Parameter Total Length表示所有参数总长度
所有BLE相关的HCI Command的OGF都是0x08
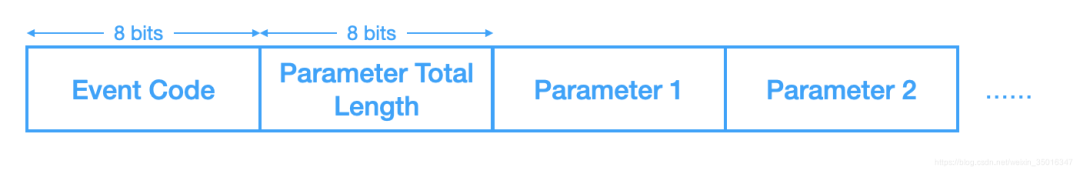
GAP
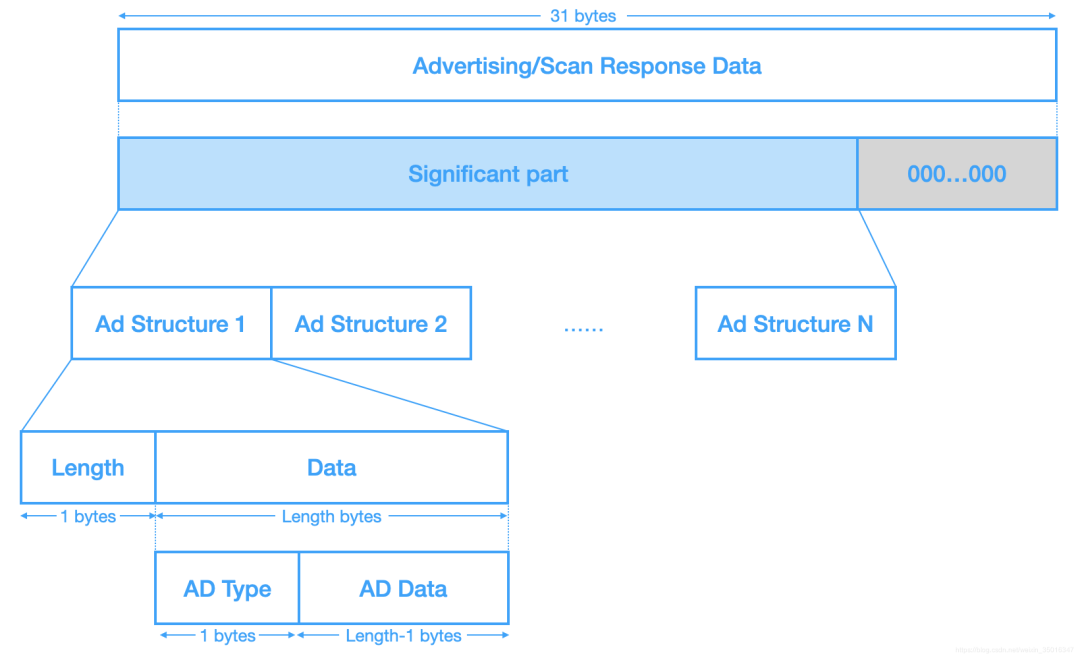
广播/扫描应答数据,包含有意义部分和无意义部分(补齐为0),有意义部分是由一个个广播块(AD Structure)组成,每个广播块包含1字节长度(指示数据部分长度)和剩下的数据部分,数据部分又分为数据类型和数据内容,数据类型会指示真实Data部分的内容,例如0x01表示Data内容是描述设备物理连接状态,再例如0x08表示Data内容是设备名称,更多可以参考generic-access-profile
举个广播数据的例子
02 01 06 03 03 aa fe 17 16 aa fe 00 -10 00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 0a 0b 0e 0f 00 00 00 00
1
02 01 06是一个AD Structure,数据部分长度为2字节,类型是0x01,描述设备物理连接状态,数据部分0x06,1字节8bit,每bit都是一个标志位([预留]|[预留]|[预留]|[同时支持BLE和BR/EDR(Host)]|[同时支持BLE和BR/EDR(Controller)]|[不支持BR/EDR]|[普通发现模式]|[有限发现模式]),那么这个广播就是普通发现模式,不支持BR/EDR
03 03 aa fe是第二个AD Structure,数据部分长度为3字节,类型是0x03,表示16-bits的Service UUID
17 16 aa fe 00 -10 00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 0a 0b 0e 0f 00 00 00 00是最后一个AD Structure,数据部分长度为0x17即23字节,类型是0x16,表示服务数据
| AD Type | Description | AD Data |
|---|---|---|
| 0x01 | 设备物理连接状态 | 1字节8bit,每个bit都是一个标志位 [预留]|[预留]|[预留]|[同时支持BLE和BR/EDR(Host)]|[同时支持BLE和BR/EDR(Controller)]|[不支持BR/EDR]|[普通发现模式]|[有限发现模式] |
| 0x02 | UUID | 非完整的16-bit UUID |
| 0x03 | UUID | 完整的16-bit UUID |
| 0x04 | UUID | 非完整的32-bit UUID |
| 0x05 | UUID | 完整的32-bit UUID |
| 0x06 | UUID | 非完整的128-bit UUID |
| 0x07 | UUID | 完整的128-bit UUID |
| 0x08 | 设备名称 | 缩写设备名称 |
| 0x09 | 设备名称 | 完整设备名称 |
| 0x0a | TX Power Level | TX Power Level |
| 0xff | 厂商数据 | [厂商ID]|[厂商自定义数据] |
经典蓝牙中保持连接非常耗费资源,但是每次连接建立效率又非常低,为了优化体验,BLE简化了连接过程(毫秒级),极大的降低了面向连接通信的代价
蓝牙通信系统中,对于连接的定义是:在约定的时间段内,双方都到一个指定的物理Channel上通信。
LL
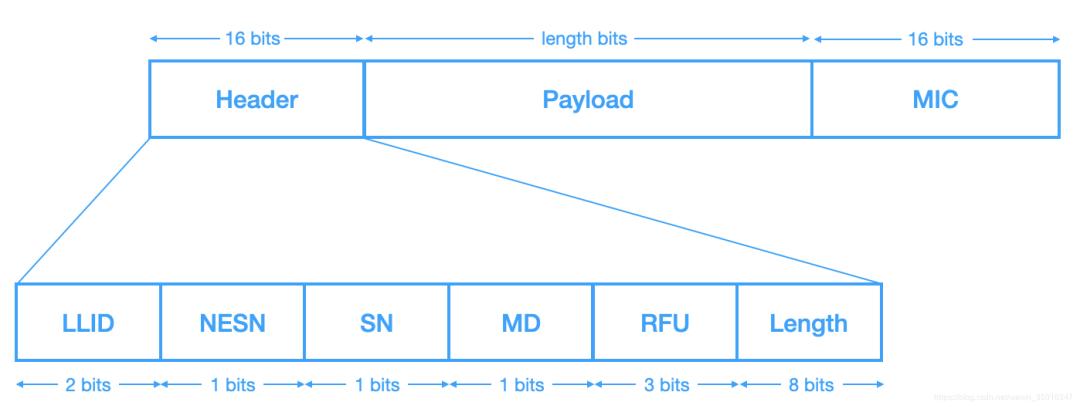
面向连接的通信使用特定的PDU,称为Data channel PDU
LLID指示Data Channel传输的PDU类型,传输数据是LL Data PDU,传输控制信息是LL Control PDU,NESN(Next Expected Sequence Number)和SN(Sequence Number)用于数据传输过程中的应答和流控,MD(More Data)用于关闭连接,RFU是预留位,Length指示有效数据长度,包括Payload和MIC
| LLID | type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 01b | LL Data PDU | 空包或未传输完成的消息(被拆包) |
| 10b | LL Data PDU | (不需拆包)完整消息或第一个包 |
| 11b | LL Control PDU | 用于控制、管理LL连接的数据包,此时Payload为1字节Opcode和剩余的控制数据 |
HCI
GAP
White List
白名单就是一组蓝牙地址列表,通过设置白名单可以允许扫描、连接特定的蓝牙设备,以及被扫描、连接
LL Privacy
在白名单的基础上将设备地址进行加密,转变成Resolvable Private addresses
LL Encryption
数据发送和接收过程进行加解密
SecurityManager
为BLE设备提供加密连接相关的key,包含以下规范:
SMP规范中,配对的定义是,Master和Slave通过协商确定用于加密通信的key的过程,包含三个阶段:
具体可以参考开发的蓝牙测试工具:BLETool
BLE,蓝牙低功耗(极低的运行和待机功耗)
Android 4.3(API 18) 开始引入 BLE ,即蓝牙4.0
Android 4.3 的 BLE 只支持 Central Role(中心设备,扫描并连接外围设备)
Android 5.0 开始同时支持 Central Role 和 Peripheral Role(外围设备,向外广播发送数据)
1、权限
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.BLUETOOTH"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.BLUETOOTH_ADMIN"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION"/>
<uses-feature android:name="android.hardware.bluetooth_le" android:required="true" />
2、开启/关闭蓝牙
// 判断支持蓝牙功能
if (getPackageManager().hasSystemFeature(PackageManager.FEATURE_BLUETOOTH_LE)) {
// 获取蓝牙管理服务
BluetoothManager bluetoothManager = (BluetoothManager) getSystemService(Context.BLUETOOTH_SERVICE);
// 获取蓝牙适配器
BluetoothAdapter bluetoothAdapter = bluetoothManager.getAdapter();
if (bluetoothAdapter != null) {
// 判断蓝牙是否开启
if (bluetoothAdapter.isEnabled()) {
// 关闭蓝牙
bluetoothAdapter.disable();
} else {
// 1、静默开启蓝牙
bluetoothAdapter.enable();
// 2、显式请求开启蓝牙
Intent intent = new Intent(BluetoothAdapter.ACTION_REQUEST_ENABLE);
startActivityForResult(intent, REQUEST_BLUETOOTH_ENABLE);
}
}
}
3、扫描与监听
if (getPackageManager().hasSystemFeature(PackageManager.FEATURE_BLUETOOTH_LE)) {
// 获取蓝牙管理服务
BluetoothManager bluetoothManager = (BluetoothManager) getSystemService(Context.BLUETOOTH_SERVICE);
// 获取蓝牙适配器
BluetoothAdapter bluetoothAdapter = bluetoothManager.getAdapter();
if (bluetoothAdapter != null) {
// 判断蓝牙是否开启
if (bluetoothAdapter.isEnabled()) {
// 获取扫描器实例
BluetoothLeScanner bluetoothLeScanner = bluetoothAdapter.getBluetoothLeScanner();
boolean isScanning = false;
if (bluetoothLeScanner != null) {
if (isScanning) {
// 停止扫描
isScanning = false;
bluetoothLeScanner.stopScan(scanCallback);
} else {
// 开始扫描
isScanning = true;
bluetoothLeScanner.startScan(scanCallback);
}
}
}
}
}
Android 8 开始提供一个后台持续扫描的API,应用杀死后也可以继续扫描,直到关闭蓝牙【待验证】
public int startScan (List filters, ScanSettings settings, PendingIntent callbackIntent) ;
// 设置拦截器和扫描选项
bluetoothLeScanner.startScan(scanFilters, scanSettings, scanCallback);
初始化扫描过滤器
scanFilters = new ArrayList<>();
ScanFilter scanFilter = new ScanFilter.Builder()
.setDeviceName("lalala")
.setServiceUuid(new ParcelUuid(UUID.randomUUID()))
.build();
scanFilters.add(scanFilter);
初始化扫描设置
scanSettings = new ScanSettings.Builder()
// 设置扫描模式
.setScanMode(ScanSettings.SCAN_MODE_BALANCED)
