中国最活跃的射频微波天线雷达微信技术群
电子猎头:帮助电子工程师实现人生价值!
电子元器件:价格比您现有供应商最少降低5%

What is RADAR an acronym for? Radio Detection and Ranging.
Radio wave is generated, transmitted, reflected, and detected.
RADAR unimpaired by night, fog, clouds, smoke.
Not as detailed as actual sight.
RADAR is good for isolated targets against a relatively featureless background.
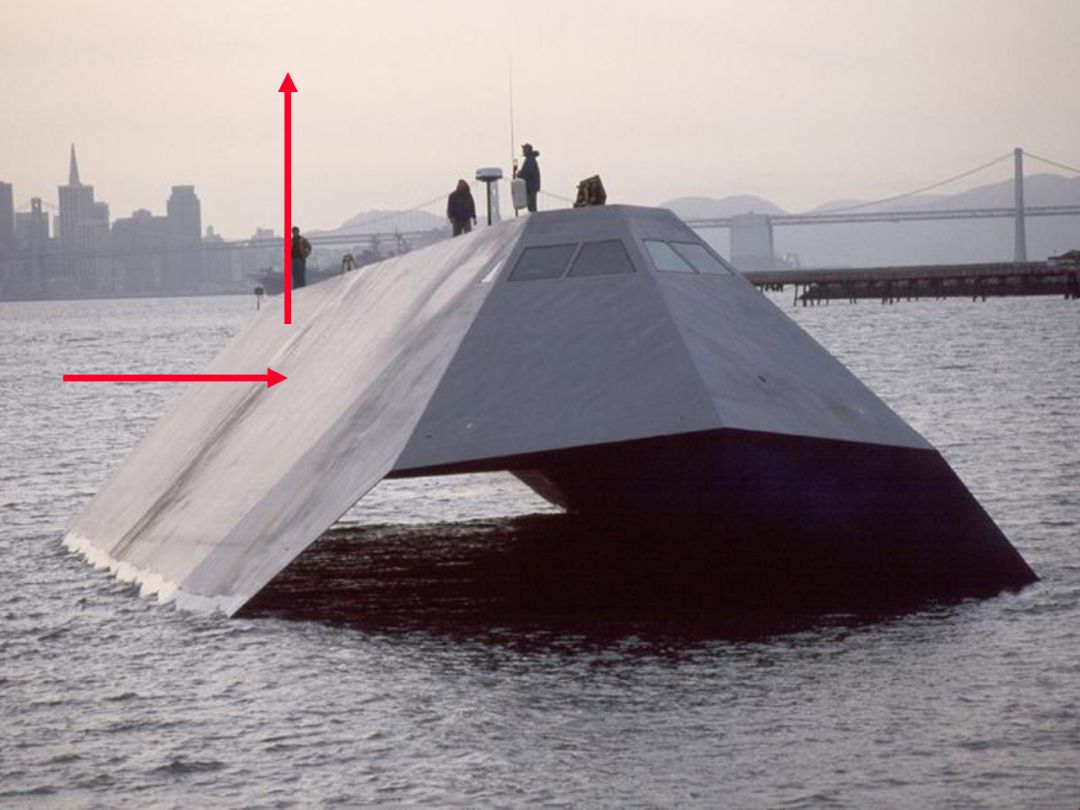

Stealth Ship
Designed to test the effects of stealth technology on Naval Warships.
What kind of radar reflection will we get off this target?
Note the angles, also coated with radar absorbing material.

Pulse - RADAR transmits a series of pulses separated by non-transmission intervals during which the radar “listens” for a return.
Continuous Wave - Constantly emitting radar. Relative motion of either the radar or the target is required to indicate target position. Frequency shift.

