如果我们从串口接收到4个字节数据{0x43,0x67,0x80,0x00},如何把这4个字节的数据转换为float型呢?
直接令float a=0x43678000这是不行的(不信的读者可以自行验证),这就是串口通讯当中经常遇到的问题,如果数据传输中包括了浮点型数据,在这里我们可以通过共用体或者结构体来解决。
对于共用体:
typedef union
{
float f;
unsigned char s[4];
}Union_test;
f的4个字节和s[4]的4个字节是共用一个区域,如果我们令f=231.5,然后通过VS的监视窗查看s[4]的数值,下面是测试程序:
#include
//共用体
//float f;//4个字节
//char s[4];//4个字节
typedef union
{
float f;
unsigned char s[4];
}Union_test;
typedef struct st
{
float f1;
}Struct_test;
void main(void)
{
float a=231.5;
Union_test x;
Struct_test z;
x.f = a;
z = *(Struct_test *)(&(x.s));
printf("z=%.2f\r\n",(double)z.f1);
printf("End of this programme\r\n");
}
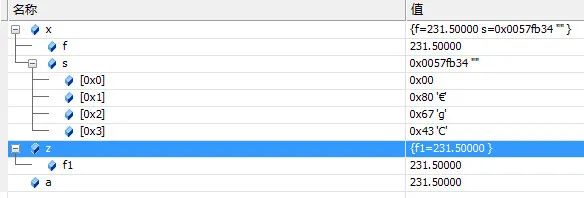
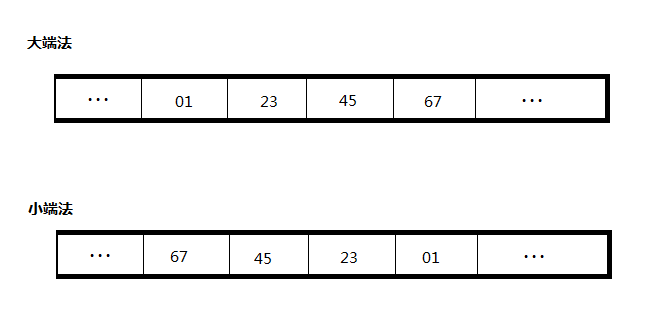
我们可以通过下面的函数测试是大端存储还是小端存储:
void test(void)
{
int a = 1;
unsigned char *start=&a;
if(*start == 1)
printf("小端存储");
else if(*start == 0)
printf("大端存储");
}
关注公众号,加星标,回复1024获取学习资料,每天进步一点点。
声明:
本号原创、转载的文章、图片等版权归原作者所有,如有侵权,请联系删除。
 关注、点赞、在看、转发,支持优质内容!
关注、点赞、在看、转发,支持优质内容!