Protobuf(Protocol Buffers)是由 Google 开发的一种轻量级、高效的结构化数据序列化方式,用于在不同应用之间进行数据交换和存储。它可以用于多种编程语言,并支持自动生成代码,使得数据结构定义和序列化/反序列化过程更加简洁和高效。
Protobuf-C 是 Protocol Buffers 的 C 语言实现,它专门针对 C 语言环境进行了优化,提供了类似于官方实现的功能,同时支持与其他语言生成的 Protobuf 数据进行交互。Protobuf-C 生成的库文件可以被 C 语言项目使用,使得在 C 语言环境中进行高效的数据序列化和反序列化成为可能。
Protobuf优点包括:
高效性:protobuf 生成的数据格式通常比 XML 和 JSON 更加紧凑,序列化和反序列化速度更快。
可扩展性:支持向已有消息类型添加新的字段或消息,而不破坏向后兼容性。
语言无关性:protobuf 支持多种编程语言,包括 C++, Java, Python, Go, 和 C# 等。
自动代码生成:通过 .proto 文件定义消息格式后,可以使用编译器自动生成目标语言的代码,简化开发工作。
Protobuf代码仓库:https://github.com/protocolbuffers/protobuf
Protobuf-C代码仓库:https://github.com/protobuf-c/protobuf-c
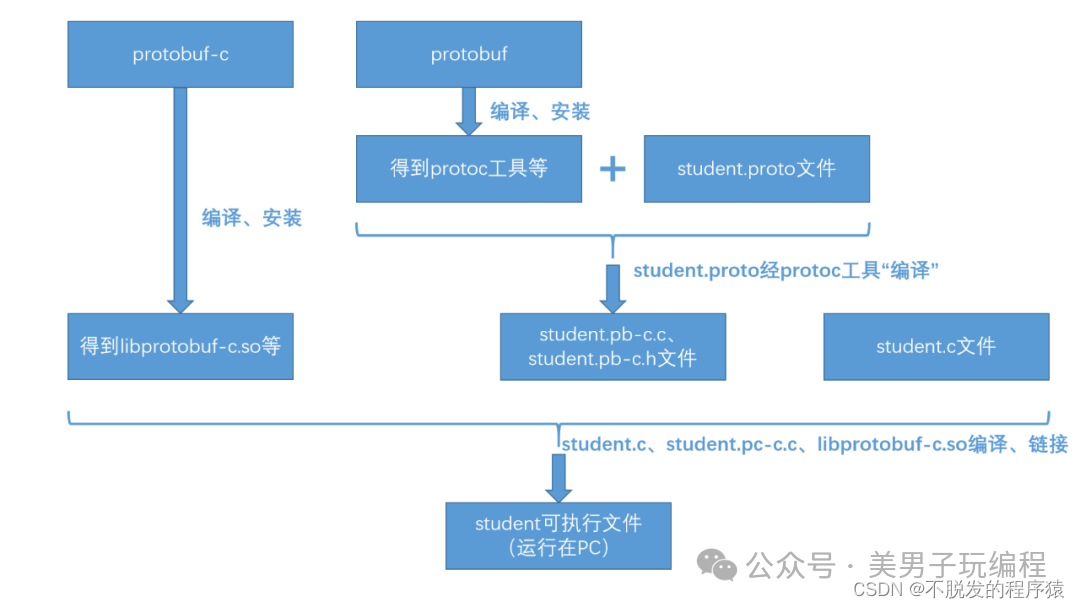
由于我需要在SoC开发板上使用C语言版的Protobuf库,所以需要使用到Protobuf
和Protobuf-C。
Protobuf 提供了 Protobuf 工具,用于将 .proto 文件转换为 C 源代码和头文件,而 Protobuf-c 生成了编译所需的动态库。
1
开发环境和工具
硬件环境
台湾联咏NT96570BG
软件环境
Ubuntu 18.04.6
SDK
na51055_linux_sdk-release.tar.gz
交叉编译工具链
nvt-96570-toolchain.tar.gz
Protobuf版本
V3.6.1(SoC需要和上位机通信,保持双方版本一致)
2
安装和编译Protobuf、Protobuf-C库
SoC编译和使用Protobuf库有2种方式:
下载Protobuf、Protobuf-C源码,集成到SoC SDK包中,修改makefile文件和相关配置,每次编译SDK固件时,也会编译和生成Protobuf所需的库和文件。
在Ubuntu系统下载和编译Protobuf、Protobuf-C源码,将编译好的库和文件拷贝到SoC APP应用工程中,修改makefile文件和相关配置,直接使用。
这里我们使用第二种方式。
1、安装依赖项
sudo apt-get install autoconf automake libtool curl make g++ unzip pkg-config2、安装Protobuf
下载Protobuf V3.6.1,解压后进入文件夹,指令如下:
cd protobuf./autogen.sh./configuremakesudo make installsudo ldconfig
含义如下:
cd protobuf: 进入名为 protobuf 的目录。
./autogen.sh: 运行 autogen.sh 脚本,用于生成 configure 配置脚本。