1. The pulse width determines the minimum range that the target can be detected.
a. If transmitter is still on when the pulse (echo)is returned then won’t see
the return.
b. Need short pulses to detect close targets.
2. Need long pulses to have sufficient power to reach targets that have long ranges.
3. Pulse Repetition Time, Frequency or Rate.
a. The length of time the transmitter is off (longer PRF) the longer the
radar’s maximum range will be. (Use the drawing to explain)
KEY Points:
1. Varying the pulse width affects the range of the radar.
2. Need short pulses for short range targets.
3. PW determines radar’s minimum range resolution.
4. The slower the PRF the greater the radar’s maximum
range.
5. The faster the PRF the greater the radar’s accuracy.
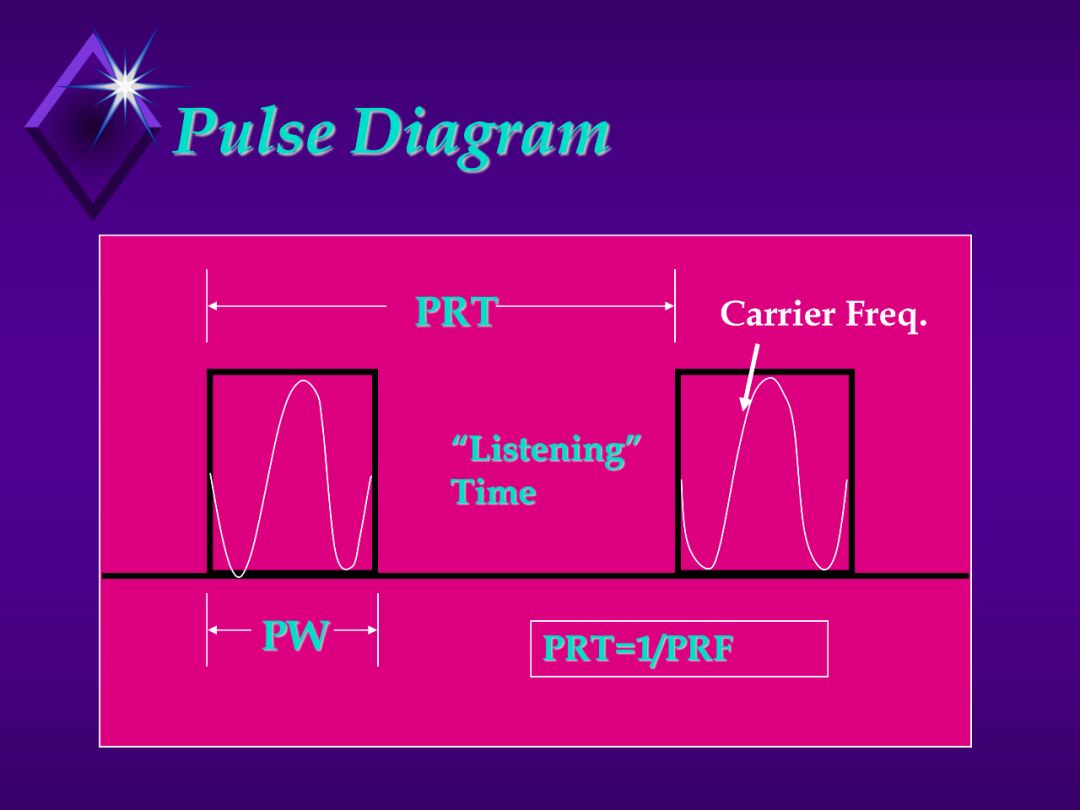
PW - Minimum range and Maximum Range
Minimum - PW determines when the radar begins listening for a target return
Maximum - PW determines on time for average power, need power to look long distances.
PRF - Maximum Range
Quit listening for a return pulse and transmit again
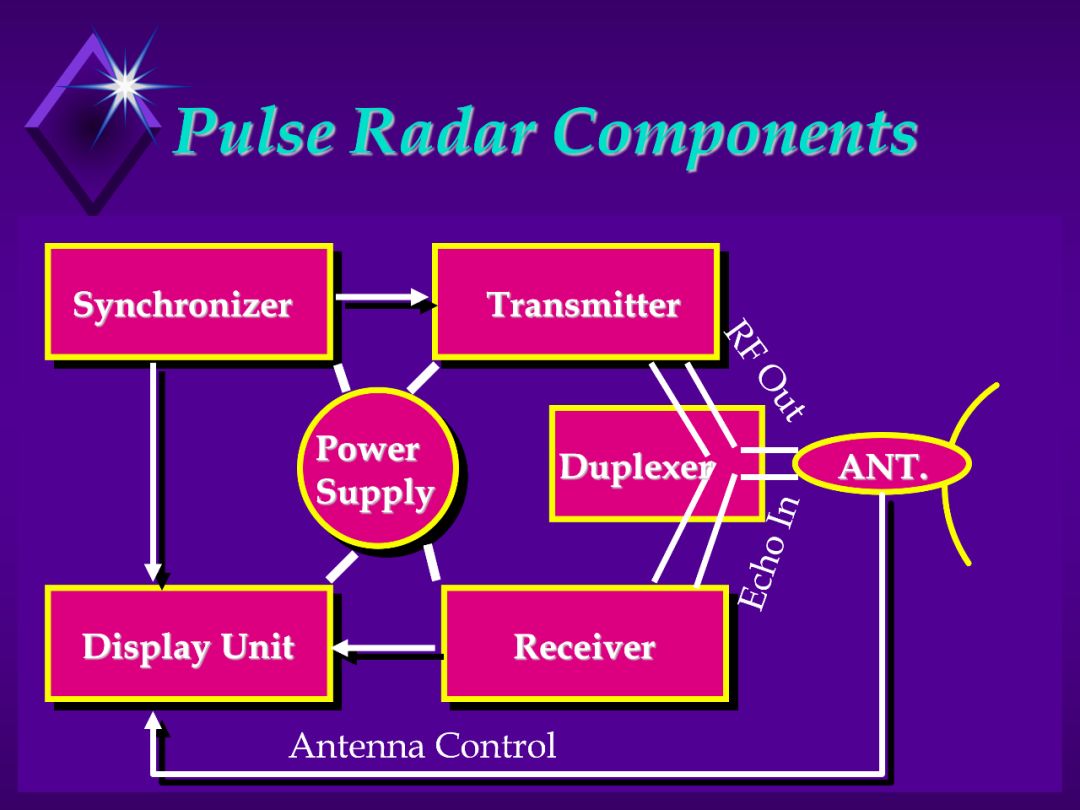
1. Synchronizer:
a. Coordinates the entire system
b. Determines the timing of the transmitted pulse
c. Includes timers, modulator and central control.
2. Transmitter:
a. Generate the pulse (RF) at the proper frequency and amplify.
3. Antenna:
A. Receives energy from the transmitter, radiates it in the form of a
highly directional beam.
B. Receives the echoes for pulse radars.
4. Duplexer:
a. Allows one antenna to be used to transmit and receive.
b. Prevents transmitted RF energy from going directly to the receiver.
c. Tells the antenna to radiate or receive.
5. Receiver: receives incoming echoes from antenna, detects and amplifies
the signal, and sends them to the display.
6. Display: Displays the received video to the operator.
7. Power Supply: Provides power to all the components of the system.
8. Discuss the antenna Bearing loop back to the display and its function.

