点击左上角“锂电联盟会长”,即可关注!


Highlights
•提出了一种残差卷积和Transformer网络来确保随机电压段的SOH估计。
•利用了交叉注意机制来整合充电段老化特征和运行条件的信息。
•采用了残差卷积作为Transformer的嵌入层,将充电段提取的信息映射到高维向量。
•设计了一种基于 ElasticNet 的特征传输策略来使用任意长度的电压段。
Abstract
Accurately monitoring the state of health (SOH) of lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) is crucial for battery management systems (BMS), yet there lack of the possibility to fully use the random charging segments with any length. To this end, a residual convolution and transformer network (R-TNet) is proposed to enable an accurate LIB SOH estimation with the sparse dimension of feature in random segments, where the start and end voltage, the Ampere-hour (Ah) throughput, temperature, and current rate of a charging segment are required for the estimation task. Through the cross-attention mechanism of R-TNet, the operation condition and the position of the partial voltage can be integrated to enable the LIBs SOH estimation within a charging segment. To extend the flexibility with arbitrary charging behaviors, an ElasticNet-based feature transfer strategy is designed to use any charging length. 121 cells with different chemistries and cycling conditions are used to validate the performance of the proposed method. The results of the proposed method show that the root mean square error (RMSE) of SOH estimation can reach 1.6% even for a 50 mV voltage segment.
Keywords
State of health estimation;
Residual convolution and transformer network;
Charging segment;
Feature transfer;
ElasticNet;
Graphics
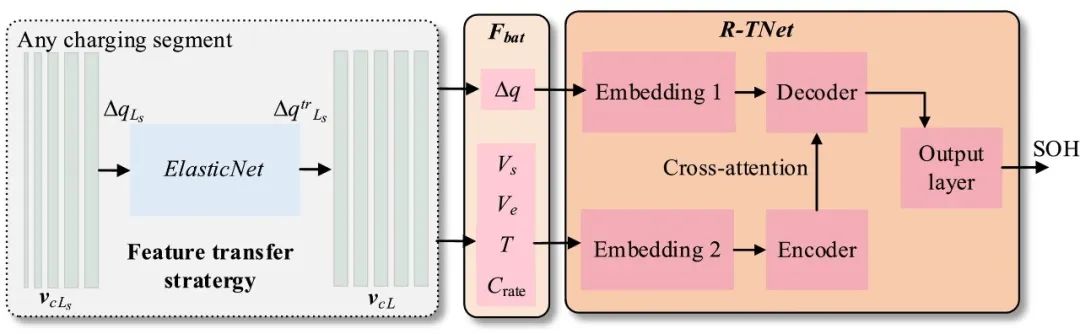
