ELISA 酶联免疫吸附试验测试技术
1. Introduction
The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is a robust and highly selective plate-based assay technique for quantifying the levels of biomolecules(生物分子) such as proteins(蛋白质), peptides(肽), hormones(激素) or antibodies(免疫抗体), using either an antibody or an antigen(抗原) as a biorecognition agent(生物识别剂). The most crucial element of the detection strategy is a highly specific antibody-antigen interaction(高度特异性的抗体-抗原相互作用). Samples routinely used in ELISAs include serum(血清), plasma(血浆), cell culture supernatants(细胞培养上清中), cell lysates(细胞溶解物), saliva(唾液), tissue lysates(细胞和组织裂解物) and urine(尿液), as well as food and environmental samples.
ELISAs are typically performed in 96- or 384-well microplates coated with an antibody that will capture a specific target analyte(分析物), immobilizing it to the microplate surface to make it easy to separate the bound target from other molecules present. The non-bound materials can then be washed away, before a substrate solution is added to the plate to generate an enzyme-triggered change in color, fluorescence, or luminescence proportional to the amount of bound target molecule.
2. Basic ELISA Protocol
ELISAs can be quite complex and include multiple intervening steps, especially when measuring protein concentration in heterogeneous samples such as blood. The most complex and varying step in the overall process is detection, where multiple layers of antibodies can be used to amplify signal.
ELISAs all include the same basic steps regardless of the assay variant:
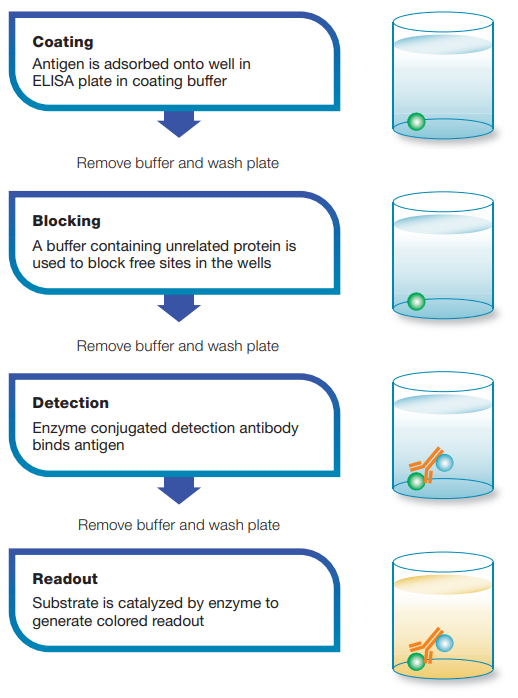
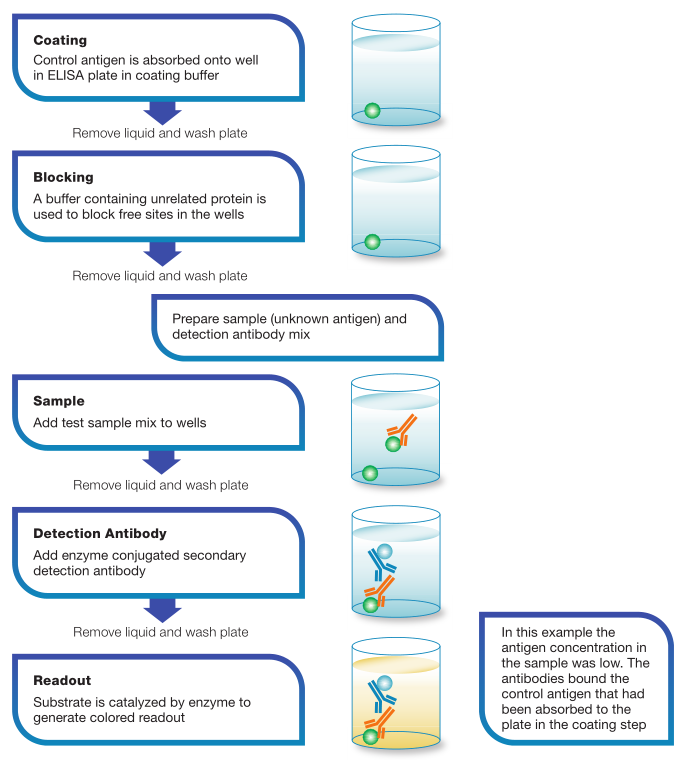
Step1 Coating:
A majority of ELISA kits use microplates that have been pre-coated with a target specific antibody/antigen. Alternatively, a coating step is required to coat the plate with the relevant antibody/antigen. direct or indirect immobilization of antigens to the surface of polystyrene(聚苯乙烯) microplate wells.