Second major type of radar.
Produces a constant stream of energy.
Can’t distinguish distances (range) because no interval between pulses.
Can distinguish between moving and non-moving targets by using Doppler frequency shifts.
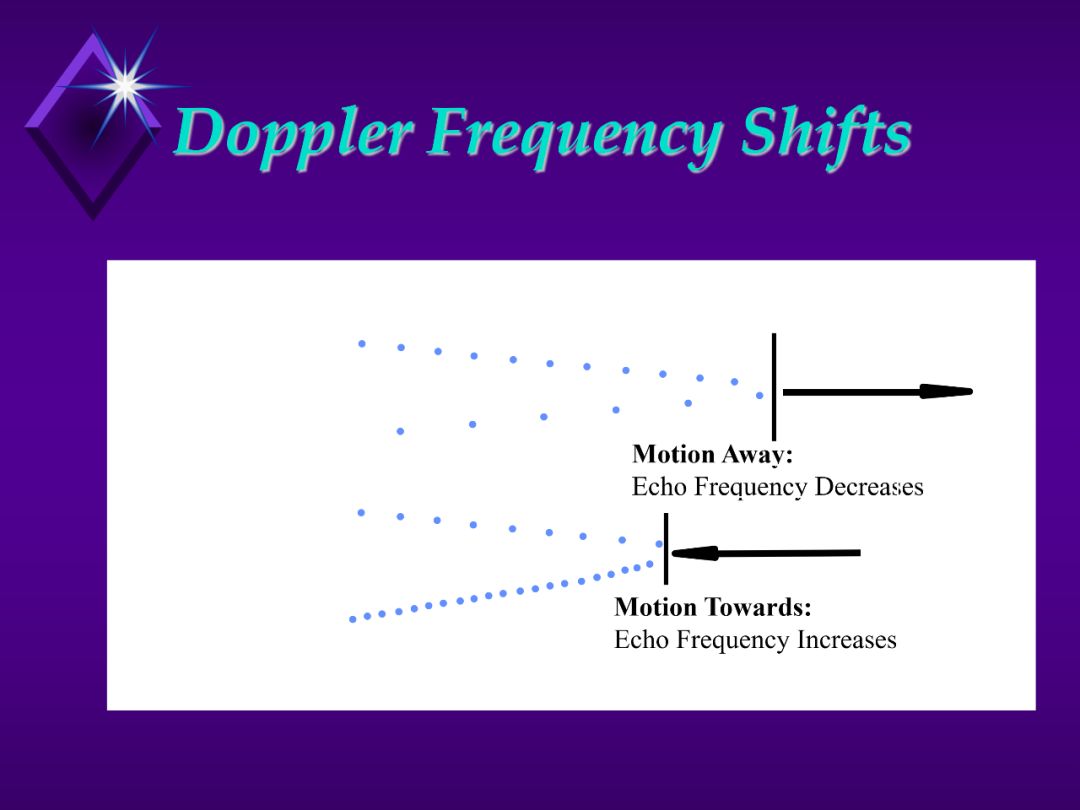
1. Doppler frequency shift describes the effect that motion has on a reflected
frequency.
2. Use the diagram to show:
a. If the wall is moving away a ball will have to travel farther than the
previous ball so the reflected balls are further apart.
b. If the wall is moving toward, a ball will have to travel a shorter distance
than the previous ball so the reflected balls are closer together.
3. If you assume that each ball represents the top of a wave so the distance
between each ball represents a wave cycle then you find:
a. The frequency of the echo is lower if the target is moving away.
b. The frequency of the echo is higher if the target is coming towards.
** This is why the sound of a passing train or airplane goes from
higher pitch to lower pitch.
4. Key Points:
a. Frequency expansion is the lowering of the echo frequency caused
by an opening target (target moving away). DOWN DOPPLER
b. Frequency compression is the raising of the echo frequency caused
by the closing target (target moving closer). UP DOPPLER
c. The moving of the transmitter can also cause frequency shifts (it’s
relative motion that produces the effect).
d. The faster the relative motion change the greater the frequency shift.
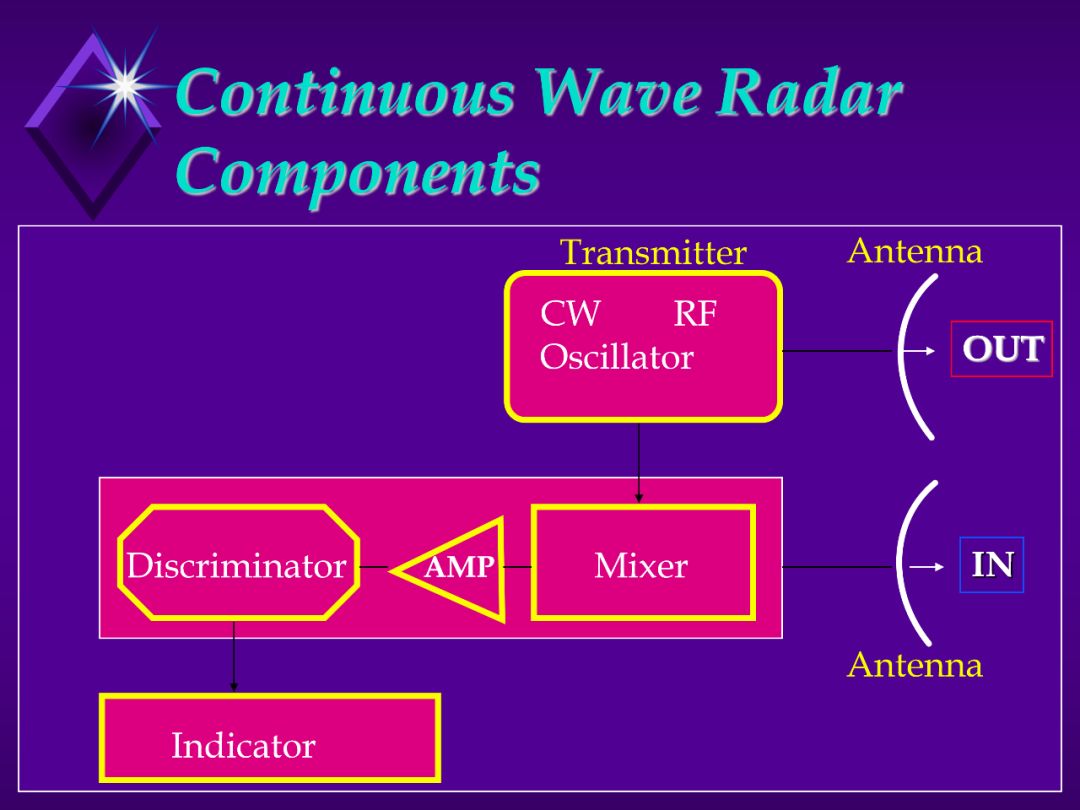
1. Transmit/Receive Antennas. Since must operate simultaneously, must be located separately so receiving antenna doesn’t pick up transmitted signal.
2. Oscillator or Power Amplifier. Sends out signal to transmit antenna. Also sends sample signal to Mixer. (used as a reference)
3. Mixer.
a. A weak sample of the transmitted RF energy is combined with the received echo signal.
b. The two signal will differ because of the Doppler shift.
c. The output of the mixer is a function of the difference in frequencies.
4. Amplifier. Increases strength of signal before sending it to the indicator.
5. Discriminator.
a. Selects desired frequency bands for Doppler shifts, eliminates
impossible signals.
b. The unit will only allow certain frequency bands so won’t process stray
signals.
6. Indicator. Displays data. Displays velocity or the component directly inbound or directly outbound. Range is not measured.
7. Filters. Used to reduce noise, used in amp to reduce sea return, land clutter, and other non-desirable targets.

