5.5 使用用户态接口访问I2C设备
i2c-tools帮我们封装好了用户态访问I2C设备的接口,它是一套好用的工具,也是一套示例代码。
5.5.1体验I2C-Tools
使用一句话概括I2C传输:APP通过I2C Controller与I2CDevice传输数据。
所以使用I2C-Tools时也需要指定:
⚫ 哪个I2C控制器(或称为I2C BUS、I2C Adapter)
⚫ 哪个I2C设备(设备地址)
⚫ 数据:读还是写、数据本身
1. 交叉编译
⚫ 配置环境:
source /opt/remi-sdk/environment-setup-aarch64-poky-linux
在Makefile中,“?=”在第一次设置变量时才会起效果,如果之前设置过该变量,则不会起效果。
注意:
①执行make时,是动态链接,需要把libi2c.so也放到单板上。
②想静态链接的话,执行:make USE_STATIC_LIB=1
2. 用法
⚫ i2cdetect:I2C检测。
// 列出当前的 I2C Adapter(或称为 I2C Bus、I2C Controller)i2cdetect -l// 打印某个 I2C Adapter 的 Functionalities, I2CBUS 为 0、1、2 等整数i2cdetect -F I2CBUS// 看看有哪些 I2C 设备, I2CBUS 为 0、1、2 等整数i2cdetect -y -a I2CBUS// 效果如下# i2cdetect -li2c-3 i2c Renesas RIIC adapter I2C adapteri2c-1 i2c Renesas RIIC adapter I2C adapteri2c-0 i2c Renesas RIIC adapter I2C adapter# i2cdetect -F 0Functionalities implemented by /dev/i2c-0:I2C yesSMBus Quick Command yesSMBus Send Byte yesSMBus Receive Byte yesSMBus Write Byte yesSMBus Read Byte yesSMBus Write Word yesSMBus Read Word yesSMBus Process Call yesSMBus Block Write yesSMBus Block Read yesSMBus Block Process Call yesSMBus PEC yesI2C Block Write yesI2C Block Read yes// --表示没有该地址对应的设备, UU 表示有该设备并且它已经有驱动程序,// 数值表示有该设备但是没有对应的设备驱动# i2cdetect -y -a 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f00: 00 -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --10: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- UU -- -- -- 1e --20: -- -- UU -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --30: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --40: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --50: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --60: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --70: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
⚫ i2cget:I2C读
使用说明如下:
# i2cgetUsage: i2cget [-f] [-y] [-a] I2CBUS CHIP-ADDRESS [DATA-ADDRESS [MODE]]I2CBUS is an integer or an I2C bus nameADDRESS is an integer (0x03 - 0x77, or 0x00 - 0x7f if -a is given)MODE is one of:b (read byte data, default)w (read word data)c (write byte/read byte)Append p for SMBus PEC
使用示例:
// 读一个字节: I2CBUS 为 0、1、2 等整数, 表示 I2C Bus; CHIP-ADDRESS 表示设备地址i2cget -f -y I2CBUS CHIP-ADDRESS// 读某个地址上的一个字节:// I2CBUS 为 0、1、2 等整数, 表示 I2C Bus// CHIP-ADDRESS 表示设备地址// DATA-ADDRESS: 芯片上寄存器地址// MODE:有 2 个取值, b-使用`SMBus Read Byte`先发出 DATA-ADDRESS, 再读一个字节, 中间无P 信号// c-先 write byte, 在 read byte,中间有 P 信号i2cget -f -y I2CBUS CHIP-ADDRESS DATA-ADDRESS MODE // 读某个地址上的 2 个字节: // I2CBUS 为 0、1、2 等整数, 表示 I2C Bus// CHIP-ADDRESS 表示设备地址// DATA-ADDRESS: 芯片上寄存器地址// MODE:w-表示先发出 DATA-ADDRESS,再读 2 个字节i2cget -f -y I2CBUS CHIP-ADDRESS DATA-ADDRESS MODE
⚫ i2cset:I2C写
使用说明如下:
# i2csetUsage: i2cset [-f] [-y] [-m MASK] [-r] [-a] I2CBUS CHIP-ADDRESS DATA-ADDRESS [VALUE]... [MODE]I2CBUS is an integer or an I2C bus nameADDRESS is an integer (0x03 - 0x77, or 0x00 - 0x7f if -a is given)MODE is one of:c (byte, no value)b (byte data, default)w (word data)i (I2C block data)s (SMBus block data)Append p for SMBus PEC
使用示例:
// 写一个字节: I2CBUS 为 0、1、2 等整数, 表示 I2C Bus; CHIP-ADDRESS 表示设备地址// DATA-ADDRESS 就是要写的数据i2cset -f -y I2CBUS CHIP-ADDRESS DATA-ADDRESS// 给 address 写 1 个字节(address, value):// I2CBUS 为 0、1、2 等整数, 表示 I2C Bus; CHIP-ADDRESS 表示设备地址// DATA-ADDRESS: 8 位芯片寄存器地址;// VALUE: 8 位数值// MODE: 可以省略,也可以写为 bi2cset -f -y I2CBUS CHIP-ADDRESS DATA-ADDRESS VALUE [b]// 给 address 写 2 个字节(address, value):// I2CBUS 为 0、1、2 等整数, 表示 I2C Bus; CHIP-ADDRESS 表示设备地址// DATA-ADDRESS: 8 位芯片寄存器地址;// VALUE: 16 位数值// MODE: wi2cset -f -y I2CBUS CHIP-ADDRESS DATA-ADDRESS VALUE w// SMBus Block Write:给 address 写 N 个字节的数据// 发送的数据有:address, N, value1, value2, ..., valueN// 跟`I2C Block Write`相比, 需要发送长度 N// I2CBUS 为 0、1、2 等整数, 表示 I2C Bus; CHIP-ADDRESS 表示设备地址// DATA-ADDRESS: 8 位芯片寄存器地址;// VALUE1~N: N 个 8 位数值// MODE: si2cset -f -y I2CBUS CHIP-ADDRESS DATA-ADDRESS VALUE1 ... VALUEN s// I2C Block Write:给 address 写 N 个字节的数据// 发送的数据有:address, value1, value2, ..., valueN// 跟`SMBus Block Write`相比, 不需要发送长度 N// I2CBUS 为 0、1、2 等整数, 表示 I2C Bus; CHIP-ADDRESS 表示设备地址// DATA-ADDRESS: 8 位芯片寄存器地址;// VALUE1~N: N 个 8 位数值// MODE: ii2cset -f -y I2CBUS CHIP-ADDRESS DATA-ADDRESS VALUE1 ... VALUEN i
⚫ i2ctransfer:I2C传输(不是基于SMBus)
使用说明如下:
# i2ctransferUsage: i2ctransfer [-f] [-y] [-v] [-V] [-a] I2CBUS DESC [DATA] [DESC [DATA]]...I2CBUS is an integer or an I2C bus nameDESC describes the transfer in the form: {r|w}LENGTH[@address]1) read/write-flag 2) LENGTH (range 0-65535) 3) I2C address (use last one if omitted)DATA are LENGTH bytes for a write message. They can be shortened by a suffix:= (keep value constant until LENGTH)+ (increase value by 1 until LENGTH)- (decrease value by 1 until LENGTH)p (use pseudo random generator until LENGTH with value as seed)Example (bus 0, read 8 byte at offset 0x64 from EEPROM at 0x50):# i2ctransfer 0 w1@0x50 0x64 r8Example (same EEPROM, at offset 0x42 write 0xff 0xfe ... 0xf0):# i2ctransfer 0 w17@0x50 0x42 0xff
使用举例:
// Example (bus 0, read 8 byte at offset 0x64 from EEPROM at 0x50):# i2ctransfer -f -y 0 w1@0x50 0x64 r8// Example (bus 0, write 3 byte at offset 0x64 from EEPROM at 0x50):# i2ctransfer -f -y 0 w9@0x50 0x64 val1 val2 val3// Example// first: (bus 0, write 3 byte at offset 0x64 from EEPROM at 0x50)// and then: (bus 0, read 3 byte at offset 0x64 from EEPROM at 0x50)# i2ctransfer -f -y 0 w9@0x50 0x64 val1 val2 val3 r3@0x50# i2ctransfer -f -y 0 w9@0x50 0x64 val1 val2 val3 r3 //如果设备地址不变,后面的设备地址可省略
5.5.2 I2C-Tools访问I2C设备的2种方式
I2C-Tools可以通过SMBus来访问I2C设备,也可以使用一般的I2C协议来访问I2C设备。
使用一句话概括I2C传输:APP通过I2C Controller与I2C Device传输数据。
在APP里,有这几个问题:
①怎么指定I2C控制器?
