关注、星标公众号,直达精彩内容
源码地址:https://gitee.com/MR_Wyf/hal-cubemx-rt-thread/tree/hal_rttNano_st7789_menu/
或者关注公众号,后台回复“SPI DMA”,获取本章节源码
配置非常简单,只需要选择SPI1的TX配置为DMA模式即可,选择正常模式即可,不需要循环模式,否则LVGL可能会显示异常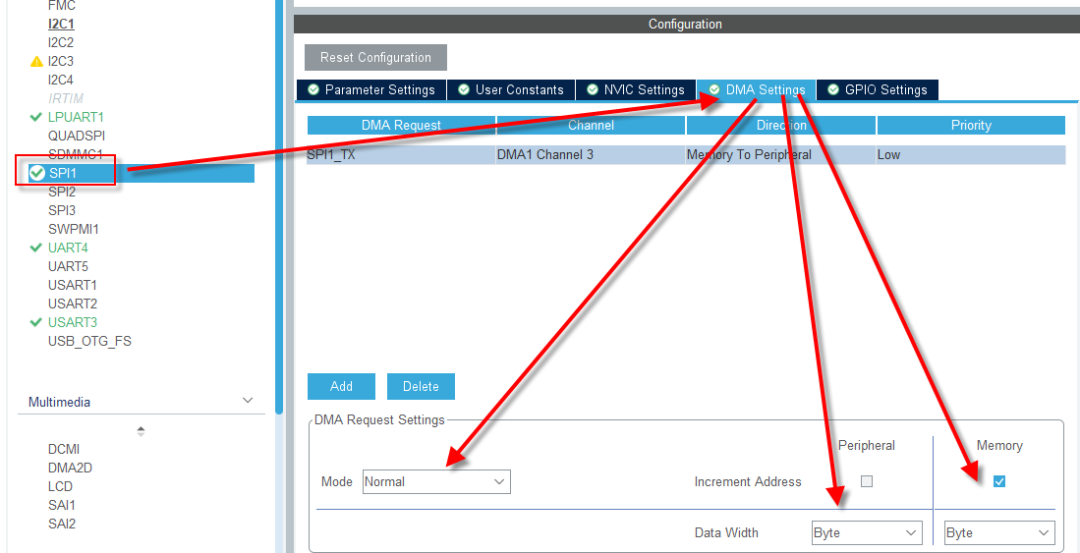
先来看上面配置生成的代码,主要就是DMA的模式配置参数
/* SPI1 DMA Init */
/* SPI1_TX Init */
hdma_spi1_tx.Instance = DMA1_Channel3;
hdma_spi1_tx.Init.Request = DMA_REQUEST_1;
hdma_spi1_tx.Init.Direction = DMA_MEMORY_TO_PERIPH;
hdma_spi1_tx.Init.PeriphInc = DMA_PINC_DISABLE;
hdma_spi1_tx.Init.MemInc = DMA_MINC_ENABLE;
hdma_spi1_tx.Init.PeriphDataAlignment = DMA_PDATAALIGN_BYTE;
hdma_spi1_tx.Init.MemDataAlignment = DMA_MDATAALIGN_BYTE;
hdma_spi1_tx.Init.Mode = DMA_NORMAL;
hdma_spi1_tx.Init.Priority = DMA_PRIORITY_LOW;
if (HAL_DMA_Init(&hdma_spi1_tx) != HAL_OK)
{
Error_Handler();
}
__HAL_LINKDMA(spiHandle,hdmatx,hdma_spi1_tx);
继续来看下SPI DMA的接口:
HAL_StatusTypeDef HAL_SPI_Transmit_DMA(SPI_HandleTypeDef *hspi, uint8_t *pData, uint16_t Size);
HAL_StatusTypeDef HAL_SPI_Receive_DMA(SPI_HandleTypeDef *hspi, uint8_t *pData, uint16_t Size);
HAL_StatusTypeDef HAL_SPI_TransmitReceive_DMA(SPI_HandleTypeDef *hspi, uint8_t *pTxData, uint8_t *pRxData,
uint16_t Size);
HAL_StatusTypeDef HAL_SPI_DMAPause(SPI_HandleTypeDef *hspi);
HAL_StatusTypeDef HAL_SPI_DMAResume(SPI_HandleTypeDef *hspi);
HAL_StatusTypeDef HAL_SPI_DMAStop(SPI_HandleTypeDef *hspi);
主要就是发送、接收,以及接收暂停、接受恢复、接收停止功能函数,本次驱动LCD主要用到的是DMA发送函数,主要有3个参数
/**
* @brief Transmit an amount of data in non-blocking mode with DMA.