Draw waves on the board and discuss.
1. The basic radar and communication transmission waves are modified to:
a. Allow the system to get more information out of a single transmission.
b. Enhance the signal processing in the receiver.
c. To deal with countermeasures (jamming, etc.)
d. Security (change characteristics)
2. Both CW and Pulse signals can be changed or MODULATED
3. Show slide.
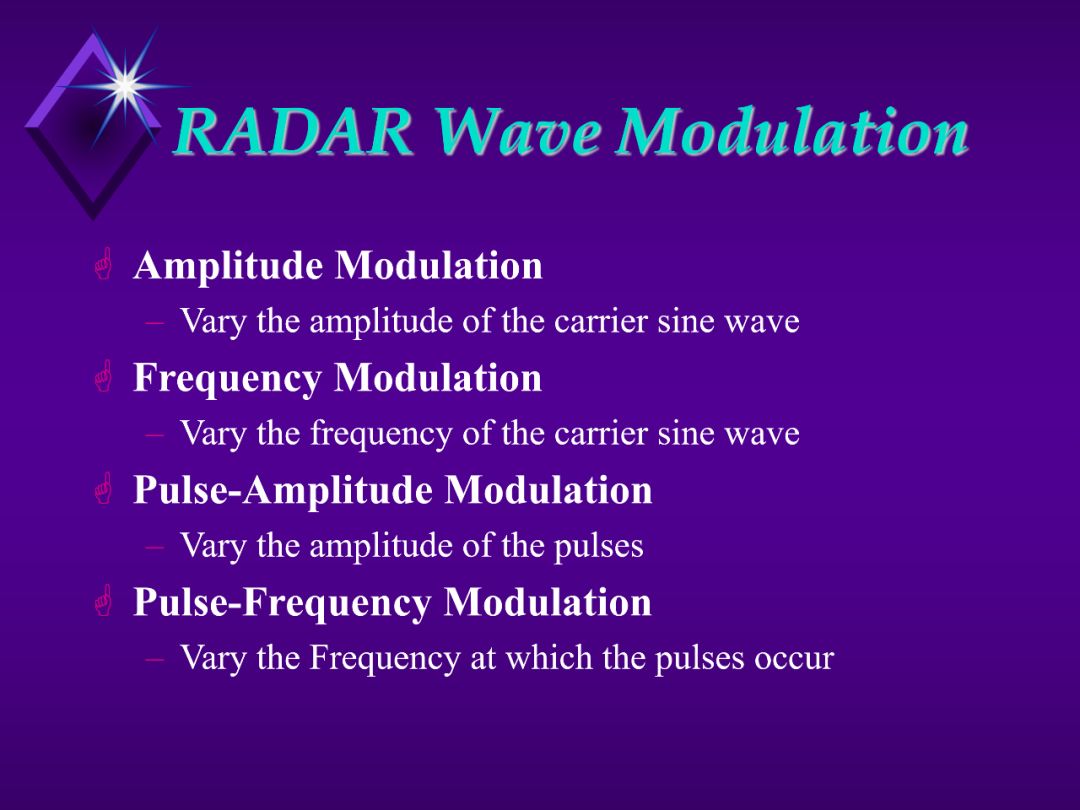
4. Common Modifications are:
a. AM
b. FM
c. Pulse Amplitude
d. Pulse Frequency
5. Modulation is achieved by adding signals together.

The antenna is used to radiate the RF energy created by the transmitter. It also receives the reflected energy and sends it to the receiver. Show slide:
1. Remember from discussion on how a RF transmission is made.
a. A dipole antenna is the simplest form of RF antenna.
b. Optimal radiation is achieved with an antenna length of 1/2
a wave length long or multiples thereof.
c. Electrical field strength is strongest in middle and least at top/bottom.
d. Maximum field strength is perpendicular to the antenna
e. Field extends 360 degrees around antenna.
2. Beam Pattern represents the electromagnetic field around antenna.
a. It is a snap shot at any given time.
b. Lines represents field strength (in the example it is strongest on x axis)
c. Field goes to near zero 30-40 degrees off horizontal axis
3. Simple antenna doesn’t help us locate a target just that he is in the cone.
It would be a help if we could:
a. Illuminate a specific area (for accurate location data)
b. Not wasting power by looking in unwanted directions
c. Focus more power in the area we want to look at
4. We improve system performance and efficiency through manipulation of the beam’s formation. The major way we do this is by the antenna.
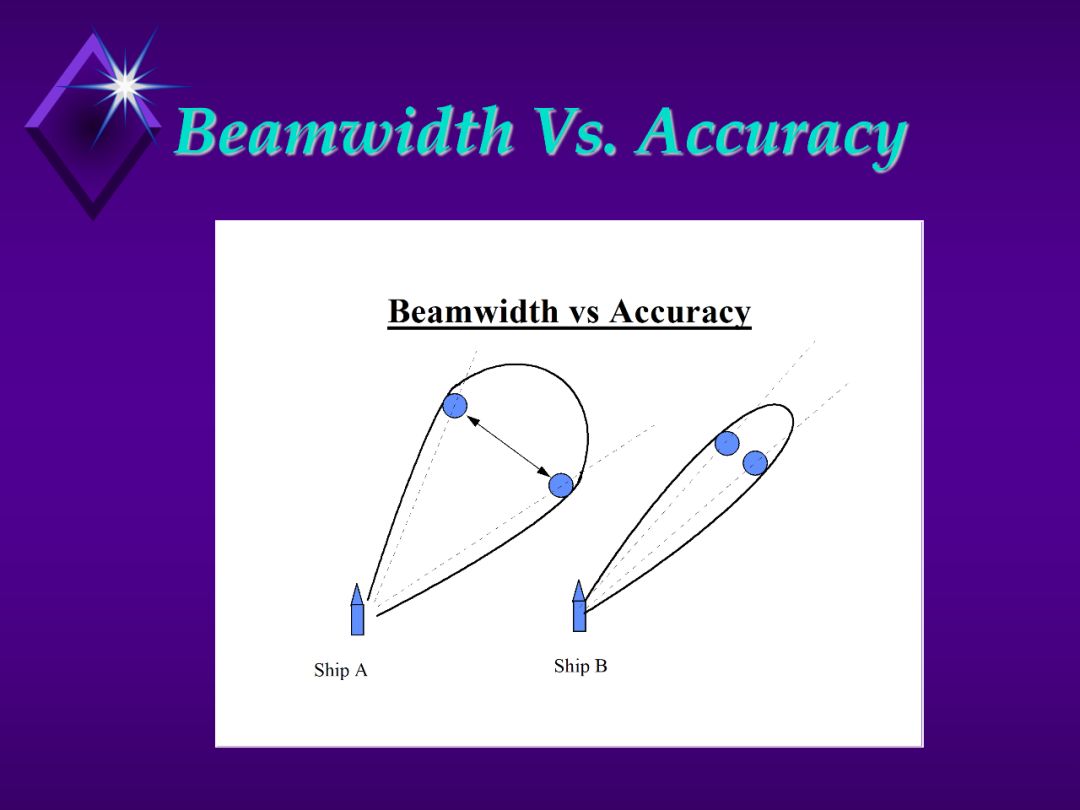
1. The size of the width of the beam (beam-width) determines the angular accuracy of the radar. From drawing we see that the target could be any where in the beam to produce a return. Ship B can more accurately determine where the target really is.
2. The function of the radar determines how narrow the beam-width is needed.
a Search radars sacrifice accuracy for range. (wide beam-widths at high
power)
b. Tracking or targeting radars require more accuracy (narrow beam-
widths)
3. If the target is located on the center line of the beam lobe, the return will be the strongest.
Key Point:. Beam-widths determine the angular accuracy of the radar.
Lead in: Angular accuracy can be use to measure azimuth and elevation depending on which way the antenna is oriented.