Step2 Blocking:
Following antibody binding, a blocking agent(阻断剂) (an irrelevant protein or another molecule) is added to the reaction to block all of the unsaturated surface binding sites on the microplate wells.
Step3 Detection:
Following a series of washes to remove non-target molecules that may interfere with the assay (分析). The target molecule is probed by incubation with analyte-specific enzyme- conjugated detection antibodies (分析物特异性酶偶联检测抗体) that affinity-bind to the target to form an antibody antigen complex. 目标分子通过被分析物特异性酶偶联检测抗体(分析物特异性酶偶联检测抗体)孵育来探测,该抗体与目标亲和结合形成抗体抗原复合物。In some assay formats, the detection antibody is not enzyme-conjugated, but acts as events are maintained. A substrate is then added to produce a colorimetric signal. performed to remove all unbound antibodies, ensuring that only specific (high affinity) binding site for a secondary conjugate. Enzymes commonly conjugated to detection antibodies include alkaline phosphatase (碱性磷酸酶AP) and horseradish peroxidase (辣根过氧化物酶HRP), and a cascade(级联) of antibodies can be used to amplify the signal. Following this complex formation step, another series of washes is performed to remove all unbound antibodies, ensuring that only specific (high affinity) binding events are maintained. A substrate is then added to produce a colorimetric signal.
Step4 Measurement:
Finally, the signal generated by the enzyme-catalyzed reaction is read. The signal observed is proportional to the amount of antigen in the original sample. Various substrates are available for performing the ELISAs with HRP or AP conjugates(偶联物). The choice of substrate depends upon the required assay sensitivity and the instrumentation available for signal detection, e.g., spectrophotometer, fluorometer or luminometer. It is the detection step that largely determines the sensitivity of an ELISA.
3. ELISA Types
The first step in an ELISA experiment is the immobilization of the antigen in a sample to the wall of the wells of a microtiter plate(微孔板). This can be achieved by direct adsorption to the plate’s surface or by using a “capture antibody(捕获抗体)”. The capture antibody has to be specific to the target antigen and is mainly used in a specific ELISA type called “sandwich ELISA”. After immobilization, a detection antibody is added, which binds to the adsorbed antigen thereby leading to the formation of an antigen-antibody complex(抗原-抗体复合物). The detection antibody is either directly conjugated to an enzyme, such as horseradish peroxidase(HRP), or provides a binding site for a secondary conjugates(偶联物).
In general, ELISAs can be grouped into four main categories – direct, indirect, sandwich, and competitive – based on how the analytes and antibodies interact. Each type of ELISA has its own advantages and disadvantages.
3.1 Direct ELISA
In a direct ELISA, an antigen or sample is immobilized directly on the plate and a conjugated detection antibody binds to the target protein. Substrate is then added, producing a signal that is proportional to the amount of analyte in the sample. Since only one antibody is used in a direct ELISA, they are less specific than a sandwich ELISA.
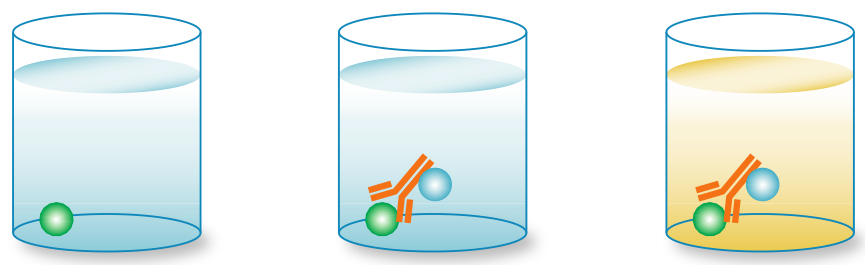
Advantages
• Quick because only one antibody and fewer steps are used.
• Cross-reactivity of secondary antibody is eliminated. 消除了二抗的交叉反应
Disadvantages
• Immunoreactivity(免疫反应性) of the primary antibody might be adversely affected by labeling with enzymes or tags.
• Labeling primary antibodies for each specific ELISA system is time-consuming and expensive.
• No flexibility in choice of primary antibody label from one experiment to another.
• Minimal signal amplification. Potential for high background if all proteins from a sample are immobilized in well.
