
来源:https://gitee.com/lengjingzju/json
LJSON 是一个远远快于 cJSON、大幅度快于 RapidJSON 的 C 实现的 JSON 库,他是目前最快的通用 JSON 库。
LJSON 支持 JSON 的解析、打印、编辑,提供 DOM 和 SAX 接口,I/O 支持字符串和文件,且完全支持 nativejson-benchmark 的测试用例。
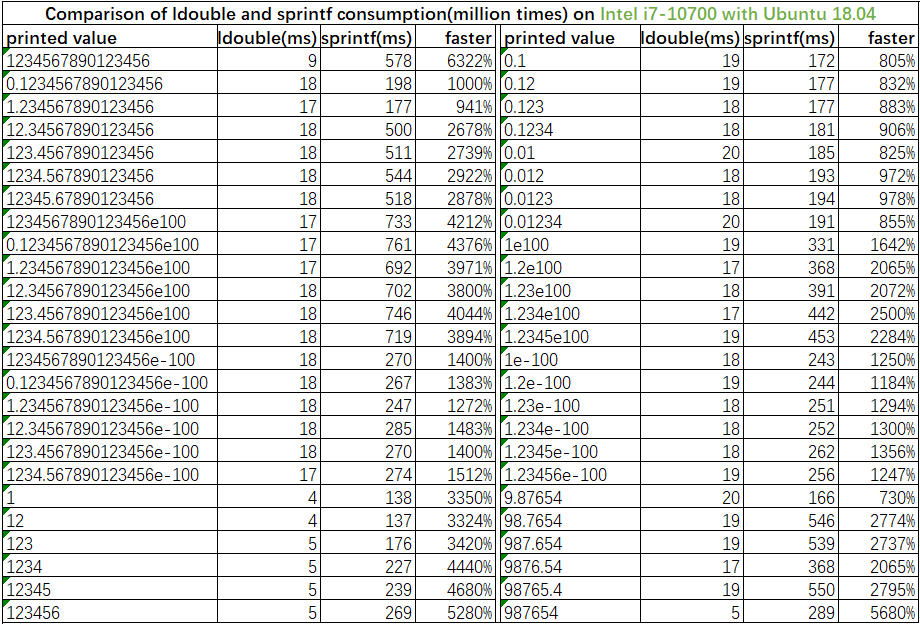
LJSON 默认使用个人开发的 ldouble 算法打印浮点数,和标准库对比可能只有第15位小数的区别,是目前最快的浮点数转字符串算法;也可选择个人优化过的 grisu2 算法或 dragonbox 算法。
gcc -o ljson json.c json_test.c -O2 -ffunction-sections -fdata-sections -W -Wall
make O=<编译输出目录> && make O=<编译输出目录> DESTDIR=<安装目录>
make O=<编译输出目录> CROSS_COMPILE=<交叉编译器前缀> && make O=<编译输出目录> DESTDIR=<安装目录>
gcc -DJSON_DTOA_ALGORITHM=n, n可能为 0 / 1 / 2 / 3./json <测试序号0-7>
JSON_ERROR_PRINT_ENABLE 的值为 1 后重新编译JSON_STRICT_PARSE_MODE 的值为 0 / 1 / 2 后重新编译注:主要是测试速度,O2 优化等级且默认选项编译,测试文件来自 nativejson-benchmark 项目
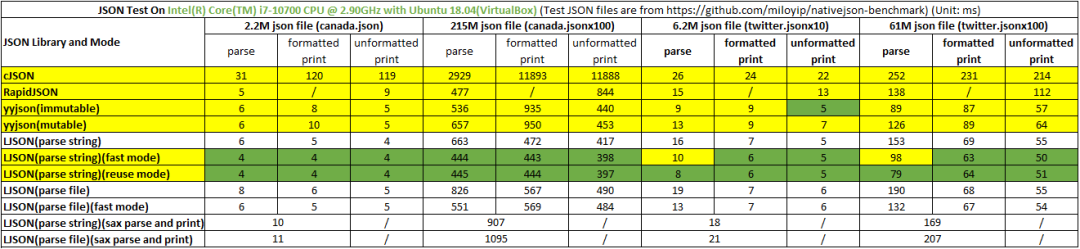
测试平台: Ambarella CV25M Board | CPU: ARM CortexA53 | OS: Linux-5.15
测试结果: LJSON 比cJSON 解析最快可达 475%,打印最快可达 2225%,LJSON 比 RapidJSON 解析最快可达 131%,打印最快可达 137%
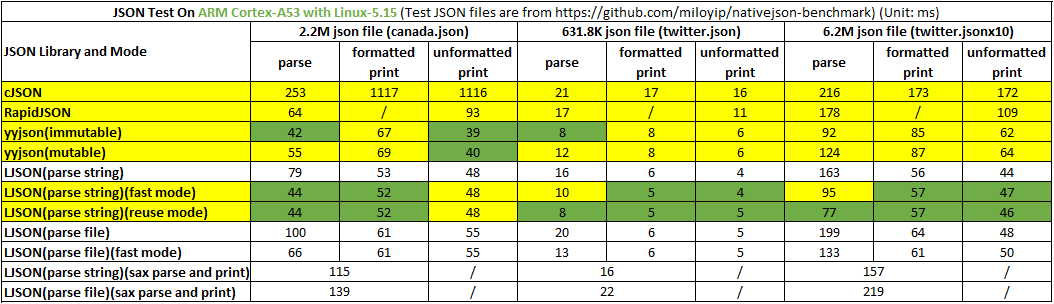
测试平台: PC | CPU: Intel i7-10700 | OS: Ubuntu 18.04 (VirtualBox)
测试结果: :LJSON 比cJSON 解析最快可达 560%,打印最快可达 2894%,LJSON 比 RapidJSON 解析最快可达 75%,打印最快可达 124%
测试平台: Nationalchip STB | CPU: CSKY | DDR3: 128MB, 533MHz | OS: ECOS
注: 老版本测试结果,新版本删除了临时buffer,且解析速度提升了两倍

使用 long long 类型支持,编译时需要设置 json.h 中的 JSON_LONG_LONG_SUPPORT 值为 1
struct json_list {
struct json_list *next;
}; // 单向链表
struct json_list_head {
struct json_list *next, *prev;
}; // 链表头,分别指向链表的第一个元素和最后一个元素
typedef enum {
JSON_NULL = 0,
JSON_BOOL,
JSON_INT,
JSON_HEX,
#if JSON_LONG_LONG_SUPPORT
JSON_LINT,
JSON_LHEX,
#endif
JSON_DOUBLE,
JSON_STRING,
JSON_ARRAY,
JSON_OBJECT
} json_type_t; // json对象类型
typedef struct {
unsigned int type:4; // json_type_t,json_string_t作为key时才有type
unsigned int escaped:1; // str是否包含需要转义的字符
unsigned int alloced:1; // str是否是malloc的,只用于SAX APIs
unsigned int reserved:2;
unsigned int len:24; // str的长度
char *str;
} json_string_t; // json string 对象或 type+key
typedef union {
bool vbool;
int vint;
unsigned int vhex;
#if JSON_LONG_LONG_SUPPORT
long long int vlint;
unsigned long long int vlhex;
#endif
double vdbl;
} json_number_t; // json数字对象值
#if JSON_SAX_APIS_SUPPORT
typedef enum {
JSON_SAX_START = 0,
JSON_SAX_FINISH
} json_sax_cmd_t; // 只用于SAX APIs,JSON_ARRAY或JSON_OBJECT有开始和结束
#endif
typedef union {
json_number_t vnum; // json数字对象的值
json_string_t vstr; // json字符串对象的值
#if JSON_SAX_APIS_SUPPORT
json_sax_cmd_t vcmd;
#endif
struct json_list_head head; // json结构体/数组对象的值
} json_value_t; // json对象值
typedef struct {
struct json_list list; // json链表节点
json_string_t jkey; // json对象的type和key
json_value_t value; // json对象的值
} json_object; // json对象
typedef struct {