⚫ i2c-dev.c为每个I2C控制器(I2C Bus、I2C Adapter)都生成一个设备节点:/dev/i2c-0、/dev/i2c-1等等;
⚫ open某个/dev/i2c-X节点,就是去访问该I2C控制器下的设备;
②怎么指定I2C设备?
通过ioctl指定I2C设备的地址
⚫ ioctl(file,I2C_SLAVE,address)
◼ 如果该设备已经有了对应的设备驱动程序,则返回失败。
⚫ ioctl(file,I2C_SLAVE_FORCE,address)
◼ 如果该设备已经有了对应的设备驱动程序但是还是想通过i2cdev驱动来访问它,则使用这个ioctl来指定I2C设备地址。
怎么传输数据?
③两种方式
⚫ 一般的I2C方式:ioctl(file,I2C_RDWR,&rdwr)
⚫ SMBus方式:ioctl(file,I2C_SMBUS,&args)
5.5.3 源码流程分析
1. 使用I2C方式
示例代码:i2ctransfer.c
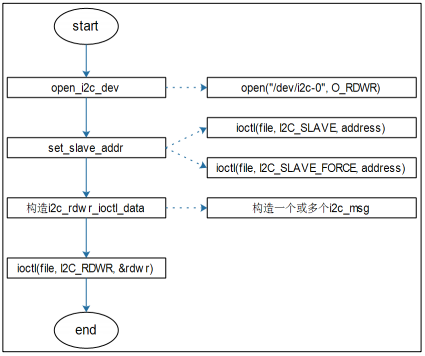
图I2C 读写源码流程
2. 使用SMBus方式
示例代码:i2cget.c、i2cset.c
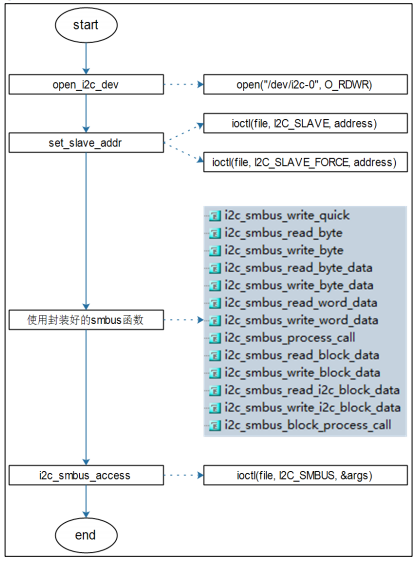
图SMBus读写源码流程
5.6 编写APP
在开始前,请先按照下图所示连接AT24C02模块
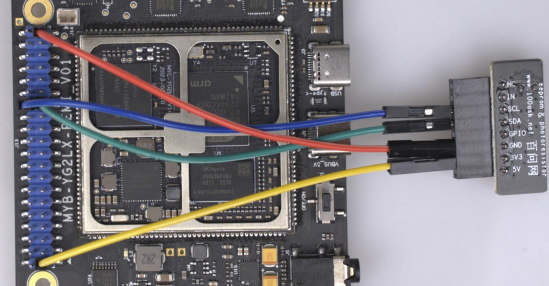
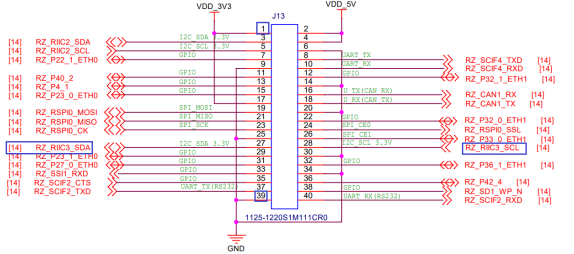
本节源码位于如下目录:
源码如下所示:
int main(int argc, char **argv)unsigned char dev_addr = 0x50;unsigned char mem_addr = 0;unsigned char buf[32];int file;char filename[20];unsigned char *str;int ret;struct timespec req;if (argc != 3 && argc != 4){printf("Usage:\n");printf("write eeprom: %sw string\n" , argv[0]);printf("read eeprom: %sr\n" , argv[0]);return -1;}//打开指定的 I2C 设备文件file = open_i2c_dev(argv[1][0]-'0', filename, sizeof(filename), 0);if (file < 0){printf("can't open %s\n", filename);return -1;}//设置 I2C 设备的从设备地址if (set_slave_addr(file, dev_addr, 1)){printf("can't set_slave_addr\n");return -1;}//如果命令行参数是 “w”,则将字符串写入 EEPROM。