1. We get range from measuring the time the pulse takes to get from the antenna until the echo is received back.
2. We can get angular range by measuring the antenna angle from the heading of the ship when it is pointing at the target.
a. Relative heading is just this angle from the ship.
b. For true direction this angle is added to the heading of the ship.
(If the summation is >360 degrees subtract 360 degrees.
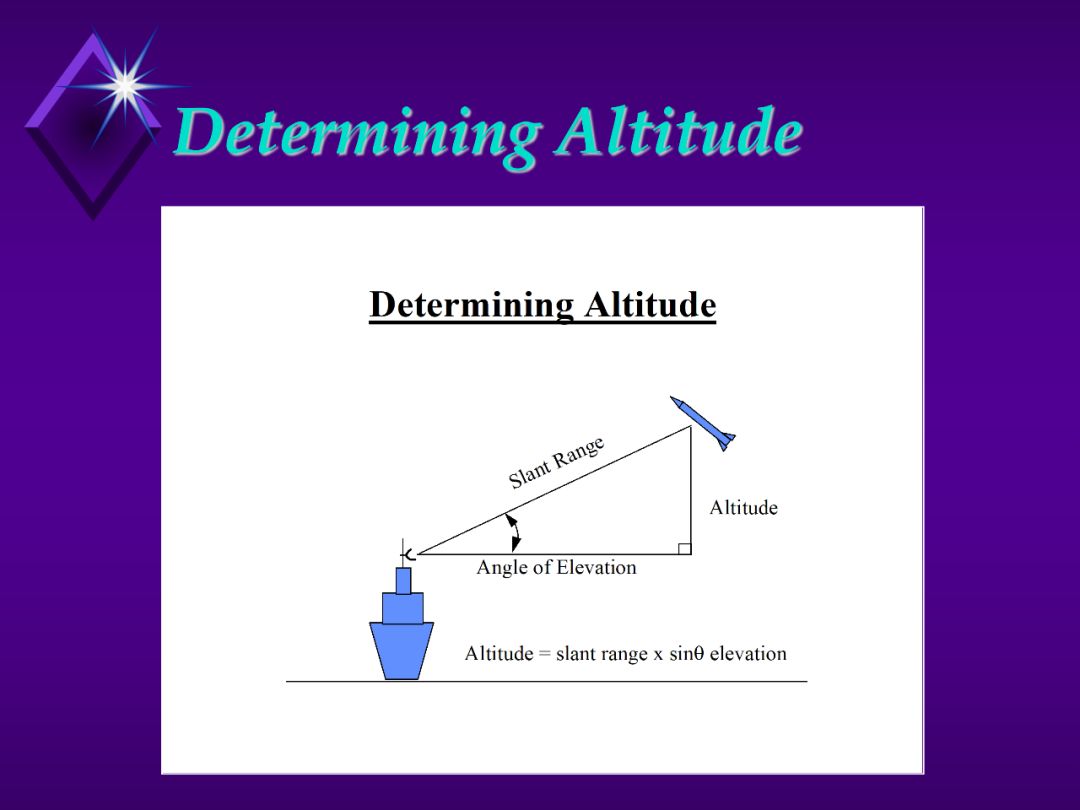
1. Show slide to show that angular measurements is simple geometry to determine height.
Note:
a. Must adjust for the height of the radar antenna.
b. If the target is low and point the beam low you could get returns from
the water surface.
- Sea Return or “Sea Clutter”

1.. We have seen the advantages of having a strong, narrow beam.
How do we produce the beam?
2. Show Slide.
3. Linear Arrays:
a. Work because can add waves together to get constructive or destructive
interference.
b. Common types of Linear arrays include: Broadside and Endfire
Arrays.
c. Can employ Parasitic Elements direct the beam.
d. SPY is a phased array radar, more than 4,000 beam for const/dest
4. Lenses:
a. Are like optical lenses they focus the beam through refraction of the
energy wave.
b. Can only effectively be used with very high frequencies such as
microwaves.
c. When you hear of a microwave horn... that is the “lens.”