// 设置回调类型
.setCallbackType(ScanSettings.CALLBACK_TYPE_ALL_MATCHES)
// 设置配对模式
.setMatchMode(ScanSettings.MATCH_MODE_STICKY)
// 设置报告延迟
.setReportDelay(0)
.build();
两个类都是通过 Builder 构造,提供系列函数用于参数设置,如 setDeviceName()、setScanMode()、setMatchMode() 等
4、扫描回调
scanCallback = new ScanCallback {
@Override
public void onScanResult(int callbackType, ScanResult result) {
super.onScanResult(callbackType, result);
}
@Override
public void onScanFailed(int errorCode) {
super.onScanFailed(errorCode);
}
@Override
public void onBatchScanResults(List results) {
super.onBatchScanResults(results);
}
}
其中 onBatchScanResults() 是批量返回扫描结果。可通过下面的接口判断蓝牙芯片是否支持批处理
Bluetoothadapter.isOffloadedScanBatchingSupported();
1
注意 onScanResult() 和 onBatchScanResults() 是互斥的,ScanSettings 中 setReportDelay() 设置为0(默认)则通过 onScanResult() 返回扫描结果,否则开启批处理扫描模式,并触发 onBatchScanResults() 回调。
5、广播数据解析
扫描成功会返回 ScanResult 广播数据类,然后进一步解析
// 返回远程设备类
BluetoothDevice device = scanResult.getDevice();
// 返回扫描记录,包含广播和扫描响应
ScanRecord scanRecord = scanResult.getScanRecord();
// 返回信号强度,[-127, 126]
int rssi = scanResult.getRssi()
BluetoothDevice 是设备信息类,常用的方法有
// 获取硬件地址
String address = device.getAddress();
// 获取蓝牙名称
String name = device.getName();
// 获取设备类型,如DEVICE_TYPE_CLASSIC、DEVICE_TYPE_LE、DEVICE_TYPE_DUAL、DEVICE_TYPE_UNKNOWN
int type = device.getType();
// 获取绑定状态,如BOND_NONE、BOND_BONDING、BOND_BONDED
int state = device.getBondState();
6、连接设备
扫描返回的广播消息中可以获取到远程设备的MAC地址,可用于设备的连接
if (bluetoothAdapter.isEnabled()) {
// 获取远程设备对象
BluetoothDevice bluetoothDevice = bluetoothAdapter.getRemoteDevice(address);
if (bluetoothDevice != null) {
handler.post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
BluetoothGatt bluetoothGatt;
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.M) {
// 连接远程设备
bluetoothGatt = bluetoothDevice.connectGatt(context, false, bluetoothGattCallback, BluetoothDevice.TRANSPORT_LE);
} else {
bluetoothGatt = bluetoothDevice.connectGatt(context, false, bluetoothGattCallback);
}
}
});
}
}
bluetoothGatt 是蓝牙通用属性协议的封装,定义了BLE通信的一些基本规则和连接通信操作
7、连接回调
bluetoothGattCallback 则是 bluetoothGatt 连接的回调类,通知客户端连接状态和结果
bluetoothGattCallback = new BluetoothGattCallback {
@Override
public void onConnectionStateChange(BluetoothGatt gatt, final int status, final int newState) {
super.onConnectionStateChange(gatt, status, newState);