* @param hspi pointer to a SPI_HandleTypeDef structure that contains
* the configuration information for SPI module.
* @param pData pointer to data buffer
* @param Size amount of data to be sent
* @retval HAL status
*/
HAL_StatusTypeDef HAL_SPI_Transmit_DMA(SPI_HandleTypeDef *hspi, uint8_t *pData, uint16_t Size);
上一章节中我们使用的是SPI驱动的LCD,并没有加入DMA,本章节咱们对驱动函数进行改造,加入DMA驱动,只需要把我们的SPI发送函数改为DMA发送函数即可,以下几个函数同理改动
// ST7789写函数
static HAL_StatusTypeDef lcd_st7789_write(int is_cmd, uint8_t data)
{
uint8_t pData[2] = { 0 };
assert_param(NULL != hspi_lcd);
pData[0] = data;
if (is_cmd)
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(LCD_DC_GPIO_Port, LCD_DC_Pin, GPIO_PIN_RESET);
else
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(LCD_DC_GPIO_Port, LCD_DC_Pin, GPIO_PIN_SET);
// return HAL_SPI_Transmit(hspi_lcd, pData, 1, HAL_MAX_DELAY);
return HAL_SPI_Transmit_DMA(hspi_lcd, pData, 1);
}
/********************************************************************
*
* LcdWriteReg
*
* Function description:
* Sets display register
*/
void lcd_st7789_write_reg(uint8_t Data)
{
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(LCD_DC_GPIO_Port, LCD_DC_Pin, GPIO_PIN_RESET);
// HAL_SPI_Transmit(&hspi1, &Data, 1, 10);
HAL_SPI_Transmit_DMA(&hspi1, &Data, 1);
}
/********************************************************************
*
* LcdWriteData
*
* Function description:
* Writes a value to a display register
*/
void lcd_st7789_write_data(uint8_t Data)
{
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(LCD_DC_GPIO_Port, LCD_DC_Pin, GPIO_PIN_SET);
HAL_SPI_Transmit_DMA(&hspi1, &Data, 1);
//HAL_SPI_Transmit(&hspi1, &Data, 1, 10);
}
/********************************************************************
*
* lcd_st7789_write_data_multiple
*
* Function description:
* Writes multiple values to a display register.
*/
extern uint8_t g_spi_dma_tc;
void lcd_st7789_write_data_multiple(uint8_t *pData, int NumItems)
{
if (g_spi_dma_tc) {
g_spi_dma_tc = 0;
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(LCD_DC_GPIO_Port, LCD_DC_Pin, GPIO_PIN_SET);
//HAL_SPI_Transmit(&hspi1, pData, NumItems, 10);
HAL_SPI_Transmit_DMA(&hspi1, pData, NumItems);
}
}
本次移植的是lvgl V8.3,源码在lvgl官方github上就可以下载到,想下载的兄弟小手动一动,不想下载的也没关系,小飞哥会把源码开源,直接拿过去就行了
至于LVGL的移植,就不再赘述了,相信网上有成堆的教程,小飞哥也不再废话浪费大家伙时间了,直接下载源码即可
主要强调几个移植的点:
在定时器3回调函数中调用lv_tick_inc(1),为LVGL提供心跳,周期10ms足够
void HAL_TIM_PeriodElapsedCallback(TIM_HandleTypeDef *htim)
{
/**timer for lvgl,period 1ms*/
if (htim->Instance == TIM3)
{
lv_tick_inc(1);
}
if (htim->Instance == TIM15)
{
// if(RT_EOK==rt_sem_take(sem_uart_rec,RT_WAITING_NO))
// {
if (embedded_get_uart_rec_flag())
{
/*100ms*/
if (embedded_get_uart_timeout_cnt() > 9)
{
// lv_tick_inc(1);
embedded_set_uart_rec_flag(RT_FALSE);
rt_sem_release(sem_uart_timeout);
}
}
// }
}
}
void lv_port_disp_init(void)
{
/*-------------------------
* Initialize your display
* -----------------------*/
disp_init();
/*-----------------------------
* Create a buffer for drawing
*----------------------------*/
/**
* LVGL requires a buffer where it internally draws the widgets.