1. One of the most common Quasi-Optical Systems used to enhance the beams are reflectors.
a. Reflectors are just like the reflectors used in flashlights.
b. They make use of the reflectivity of Electromagnetic waves.
c. Take a simple half-wave dipole antenna and reflect the energy into
one large beam.
2. Because the reflecting surface is not exact and there is some scattering, will get some smaller beams in addition to the major beam. These are called MINOR LOBES. The large beam is the MAJOR LOBE.
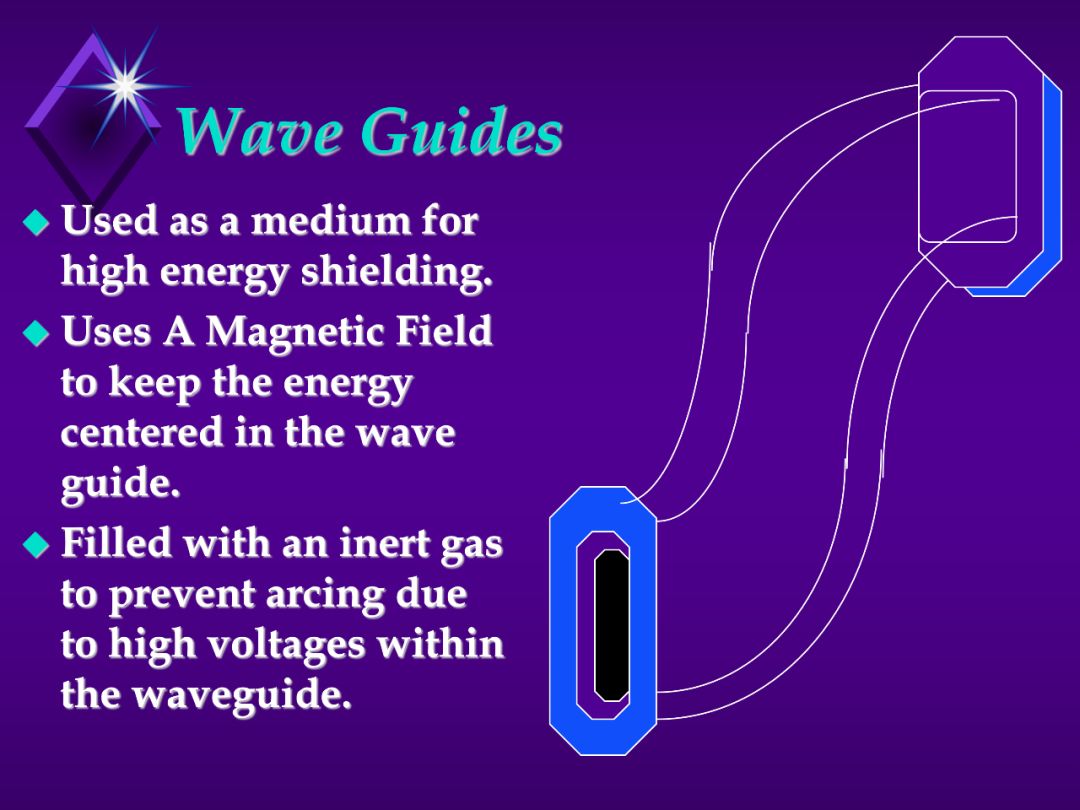
Most efficient means of conducting energy from transmitter to the antenna.
A cable would act as a short circuit if use at that high of frequency.
Hollow dialectic gas filled tube of specific dimensions.
Doesn’t work like a wire conducting current. A totally different concept.
Can end in flared tube which transmits the energy
Should know what a wave guide is for and that if dented, crushed or punctured, it can adversely effect the performance of the system.
Don’t bang on wave guides!!

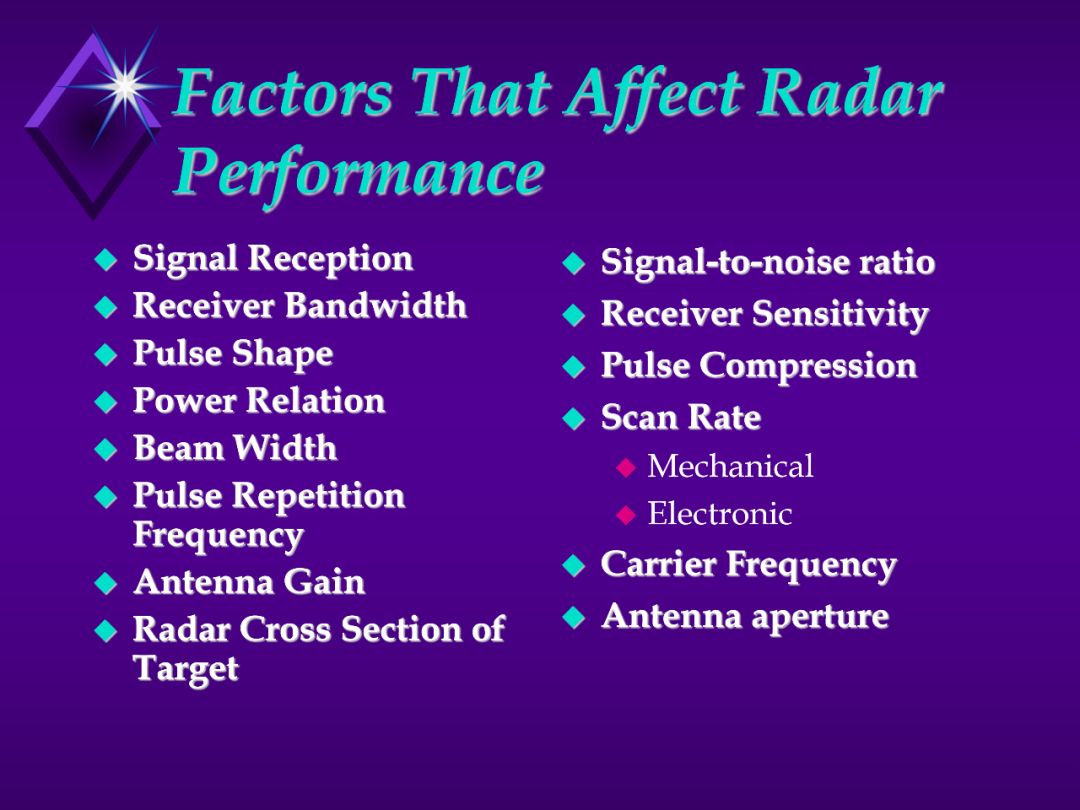
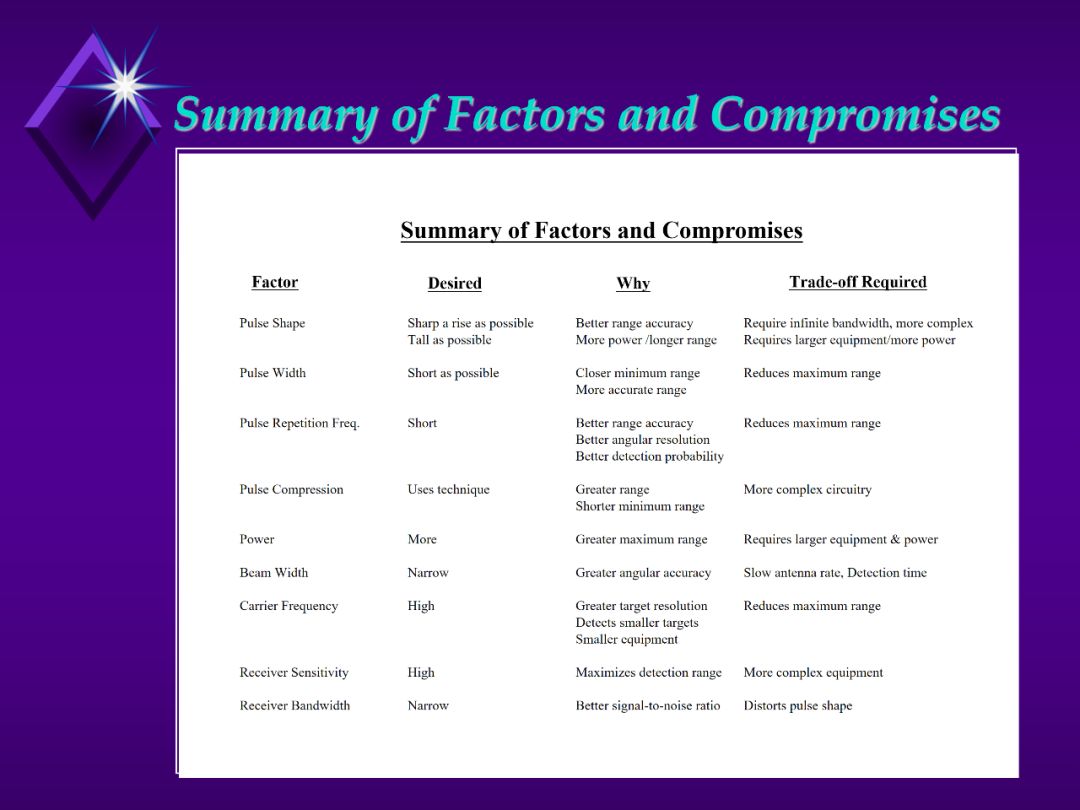
Go through this slide.
See following slides for definitions of the various factors.
Signal Reception:
a. Only a minute portion of the RF is reflected off the target.
b. Only a fraction of that returns to the antenna.
c. The weaker the signal that the receiver can process, the greater the effective range.
Signal-to-Noise Ratio:
a. Noise(always present) sets the absolute lower limit of the sensitivity of the radar sets. (At some range the noise will be greater than the echo)
b. Noise includes atmospheric disturbances, jamming, stray signal. Noise is inherent in the electronic circuits as random electron motion through a resister causes stray noise.
c. To cope with this problem, the operator can set a threshold level. If signals are below this threshold level, they will not be displayed.
If threshold level is set too low, you get many false detections.
If set too high, could mask out real contact, (therefore, operator must compromise the gain).