./configure: 根据生成的配置脚本,配置编译环境。
make: 编译源代码。
sudo make install: 安装编译生成的文件到系统中。
sudo ldconfig: 更新动态链接库缓存,使得系统能够找到新安装的库文件。
如果不需要使用指定版本的Protobuf,可以使用git指令下载库:
git clone https://github.com/protocolbuffers/protobuf.git3、安装protobuf-c
protobuf-c不需要指定版本,直接使用git指令下载仓库,指令如下:
git clone https://github.com/protobuf-c/protobuf-c.gitcd protobuf-c./autogen.sh./configure --host=arm-linux-gnueabihf CC=/opt/arm/arm-ca9-linux-gnueabihf-6.5/usr/bin/arm-ca9-linux-gnueabihf-gcc CXX=/opt/arm/arm-ca9-linux-gnueabihf-6.5/usr/bin/arm-ca9-linux-gnueabihf-g++ --disable-protoc --prefix=$PWD/tmp_outmakesudo make install
含义如下:
cd protobuf-c: 进入名为 protobuf-c 的目录。
./autogen.sh: 运行 autogen.sh 脚本,用于生成 configure 配置脚本。
./configure --host=arm-linux-gnueabihf CC=/opt/arm/arm-ca9-linux-gnueabihf-6.5/usr/bin/arm-ca9-linux-gnueabihf-gcc CXX=/opt/arm/arm-ca9-linux-gnueabihf-6.5/usr/bin/arm-ca9-linux-gnueabihf-g++ --disable-protoc --prefix=$PWD/tmp_out: 配置编译环境,指定目标架构为 arm-linux-gnueabihf,并使用指定的交叉编译器进行编译。
make: 编译源代码。
sudo make install: 安装编译生成的文件到系统中。
重点说一下configure配置编译环境指令:
./configure: 运行配置脚本。
--host=arm-linux-gnueabihf: 指定目标系统架构为 arm-linux-gnueabihf,表示编译生成的程序将在 ARM 架构上运行。
CC=/opt/arm/arm-ca9-linux-gnueabihf-6.5/usr/bin/arm-ca9-linux-gnueabihf-gcc: 指定 C 编译器为 /opt/arm/arm-ca9-linux-gnueabihf-6.5/usr/bin/arm-ca9-linux-gnueabihf-gcc,即指定了交叉编译器。
CXX=/opt/arm/arm-ca9-linux-gnueabihf-6.5/usr/bin/arm-ca9-linux-gnueabihf-g++: 指定 C++ 编译器为 /opt/arm/arm-ca9-linux-gnueabihf-6.5/usr/bin/arm-ca9-linux-gnueabihf-g++,即指定了交叉编译器。