Fig. 1. The overall framework of the proposed method.
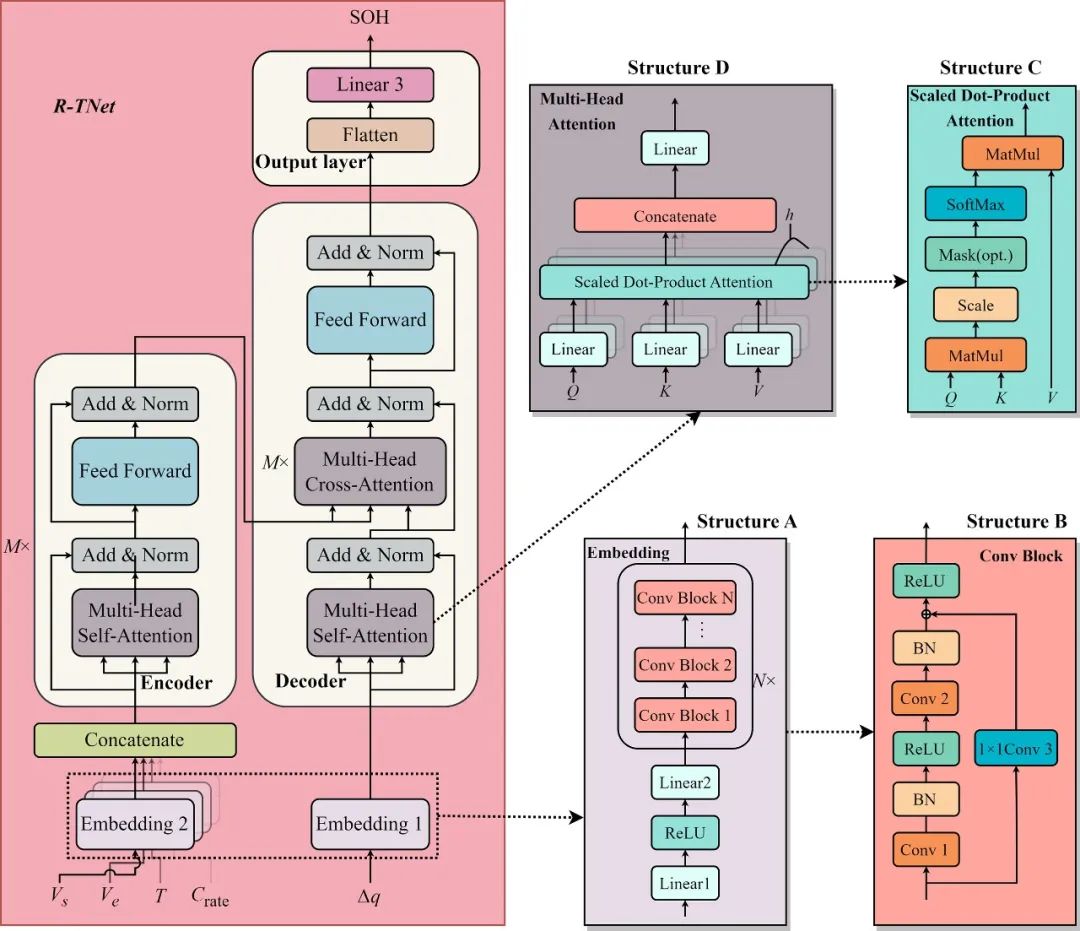
Fig. 3. The detailed structure of the R-TNet.
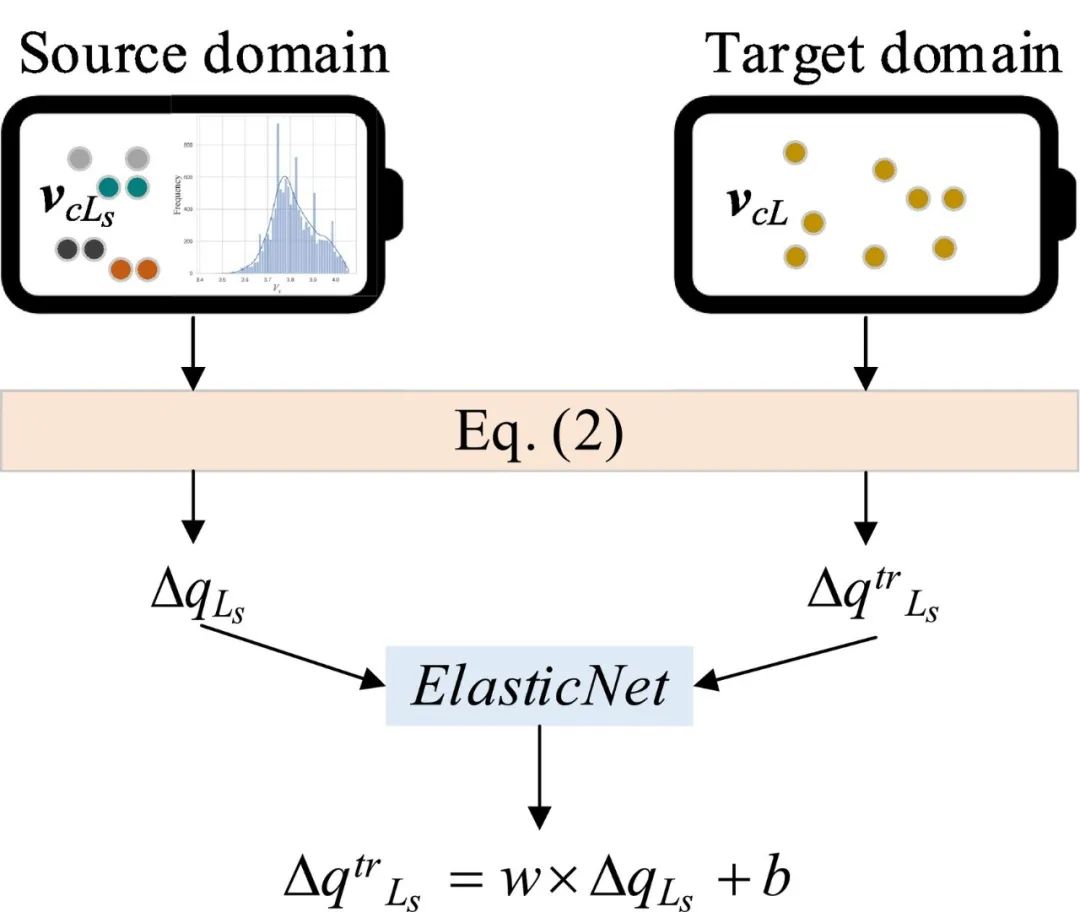
Fig. 4. The proposed feature transfer strategy.

Fig. 6. Results of SOH estimation for NCA cells. (a) RMSE (%); (b) MAE (%); (c) R2.
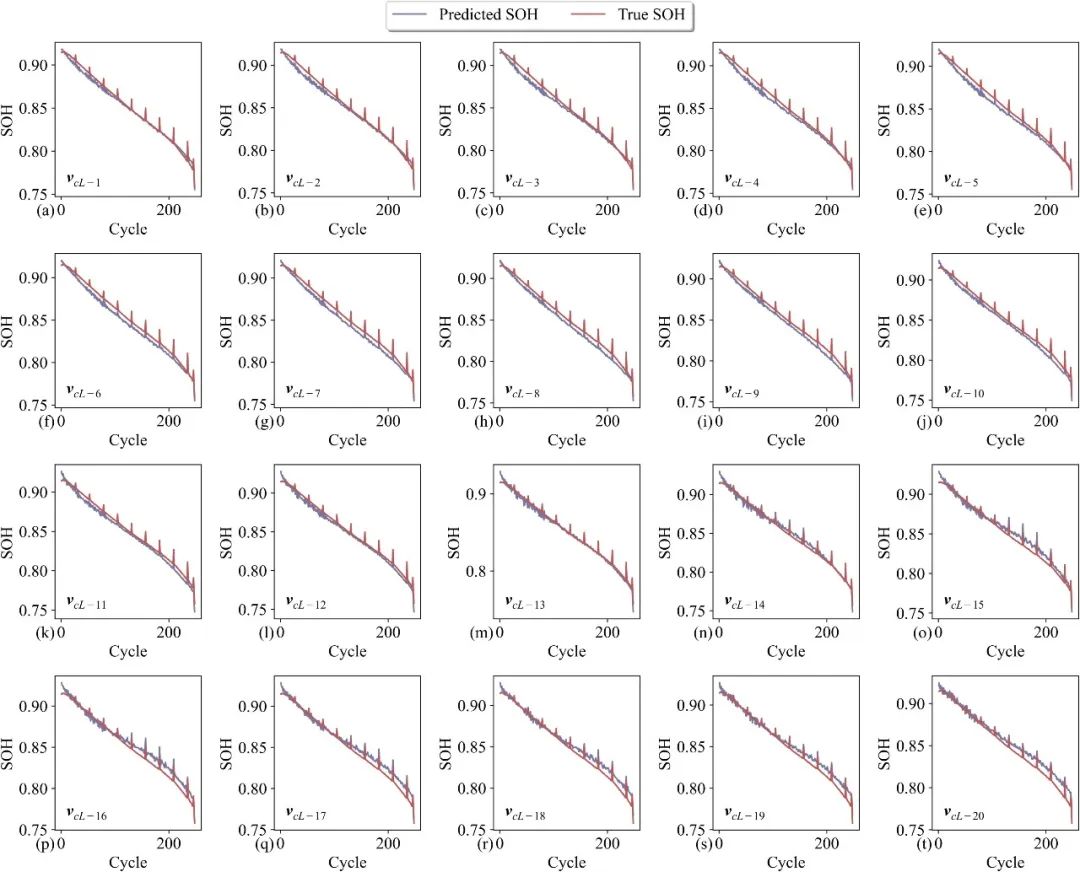
Fig. 7. Results of SOH estimation for Cell 1
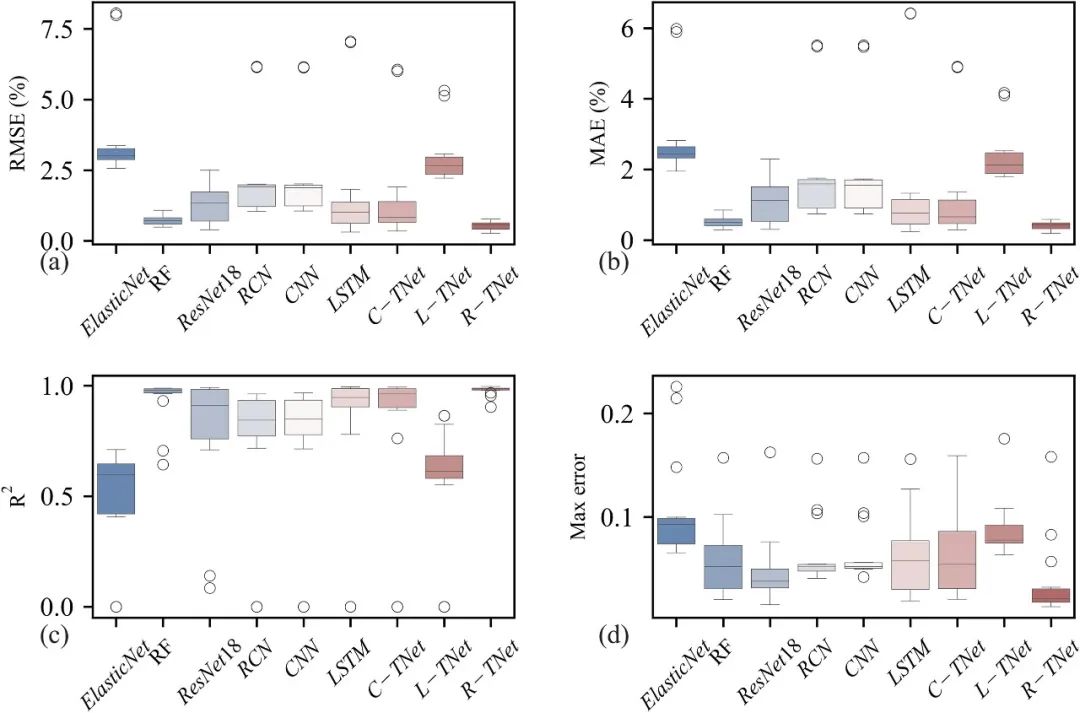
Fig. 9. The errors of the comparison methods for Cell 1~14. (a) RMSE (%); (b) MAE (%); (c) R2; (d) Max error.