These are all factors of the design of the radar receiver.

1. Explain why only portion of the signal gets to the target and only a fraction of that signal gets back to the receiver.

Signal-to-Noise Ratio:
a. Noise (always present) sets the absolute lower limit of the sensitivity of
the radar sets. (At some range the noise will be greater than the echo)
Example: Look at a cb radio. If you turn down the volume eventual you will not hear the music only the static. The static is noise.
b. Noise includes atmospheric disturbances, Jamming, stray signals.
Noise is inherent in electronic circuits as random electron
motion through a resister causes stray noise.
c. To cope with this problem, the operator can set a threshold level. If
signals are below this threshold level, they will not be displayed.
* If threshold level is set too low - you get many false detentions.
* If set to high - could mask out the real contact. Must compromise.

Receiver Bandwidth:
a. To create a pulse many different frequency sine waves are summed so a
radar must combine RF energy of different frequencies.
b. Doppler effects also shift the frequencies so the radar must be capable of
receiving and processing many frequencies.
c. The range of frequencies is the bandwidth of the receiver.
d. Reduce the bandwidth increases the signal-to-noise & distorts the pulse.

Receiver Sensitivity:
a. Defined as the smallest return signal that can produce an electrical signal
to the indicator that is discernible against the noise background.
b. Sensitivity is an important factor in determining the maximum radar
range.
c. Smallest discernible signal is measured in milliwatts and is referred to
the Minimum Detectable Signal.


Pulse Shape
a. A pulse is made by summing several sinusoid waves of various
frequencies.
- A perfect pulse (vertical leading and trailing edges requires
the receiver to process an infinite number of sine wave freq.
- Internal circuit noise will also distort a pulse.
b. Determines the range accuracy. (closer to vertical the better)
Use graphic pulse to show rise time can confuse timing to get range.
c. Pulse shape can also effect minimum detection range.
- Already discussed that. Pulse must be off before echo returns.

. Pulse Width.
a. Determines range resolution and minimum detection range for same
reasons as pulse shape. Can’t have pulse on when the echo returns.
b. To lesser extent, pulse width can determine maximum range.
- Pulse has to be big enough to hold enough energy to travel to the
target and return.
- The bigger the pulse the more energy it can hold and the further
away the target can be an still get a measurable return.
- [Power in wave is product of peak power and pulse width]
c. The narrower the pulse the better the range resolution
- This is a trade off with amount of power in the pulse and the effective maximum range of the radar. LIMITS the range.