--disable-protoc: 禁用 protoc 工具的构建,这表示只编译动态库,而不会生成 .proto 文件对应的 C 源码和头文件。
--prefix=$PWD/tmp_out: 指定安装路径为当前目录下的 tmp_out 目录。
如果不是ARM SoC使用,只是Ubuntu系统使用,配置编译环境就无需指定交叉编译工具链,指令如下:
./configureProtobuf、Protobuf-C默认安装在/usr/local路径下:
使用指令可以查看Protobuf、Protobuf-C的版本,指令如下:
protoc-c --version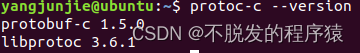
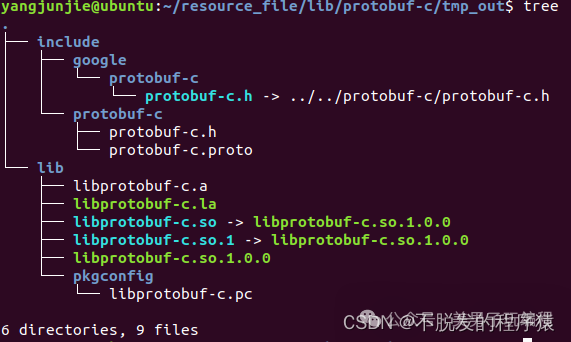
编译Protobuf-c代码时,指定了链接库输出在当前目录下的 tmp_out 目录。将编译输出物都拷贝到SoC APP应用工程中。
3
编写和编译proto文件
1、创建一个proto文件,文件命名为:LM_PCD_LD.proto,定义了一个消息类型:
syntax = "proto3";message Person {string name = 1;int32 id = 2;string email = 3;}
2、使用 Protobuf 编译器(protoc)生成对应的C代码:
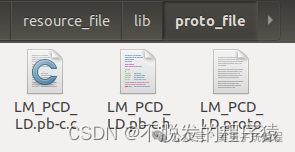
protoc --c_out=. LM_PCD_LD.proto.proto编译生成:LM_PCD_LD.pb-c.c和LM_PCD_LD.pb-h文件。将文件拷贝到SoC APP应用工程中。
4
修改makefile文件
1、添加头文件路径:
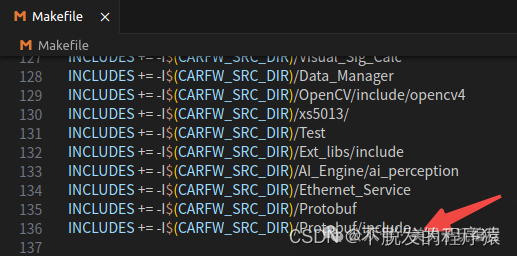
2、添加动态链接库路径:
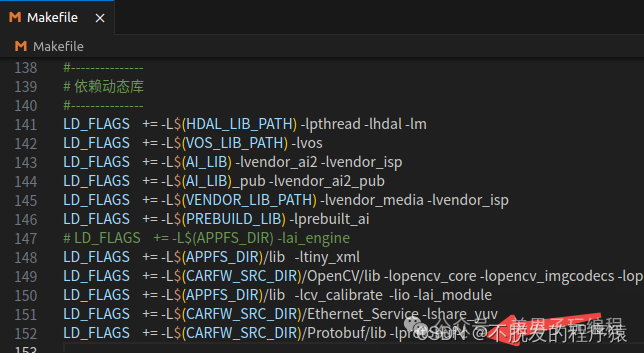
3、添加代码路径:
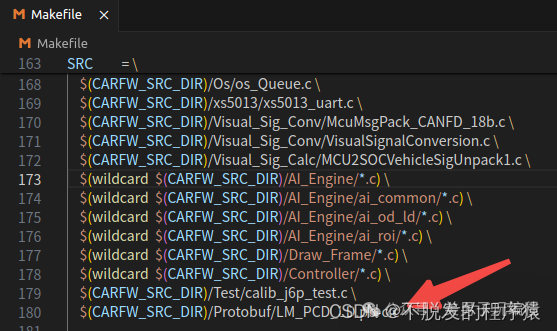
4、拷贝动态库到系统库文件下:
5
测试示例
int main() {// 创建并初始化 Person 消息对象Person person = PERSON__INIT;person.name = "John Doe";person.id = 1234;person.email = "johndoe@example.com";// 序列化消息对象size_t packed_size = person__get_packed_size(&person);uint8_t buffer[packed_size];person__pack(&person, buffer);// 反序列化消息对象Person *unpacked_person = person__unpack(NULL, packed_size, buffer);// 打印反序列化后的消息内容printf("Name: %s\n", unpacked_person->name);printf("ID: %d\n", unpacked_person->id);printf("Email: %s\n", unpacked_person->email);// 释放内存person__free_unpacked(unpacked_person, NULL);return 0;}