unsigned int hash; // json key的hash,只有JSON_OBJECT的子项才有key
json_object *json; // json对象的指针
} json_item_t;
typedef struct {
unsigned int conflicted:1; // key的hash是否有冲突
unsigned int reserved:31;
unsigned int total; // items分配的内存数目
unsigned int count; // items中子项的个数
json_item_t *items; // 存储子项的数组
} json_items_t; // 存储JSON_ARRAY或JSON_OBJECT的所有子项
void json_memory_free(void *ptr);
int json_item_total_get(json_object *json);
void json_del_object(json_object *json);
json_object *json_new_object(json_type_t type);
json_object *json_create_item(json_type_t type, void *value);
json_object *json_create_item_array(json_type_t type, void *values, int count);
static inline json_object *json_create_null(void);
static inline json_object *json_create_bool(bool value);
static inline json_object *json_create_int(int value);
static inline json_object *json_create_hex(unsigned int value);
#if JSON_LONG_LONG_SUPPORT
static inline json_object *json_create_lint(long long int value);
static inline json_object *json_create_lhex(unsigned long long int value);
#endif
static inline json_object *json_create_double(double value);
static inline json_object *json_create_string(json_string_t *value);
static inline json_object *json_create_array(void);
static inline json_object *json_create_object(void);
static inline json_object *json_create_bool_array(bool *values, int count);
static inline json_object *json_create_int_array(int *values, int count);
static inline json_object *json_create_hex_array(unsigned int *values, int count);
#if JSON_LONG_LONG_SUPPORT
static inline json_object *json_create_lint_array(long long int *values, int count);
static inline json_object *json_create_lhex_array(unsigned long long int *values, int count);
#endif
static inline json_object *json_create_double_array(double *values, int count);
static inline json_object *json_create_string_array(json_string_t *values, int count);
json_del_object删除,但是如果把该节点加入了array或object,该节点无需再删除void json_string_info_update(json_string_t *jstr);
unsigned int json_string_hash_code(json_string_t *jstr);
int json_string_strdup(json_string_t *src, json_string_t *dst);
static inline int json_set_key(json_object *json, json_string_t *jkey);
static inline int json_set_string_value(json_object *json, json_string_t *jstr);
int json_get_number_value(json_object *json, json_type_t type, void *value);
int json_set_number_value(json_object *json, json_type_t type, void *value);
static inline bool json_get_bool_value(json_object *json);
static inline int json_get_int_value(json_object *json);
static inline unsigned int json_get_hex_value(json_object *json);
#if JSON_LONG_LONG_SUPPORT