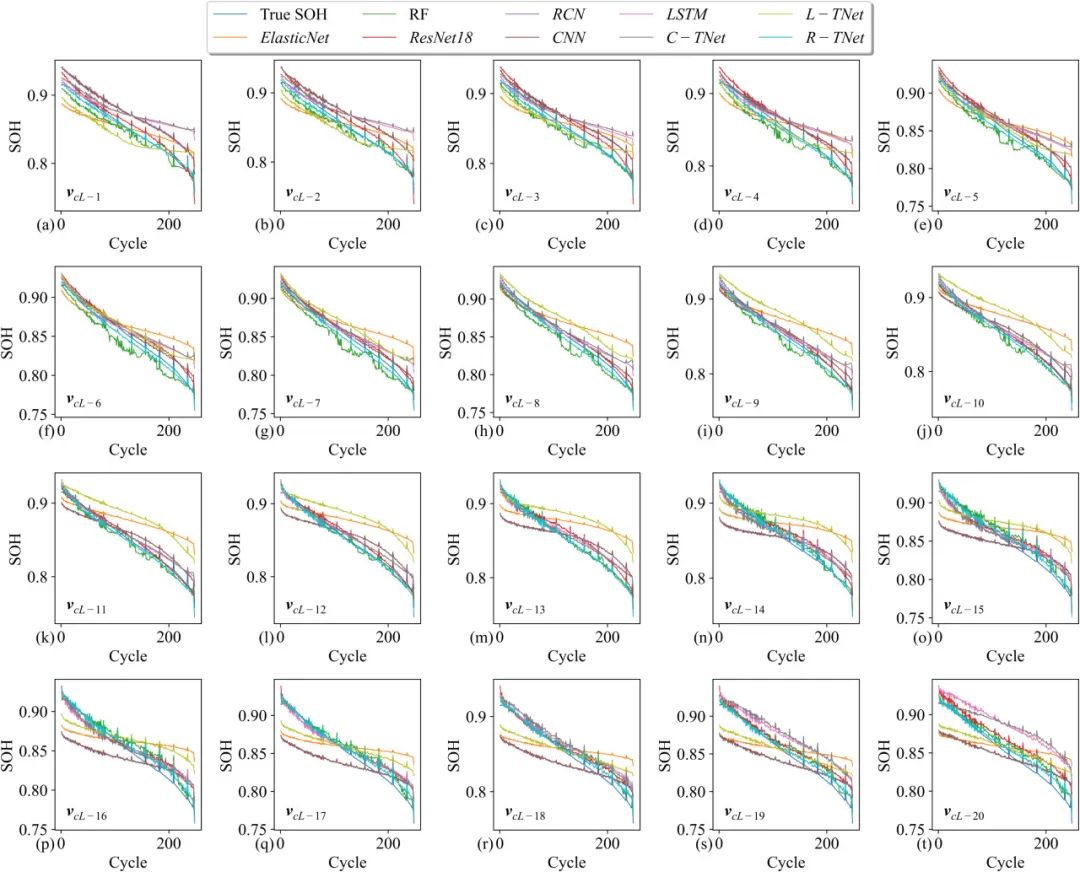
Fig. 10. SOH estimation results of different models for Cell 1.
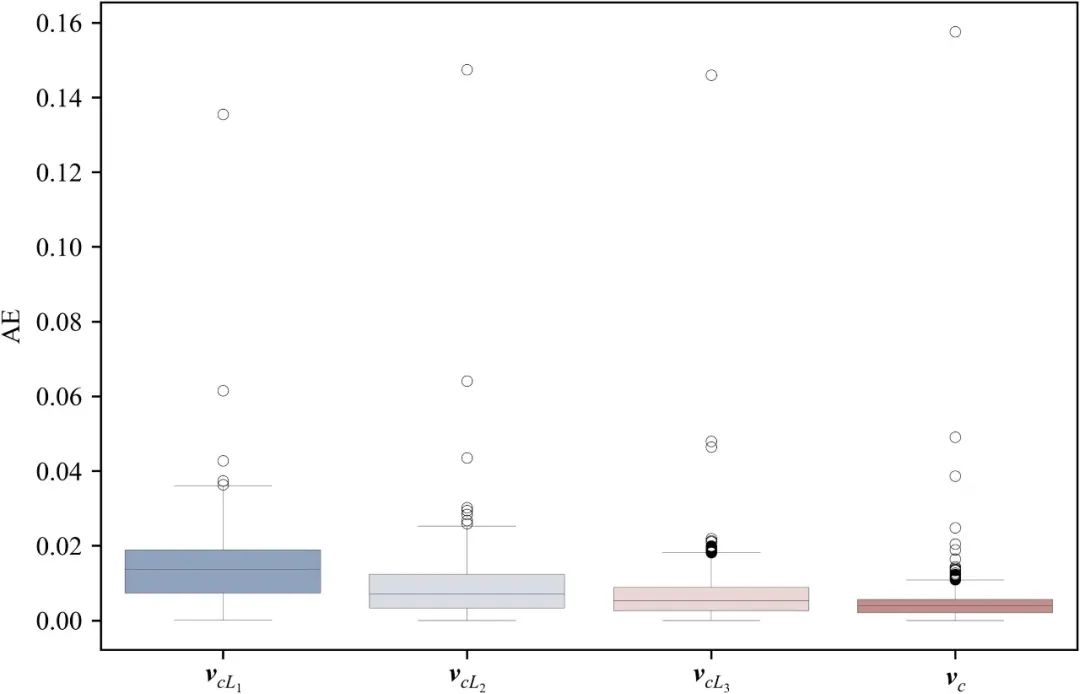
Fig. 11. SOH estimation AE results for voltage segments of different lengths.