if (argv[2][0] == 'w'){// write str: argv[3]str = argv[3];req.tv_sec = 0;req.tv_nsec = 20000000; /* 20ms */while (*str)// 逐个字符写入 EEPROM{// mem_addr, *str// mem_addr++, str++ret = i2c_smbus_write_byte_data(file, mem_addr, *str);if (ret){printf("i2c_smbus_write_byte_data err\n");return -1;}// wait tWR(10ms)nanosleep(&req, NULL);// 每次写入后等待 20 毫秒mem_addr++;str++;}ret = i2c_smbus_write_byte_data(file, mem_addr, 0); // string end charif (ret){printf("i2c_smbus_write_byte_data err\n");return -1;}}else //如果命令行参数是 “r”,则从 EEPROM 读取数据。{// read 读取 EEPROM 数据ret = i2c_smbus_read_i2c_block_data(file, mem_addr, sizeof(buf), buf);if (ret < 0){printf("i2c_smbus_read_i2c_block_data err\n");return -1;}buf[31] = '\0';printf("get data: %s\n", buf);}return 0;}
编译:由于应用程序需要借助两个库i2cbusses.c和smbus.c,那么在编译应用程序时需要包含这两个程序:
source /opt/remi-sdk/environment-setup-aarch64-poky-linux$CC -I ./include -o at24c02_test at24c02_test.c i2cbusses.c smbus.c
假设设置开发板的IP为:192.168.5.9,上传程序到开发板上。
scp ./input_read_fasync root@192.168.5.9:/mnt/测试:进入/mnt目录运行程序:
root@myir-remi-1g:~root@myir-remi-1g:/mntat24c02_test
接上at24c02模块,向模块中写入数据,再读出来:
root@myir-remi-1g:/mnt# ./at24c02_test 3 w 123456789root@myir-remi-1g:/mnt# ./at24c02_test 3 rget data: 123456789
如您在使用瑞萨MCU/MPU产品中有任何问题,可识别下方二维码或复制网址到浏览器中打开,进入瑞萨技术论坛寻找答案或获取在线技术支持。
https://community-ja.renesas.com/zh/forums-groups/mcu-mpu/
未完待续
推荐阅读
Linux串口应用编程 - RZ MPU工业控制教程连载(6)
赢瑞米派 | 瑞萨RZ/G通用MPU研讨会火热报名中
函数应用及数据读取 - RZ MPU工业控制教程连载(5)