static inline long long int json_get_lint_value(json_object *json);
static inline unsigned long long int json_get_lhex_value(json_object *json);
#endif
static inline double json_get_double_value(json_object *json);
static inline int json_set_bool_value(json_object *json, bool value);
static inline int json_set_int_value(json_object *json, int value);
static inline int json_set_hex_value(json_object *json, unsigned int value);
#if JSON_LONG_LONG_SUPPORT
static inline int json_set_lint_value(json_object *json, long long int value);
static inline int json_set_lhex_value(json_object *json, unsigned long long int value);
#endif
static inline int json_set_double_value(json_object *json, double value);
int json_get_array_size(json_object *json);
int json_get_object_size(json_object *json);
json_object *json_get_array_item(json_object *json, int seq, json_object **prev);
json_object *json_get_object_item(json_object *json, const char *key, json_object **prev);
json_object *json_search_object_item(json_items_t *items, json_string_t *jkey, unsigned int hash);
void json_free_items(json_items_t *items);
int json_get_items(json_object *json, json_items_t *items);
int json_add_item_to_array(json_object *array, json_object *item);
int json_add_item_to_object(json_object *object, json_object *item);
无需再调用json_del_object删除该节点json_object *json_detach_item_from_array(json_object *json, int seq);
json_object *json_detach_item_from_object(json_object *json, const char *key);
需要使用json_del_object删除返回的子节点不需要调用json_del_object删除返回的子节点int json_del_item_from_array(json_object *json, int seq);
int json_del_item_from_object(json_object *json, const char *key);
int json_replace_item_in_array(json_object *array, int seq, json_object *new_item);
int json_replace_item_in_object(json_object *object, json_object *new_item);
json_object *json_deepcopy(json_object *json);
int json_copy_item_to_array(json_object *array, json_object *item);
int json_copy_item_to_object(json_object *object, json_object *item);
还需要再调用json_del_object删除原来传入的节点json_object *json_add_new_item_to_array(json_object *array, json_type_t type, void* value);
json_object *json_add_new_item_to_object(json_object *object, json_type_t type, json_string_t *jkey, void* value);
static inline json_object *json_add_null_to_array(json_object *array);
static inline json_object *json_add_bool_to_array(json_object *array, bool value);
static inline json_object *json_add_int_to_array(json_object *array, int value);
static inline json_object *json_add_hex_to_array(json_object *array, unsigned int value);
#if JSON_LONG_LONG_SUPPORT