* Later this buffer will passed to your display driver's `flush_cb` to copy its content to your display.
* The buffer has to be greater than 1 display row
*
* There are 3 buffering configurations:
* 1. Create ONE buffer:
* LVGL will draw the display's content here and writes it to your display
*
* 2. Create TWO buffer:
* LVGL will draw the display's content to a buffer and writes it your display.
* You should use DMA to write the buffer's content to the display.
* It will enable LVGL to draw the next part of the screen to the other buffer while
* the data is being sent form the first buffer. It makes rendering and flushing parallel.
*
* 3. Double buffering
* Set 2 screens sized buffers and set disp_drv.full_refresh = 1.
* This way LVGL will always provide the whole rendered screen in `flush_cb`
* and you only need to change the frame buffer's address.
*/
/* Example for 1) */
static lv_disp_draw_buf_t draw_buf_dsc_1;
static lv_color_t buf_1[MY_DISP_HOR_RES * 10]; /*A buffer for 10 rows*/
lv_disp_draw_buf_init(&draw_buf_dsc_1, buf_1, NULL, MY_DISP_HOR_RES * 10); /*Initialize the display buffer*/
/* Example for 2) */
static lv_disp_draw_buf_t draw_buf_dsc_2;
static lv_color_t buf_2_1[MY_DISP_HOR_RES * 10]; /*A buffer for 10 rows*/
static lv_color_t buf_2_2[MY_DISP_HOR_RES * 10]; /*An other buffer for 10 rows*/
lv_disp_draw_buf_init(&draw_buf_dsc_2, buf_2_1, buf_2_2, MY_DISP_HOR_RES * 10); /*Initialize the display buffer*/
/* Example for 3) also set disp_drv.full_refresh = 1 below*/
static lv_disp_draw_buf_t draw_buf_dsc_3;
static lv_color_t buf_3_1[MY_DISP_HOR_RES * MY_DISP_VER_RES]; /*A screen sized buffer*/
static lv_color_t buf_3_2[MY_DISP_HOR_RES * MY_DISP_VER_RES]; /*Another screen sized buffer*/
lv_disp_draw_buf_init(&draw_buf_dsc_3, buf_3_1, buf_3_2,
MY_DISP_VER_RES * MY_DISP_VER_RES); /*Initialize the display buffer*/
/*-----------------------------------
* Register the display in LVGL
*----------------------------------*/
static lv_disp_drv_t disp_drv; /*Descriptor of a display driver*/
lv_disp_drv_init(&disp_drv); /*Basic initialization*/
/*Set up the functions to access to your display*/
/*Set the resolution of the display*/
disp_drv.hor_res = MY_DISP_HOR_RES;
disp_drv.ver_res = MY_DISP_VER_RES;
/*Used to copy the buffer's content to the display*/
disp_drv.flush_cb = disp_flush;
/*Set a display buffer*/
disp_drv.draw_buf = &draw_buf_dsc_2;
disp_drv_p = &disp_drv;
/*Required for Example 3)*/
// disp_drv.full_refresh = 1;
/* Fill a memory array with a color if you have GPU.