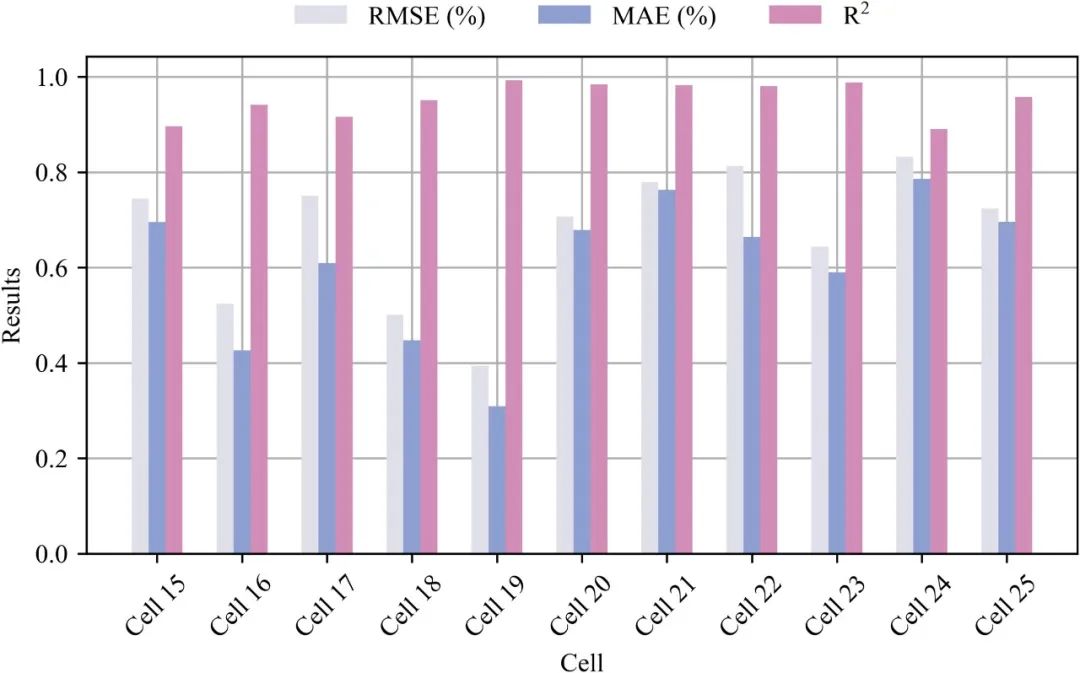
Fig. 13. SOH estimation results for Cells 15~25.
团队简介
本研究由西安交通⼤学先进电力储能技术研究中心人员完成。
通讯作者简介:
孟锦豪,博士,西安交通大学副教授,长期从事电池储能系统及能量管理方面研究。累计发表学术论文100余篇,其中,8篇ESI高被引论文,1篇ESI热点论文,授权国家发明专利10余项,参与起草团体标准1项。曾获2020年度陕西高等学校科学技术二等奖1项、陕西省自然科学优秀论文三等奖1项。主持或参与多项与电池储能应用相关课题。
第一作者简介:
郑琨,西安交通大学未来技术学院硕士研究生,研究方向为数据驱动的锂离子电池SOX估计及故障诊断。