}
@Override
public void onServicesDiscovered(BluetoothGatt gatt, final int status) {
super.onServicesDiscovered(gatt, status);
}
@Override
public void onCharacteristicChanged(BluetoothGatt gatt, final BluetoothGattCharacteristic characteristic) {
super.onCharacteristicChanged(gatt, characteristic);
}
@Override
public void onCharacteristicRead(BluetoothGatt gatt, final BluetoothGattCharacteristic characteristic, final int status) {
super.onCharacteristicRead(gatt, characteristic, status);
}
@Override
public void onCharacteristicWrite(BluetoothGatt gatt, final BluetoothGattCharacteristic characteristic, final int status) {
super.onCharacteristicWrite(gatt, characteristic, status);
}
@Override
public void onDescriptorRead(BluetoothGatt gatt, final BluetoothGattDescriptor descriptor, final int status) {
super.onDescriptorRead(gatt, descriptor, status);
}
@Override
public void onDescriptorWrite(BluetoothGatt gatt, final BluetoothGattDescriptor descriptor, final int status) {
super.onDescriptorWrite(gatt, descriptor, status);
}
}
连接成功及其他连接状态改变都会调用 onConnectionStateChange() 方法。status 表示这个操作的状态,是 BluetoothGatt.GATT_SUCCESS 或者读写受限、超过范围等其他错误状态。newState 则表示当前设备的连接状态,连接成功为 BluetoothProfile.STATE_CONNECTED,连接失败是BluetoothProfile.STATE_DISCONNECTED。
8、发现服务
连接成功后就可以开始通信,从请求服务开始(Profile只是一系列具有共同业务需求的服务的抽象集合,服务才是实体)
bluetoothGatt.discoverServices();
1
发现服务后会触发 onServicesDiscovered() 回调,然后继续获取服务
// 获取所有服务
List bleServiceList = bluetoothGatt.getServices();
// 通过uuid获取特定的服务
BluetoothGattService bleService = bluetoothGatt.getService(serviceUuid);
BluetoothGattService 是蓝牙服务类,是与某个场景相关的一系列行为的抽象,具有一个唯一的UUID,然后服务类型,如SERVICE_TYPE_PRIMARY、SERVICE_TYPE_SECONDARY(主要服务可以包含二级服务),包含的特征列表
9、获取特征
// 获取所有特征
List bleCharacteristicList = bleService.getCharacteristics();
// 通过uuid获取特定的特征
BluetoothGattCharacteristic bleCharacteristic = bleService.getCharacteristic(characteristicUuid);
BluetoothGattCharacteristic 是蓝牙特征类,是通信的基本数据单位,包含标志特征的唯一的UUID,描述特征访问权限的特性,如PROPERTY_BROADCAST、PROPERTY_READ、PROPERTY_WRITE等,特征的实际取值,以及特征的描述
10、读写特征
// 读取特征
bluetoothGatt.readCharacteristic(bleCharacteristic);
// 设置并写入特征
bleCharacteristic.setValue("XXX");
bluetoothGatt.writeCharacteristic(bleCharacteristic);
这里的读写特征函数都是返回布尔类型表示是否操作成功,如果成功真正的值会在 onCharacteristicRead/onCharacteristicWrite 回调中读取/写入