* Note that, in lv_conf.h you can enable GPUs that has built-in support in LVGL.
* But if you have a different GPU you can use with this callback.*/
// disp_drv.gpu_fill_cb = gpu_fill;
/*Finally register the driver*/
lv_disp_drv_register(&disp_drv);
}
刷新函数:
/*Flush the content of the internal buffer the specific area on the display
*You can use DMA or any hardware acceleration to do this operation in the background but
*'lv_disp_flush_ready()' has to be called when finished.*/
static void disp_flush(lv_disp_drv_t *disp_drv, const lv_area_t *area, lv_color_t *color_p)
{
if (disp_flush_enabled)
{
// /*The most simple case (but also the slowest) to put all pixels to the screen one-by-one*/
// int32_t x;
// int32_t y;
// for (y = area->y1; y <= area->y2; y++)
// {
// for (x = area->x1; x <= area->x2; x++)
// {
// /*Put a pixel to the display. For example:*/
// /*put_px(x, y, *color_p)*/
// lcd_st7789_write_pixel(x, y, color_p->full);
// color_p++;
// }
// }
// int32_t y;
// lcd_st7789_set_addr_win(area->x1, area->y1, area->x2, area->y2); // 指定填充区域
// // 一行一行 DMA
// for (y = area->y1; y <= area->y2; y++)
// {
// lcd_st7789_write_data_multiple((uint8_t *)color_p, (uint16_t)(area->x2 - area->x1 + 1) * 2);
// color_p += (area->x2 - area->x1 + 1);
// }
unsigned int size = (area->x2 - area->x1 + 1) * (area->y2 - area->y1 + 1) * 2;
lcd_st7789_set_addr_win(area->x1, area->y1, area->x2, area->y2); // 指定填充区域
lcd_st7789_write_data_multiple((uint8_t *)color_p, size);
}
/*IMPORTANT!!!
*Inform the graphics library that you are ready with the flushing*/
// lv_disp_flush_ready(disp_drv);
}
我们还是在LCD的任务中,替换掉我们上一章节展示的电子表功能,代码如下:
/**
* @function lcd menu thread
* @author:小飞哥玩嵌入式-小飞哥
* @TODO: LED控制线程
* @param:
* @return: NULL
*/
static void rt_lcd_menu_entry(void *parameter)
{
uint8_t s_cnt = 0;
key_para_t key_para = { 0 };
clock_time_t clock_time = { 0 };
lcd_st7789_init();
lcd_st7789_clear(LCD_DISP_WHITE);
rt_thread_mdelay(2);
lcd_st7789_fill_area(10, 10, 40, 40, LCD_DISP_BLUE);
embedded_tim_start_init();
// clock_time.hour = 11;
// clock_time.minute = 50;
// menu_main_window();
// lcd_menu_key_init();
lv_init(); // lvgl 系统初始化
lv_port_disp_init(); // lvgl 显示接口初始化,放在 lv_init()的后面
lv_port_indev_init(); // lvgl 输入接口初始化,放在 lv_init()的后面
// lv_example_btn_1();
// lv_example_led_1();
// lv_example_calendar_1();
lv_demo_stress();
for (;;) {
// s_cnt++;
// {
// if (s_cnt > 2)
// s_cnt = 0;
// clock_time.second++;
// }
// if (clock_time.second > 59)
// {
// clock_time.second = 0;
// clock_time.minute++;
// if (clock_time.minute > 59)
// {
// clock_time.minute = 0;
// clock_time.hour++;
// if (clock_time.hour > 12)
// {
// clock_time.hour = 1;
// }
// }
// }
// lcd_menu_keyvalue_get(&key_para, 20);
// lcd_menu_handler(&key_para);
// menu_clock_run(&clock_time);
lv_task_handler();
rt_thread_mdelay(5);
}
}
实现效果就不展示了,兄弟们拿起手里的板子,开撸吧~~~
欢迎关注公众号“小飞哥玩嵌入式”,一起解锁更多的嵌入式开发技能包。