3.2 Indirect ELISA
An indirect ELISA is similar to a direct ELISA in that an antigen is immobilized on a plate, but it includes an additional amplification detection step. First, an unconjugated primary detection antibody is added and binds to the specific antigen. A conjugated secondary antibody directed against the host species of the primary antibody is then added. Substrate then produces a signal proportional to the amount of antigen bound in the well. 间接ELISA类似于直接ELISA,将抗原固定在板上,但它包括一个额外的扩增检测步骤。首先,加入一种非偶联的一抗检测抗体并与特异性抗原结合。然后加入针对一抗宿主物种的偶联二抗。最后基板产生与孔中结合的抗原数量成比例的信号。
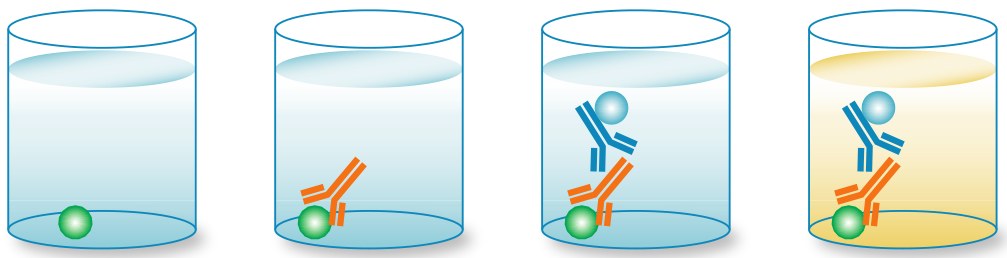
Advantages
• A wide variety of labeled secondary antibodies are available commercially.
• Versatile because many primary antibodies can be made in one species and the same labeled secondary antibody can be used for detection.
• Maximum immunoreactivity of the primary antibody is retained because it is not labeled.
• Sensitivity is increased because each primary antibody contains several epitopes(抗原表位) that can be bound by the labeled secondary antibody, allowing for signal amplification.
Disadvantages
• Cross-reactivity might occur with the secondary antibody, resulting in nonspecific signal.
• An extra incubation step is required in the procedure.
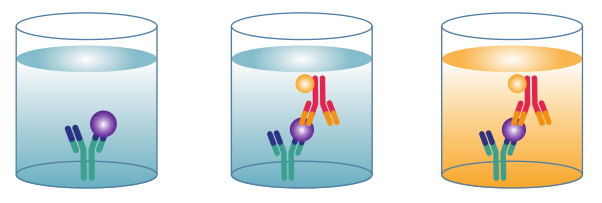
3.3 Sandwich ELISA
Sandwich ELISAs typically require the use of matched antibody pairs, where each antibody is specific for a different, non-overlapping part (epitope) of the antigen molecule. A first antibody (known as capture antibody) is coated to the wells. The sample solution is then added to the well. A second antibody (known as detection antibody) follows this step in order to measure the concentration of the sample.
Sandwich ELSIAs are particularly suited to the analysis of complex samples, since the antigen does not need to be purified prior to the assay, yet still delivers high sensitivity and specificity (e.g. measuring cytokine levels in an immune response).
Advantages
• High sensitivity-2-5 times more sensitive than direct or indirect ELISA.
• Hi specificity- two antibodies are involved in capture and detection.
• Flexibility- both direct and indirect detection can be used.
Disadvantages
• Antibody optimization can be difficult-cross-reactivity may occur between the capture and detection antibodies. Needs a standardized ELISA kit or tested antibody pair.
• longer protocol
• Challenging to develop.
3.4 Competitive ELISA 竞争法ELISA
The key event of competitive ELISA (also known as inhibition ELISA) is the process of competitive reaction between the sample antigen and antigen bound to the wells of a microtiter plate with the primary antibody. First, the primary antibody is incubated with the sample antigen and the resulting antibody–antigen complexes(抗原抗体复合物) are added to wells that have been coated with the same antigen. After an incubation period, any unbound antibody is washed off. The more antigen in the sample, the more primary antibody will be bound to the sample antigen. Therefore, there will be a smaller amount of primary antibody available to bind to the antigen coated on the well, resulting in a signal reduction. Essentially, sample antigen or antibody competes with a reference for binding to a limited amount of labeled antibody or antigen, respectively. The signal output inversely correlates with the amount of antigen in the sample.
Advantages
• Main advantage – no sample processing is required and crude or impure samples can be used.
• More robust – less sensitive to sample dilution and sample matrix effects than the sandwich ELISA.
• More consistent – less variability between duplicate samples and assays.
• Maximum flexibility – it can be based on direct, indirect, or sandwich ELISA.
Disadvantages
• Same limitations as base ELISA – as each ELISA technique can be adapted to a competitive format.