@Override
public void onCharacteristicRead(BluetoothGatt gatt, BluetoothGattCharacteristic characteristic, int status) {
switch (status) {
case GATT_SUCCESS:
String valueStr = BLEUtils.byte2HexString(characteristic.getValue());
break;
case GATT_READ_NOT_PERMITTED:
ToastUtils.showShort(context, "GATT_READ_NOT_PERMITTED");
break;
default:
ToastUtils.showShort(context, "CHARACTERISTIC_READ_FAILED");
break;
}
}
@Override
public void onCharacteristicWrite(BluetoothGatt gatt, BluetoothGattCharacteristic characteristic, int status) {
switch (status) {
case GATT_SUCCESS:
String valueStr = BLEUtils.byte2HexString(characteristic.getValue());
break;
default:
ToastUtils.showShort(context, "CHARACTERISTIC_WRITE_FAILED");
break;
}
}
11、监听特征
真正要实现通信除了单方面读写,还需要对数据变化进行监听,这样就可以进行数据交换
// 设置特征监听为true,且要求特征具有NOTIFY属性
bluetoothGatt.setCharacteristicNotification(characteristic, true);
这样,自己或对方特征改变时就会回调函数从而获取改变后的特征值
@Override
public void onCharacteristicChanged(BluetoothGattCharacteristic characteristic) {
Log.d("bledemo", "uuid = " + characteristic.getUuid().toString());
Log.d("bledemo", "value = 0x" + BLEUtils.byte2HexString(characteristic.getValue()));
}
12、获取描述
// 获取所有描述
List bleDescriptorList = bleCharacteristic.getDescriptors();
// 通过uuid获取特定的描述
BluetoothGattDescriptor bleDescriptor = bleCharacteristic.getDescriptor(descriptorUuid);
BluetoothGattDescriptor 是蓝牙特征描述类,包含对特征的一些额外描述信息
13、读写描述
// 读取描述
bluetoothGatt.readDescriptor(bleDescriptor);
// 设置并写入描述
bleDescriptor.setValue("XXX");
bluetoothGatt.writeDescriptor(bleDescriptor);
同样读写成功会触发onDescriptorRead/onDescriptorWrite 回调
@Override
public void onDescriptorRead(BluetoothGattDescriptor descriptor, int status) {
switch (status) {
case GATT_SUCCESS:
String valueStr = BLEUtils.byte2HexString(descriptor.getValue());
break;
case GATT_READ_NOT_PERMITTED:
ToastUtils.showShort(context, "GATT_READ_NOT_PERMITTED");
break;
default:
ToastUtils.showShort(context, "DESCRIPTOR_READ_FAILED");
break;
}
}
@Override
public void onDescriptorWrite(BluetoothGattDescriptor descriptor, int status) {
switch (status) {
case GATT_SUCCESS:
String valueStr = BLEUtils.byte2HexString(descriptor.getValue());
break;
default:
ToastUtils.showShort(context, "DESCRIPTOR_WRITE_FAILED");
break;
}
}
14、断开连接
// 断开连接,会触发onConnectionStateChange()回调
bluetoothGatt.disconnect();