1. Scan Rate and Beam Width
a. If have wide beam can scan area more rapidly
b. If small have to go slower, give target more time to get close without
being detected.
2. Pulse Repetition Frequency
a. Already talked about. Can’t have next pulse transmitting when the
echo from the previous one is still on the way back.
3. Carrier Frequency
a. Determines antenna size and directivity of beam.
b. Lower Frequency the longer the distance can travel, the bigger the
antenna required, and the more power required.
c. The higher the frequency the better the resolution and the ability to
detect smaller targets. Also the small the antenna size and the greater
the attenuation losses.
4. Radar cross section
a. Function of the target. Reflectivity of the target.
b Desire good flat surfaces (perpendicular to wave) so reflect signal good,
made of material that doesn’t absorb RF, and is as big as a house.
This is where Stealth comes to play. Lower the object’s radar cross section.
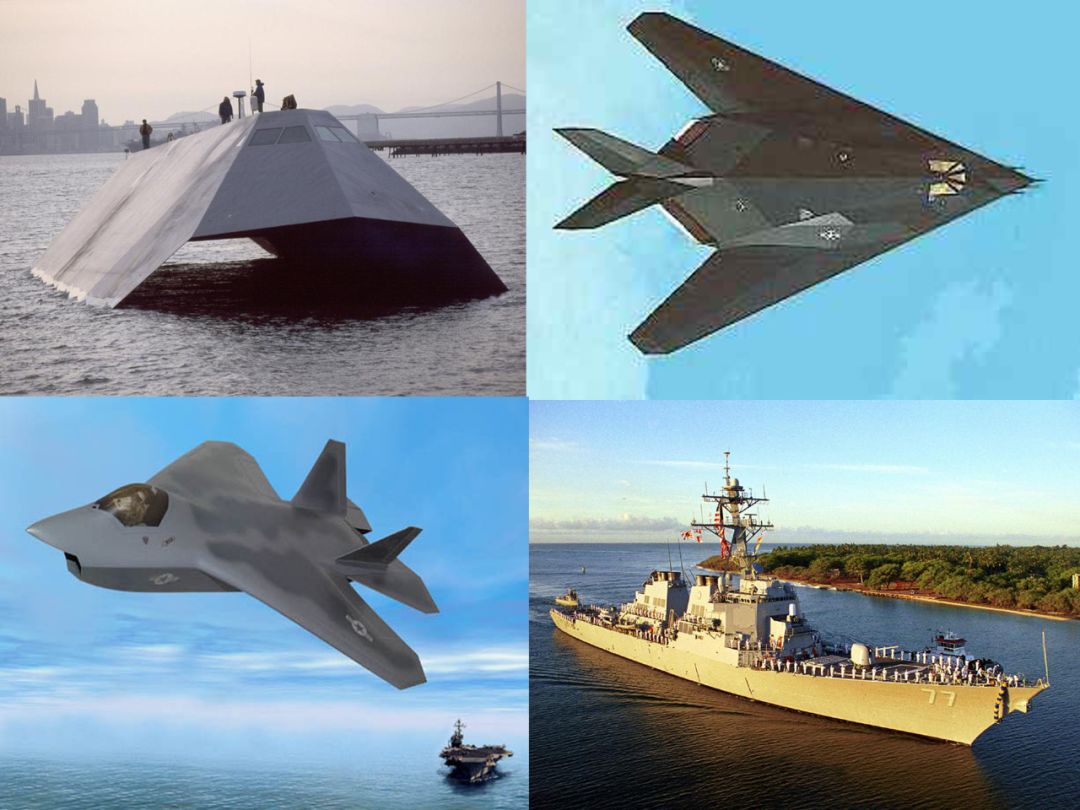

Low RCS!
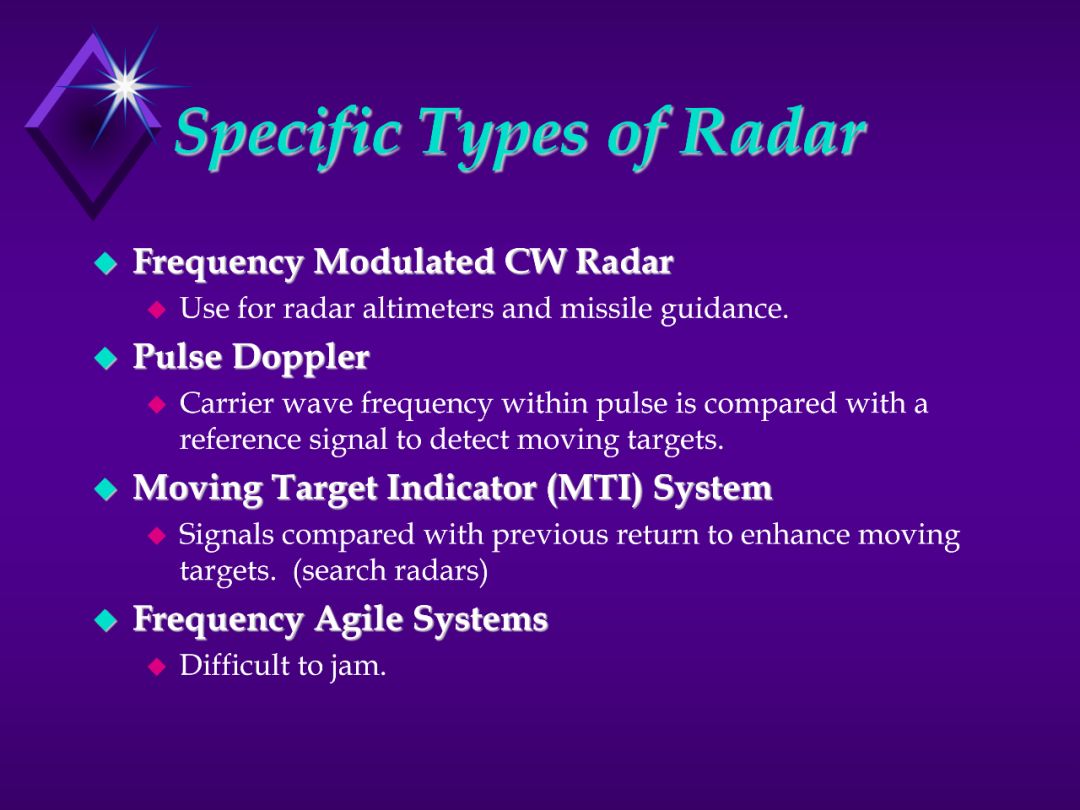
1. Frequency Modulated CW Radar (p. 106)
- Previously discussed
- Good for radar altimeters and missile guidance
2. Pulse Doppler (p. 114)
- Can use advantages of CW and Pulse radars
- Can color-code the return. Commonly used for weather radars. In military applications, the colors can represent a target moving away from you vice towards.
- The doppler shift on the return translates to a color shift in the visible spectrum.
3. MTI (p. 112)
- Can be used for enhancing targets that are moving
- Example: In a chaff environment, the stationary chaff can be deleted
and the returns of the moving target identified.
4. Frequency Agile
- Harder to jam. “Frequency Jumping”


欢迎射频微波雷达通信工程师关注公众号

电子万花筒平台自营:Xilinx ALTERA ADI TI ST NXP 镁光 三星 海力士内存芯片 等百余品牌的电子元器件,可接受BOM清单,缺料,冷门,停产,以及国外对华禁运器件业务!
欢迎大家有需求随时发型号清单,我们将在第一时间给您呈上最好的报价,微信(QQ同号):1051197468 也希望您把我们的微信推荐给采购同事,感谢对平台的支持与信任!
与我们合作,您的器件采购成本将相比原有供应商降低5%以上!!不信?那您就来试试吧!!欢迎来撩!!