// 关闭连接,不会触发回调
bluetoothGatt.close();
1234
15、开启/关闭广播
if (bluetoothAdapter.isEnabled()) {
// 设置广播设备的名称,方便搜索
bluetoothAdapter.setName("XXX");
// 获取广播类
BluetoothLeAdvertiser bluetoothLeAdvertiser = bluetoothAdapter.getBluetoothLeAdvertiser();
if (bluetoothLeAdvertiser != null) {
if (isAdvertising) {
// 关闭广播
bluetoothLeAdvertiser.stopAdvertising(advertiseCallback);
} else {
// 开始广播
bluetoothLeAdvertiser.startAdvertising(advertiseSetting, advertiseData, advertiseCallback);
}
}
}
还可以发送带响应报文的广播包
bluetoothLeAdvertiser.startAdvertising(advertiseSetting, advertiseData, advertiseResData, advertiseCallback);
1
其中 advertiseSetting 为广播设置类对象
advertiseSetting = new AdvertiseSettings.Builder()
// 广播模式,控制广播功率和延迟
.setAdvertiseMode(AdvertiseSettings.ADVERTISE_MODE_LOW_LATENCY)
// 广播发射功率级别
.setTxPowerLevel(AdvertiseSettings.ADVERTISE_TX_POWER_HIGH)
// 广播超时时间,最大值为 3*60*1000 毫秒,为 0 时禁用超时,默认无限广播
.setTimeout(advertiseTimeout)
// 广播连接类型
.setConnectable(true)
.build();
12345678910
advertiseData、advertiseResData 为广播包
advertiseData = new AdvertiseData.Builder()
// 广播是否包含设备名称
.setIncludeDeviceName(true)
// 广播是否包含发射功率
.setIncludeTxPowerLevel(true)
// 添加服务uuid
.addServiceUuid(new ParcelUuid(UUID.randomUUID()))
.build();
advertiseResData = new AdvertiseData.Builder()
// 添加自定义服务数据
.addServiceData(new ParcelUuid(UUID.randomUUID()), new byte[]{1,2,3,4})
// 添加自定义厂商数据
.addManufacturerData(0x06, new byte[]{5,6,7,8})
.build();
16、广播回调
advertiseCallback 是广播回调
advertiseCallback = new AdvertiseCallback {
@Override
public void onStartSuccess(AdvertiseSettings settingsInEffect) {
super.onStartSuccess(settingsInEffect);
}
@Override
public void onStartFailure(int errorCode) {
super.onStartFailure(errorCode);
}
}
17、启动GATT服务
只有广播仍然不够,作为外围角色的设备还需要启动GATT服务,等待中心设备与之建立连接之后就可以通过服务通信
// 启动 Gatt 服务
bluetoothGattServer = bluetoothManager.openGattServer(context, bluetoothGattServerCallback);
12
接下来可以向启动的GATT服务中添加Service
// 构造服务
BluetoothGattService bluetoothGattService = new BluetoothGattService(UUID.randomUUID(), BluetoothGattService.SERVICE_TYPE_PRIMARY);
// 构造特征
BluetoothGattCharacteristic bluetoothGattCharacteristic = new BluetoothGattCharacteristic(UUID.randomUUID(), BluetoothGattCharacteristic.PROPERTY_READ | BluetoothGattCharacteristic.PERMISSION_WRITE | BluetoothGattCharacteristic.PROPERTY_NOTIFY, BluetoothGattCharacteristic.PERMISSION_WRITE | BluetoothGattCharacteristic.PERMISSION_READ);
bluetoothGattCharacteristic.setValue("character_test_value");
// 构造描述
BluetoothGattDescriptor bluetoothGattDescriptor = new BluetoothGattDescriptor(UUID.randomUUID(), BluetoothGattDescriptor.PERMISSION_READ |BluetoothGattDescriptor.PERMISSION_WRITE);
bluetoothGattDescriptor.setValue("descriptor_test_value".getBytes());
// 添加描述到特征中
bluetoothGattCharacteristic.addDescriptor(bluetoothGattDescriptor);
// 添加特征到服务中
bluetoothGattService.addCharacteristic(bluetoothGattCharacteristic);
// 添加服务
bluetoothGattServer.addService(bluetoothGattService);
18、GATT服务回调
bluetoothGattServerCallback 是GATT服务的回调,当设备被连接、通信(读写特征)时都会触发响应的回调函数
bluetoothGattServerCallback = new BluetoothGattServerCallback {
@Override
public void onConnectionStateChange(BluetoothDevice device, int status, int newState) {
super.onConnectionStateChange(device, status, newState);
}
@Override
public void onServiceAdded(int status, BluetoothGattService service) {
super.onServiceAdded(status, service);
}
@Override
public void onCharacteristicReadRequest(BluetoothDevice device, int requestId, int offset,
BluetoothGattCharacteristic characteristic) {
super.onCharacteristicReadRequest(device, requestId, offset, characteristic);
}
@Override
public void onCharacteristicWriteRequest(BluetoothDevice device, int requestId,
BluetoothGattCharacteristic characteristic,
boolean preparedWrite, boolean responseNeeded,
int offset, byte[] value) {
super.onCharacteristicWriteRequest(device, requestId, characteristic, preparedWrite,
responseNeeded, offset, value);
}
@Override
public void onDescriptorReadRequest(BluetoothDevice device, int requestId,
int offset, BluetoothGattDescriptor descriptor) {
super.onDescriptorReadRequest(device, requestId, offset, descriptor);
}
@Override
public void onDescriptorWriteRequest(BluetoothDevice device, int requestId,
BluetoothGattDescriptor descriptor,
boolean preparedWrite, boolean responseNeeded,
int offset, byte[] value) {
super.onDescriptorWriteRequest(device, requestId, descriptor, preparedWrite, responseNeeded,
offset, value);
}
@Override
public void onNotificationSent(BluetoothDevice device, int status) {
super.onNotificationSent(device, status);
}
end
一口Linux
关注,回复【1024】海量Linux资料赠送
精彩文章合集
文章推荐