static inline json_object *json_add_lint_to_array(json_object *array, long long int value);
static inline json_object *json_add_lhex_to_array(json_object *array, unsigned long long int value);
#endif
static inline json_object *json_add_double_to_array(json_object *array, double value);
static inline json_object *json_add_string_to_array(json_object *array, json_string_t *value);
static inline json_object *json_add_array_to_array(json_object *array);
static inline json_object *json_add_object_to_array(json_object *array);
static inline json_object *json_add_null_to_object(json_object *object, json_string_t *jkey);
static inline json_object *json_add_bool_to_object(json_object *object, json_string_t *jkey, bool value);
static inline json_object *json_add_int_to_object(json_object *object, json_string_t *jkey, int value);
static inline json_object *json_add_hex_to_object(json_object *object, json_string_t *jkey, unsigned int value);
#if JSON_LONG_LONG_SUPPORT
static inline json_object *json_add_lint_to_object(json_object *object, json_string_t *jkey, long long int value);
static inline json_object *json_add_lhex_to_object(json_object *object, json_string_t *jkey, unsigned long long int value);
#endif
static inline json_object *json_add_double_to_object(json_object *object, json_string_t *jkey, double value);
static inline json_object *json_add_string_to_object(json_object *object, json_string_t *jkey, json_string_t *value);
static inline json_object *json_add_array_to_object(json_object *object, json_string_t *jkey);
static inline json_object *json_add_object_to_object(json_object *object, json_string_t *jkey);
/*
* The below APIs are also available to pool json:
* json_item_total_get
* json_string_info_update
* json_get_number_value / ...
* json_set_number_value / ...
* json_get_array_size
* json_get_object_size
* json_get_array_item
* json_get_object_item
* json_search_object_item
* json_free_items
* json_get_items
* json_add_item_to_array
* json_add_item_to_object
* json_detach_item_from_array
* json_detach_item_from_object
*/
编辑(一般模式)的一些API(内部没有调用malloc/free)也可以用于内存池json_del_object删除typedef struct {
struct json_list list; // 链表节点
size_t size; // 内存大小
char *ptr; // 首部地址
char *cur; // 当前地址
} json_mem_node_t;
typedef struct {
struct json_list_head head; // json_mem_node_t挂载节点
size_t mem_size; // 默认分配块内存大小
json_mem_node_t *cur_node; // 当前使用的内存节点
} json_mem_mgr_t;
typedef struct {
json_mem_mgr_t obj_mgr; // 对象节点的内存管理
json_mem_mgr_t key_mgr; // 字符串key的内存管理
json_mem_mgr_t str_mgr; // 字符串value的内存管理
} json_mem_t;
void pjson_memory_free(json_mem_t *mem);
void pjson_memory_init(json_mem_t *mem);
+int pjson_memory_statistics(json_mem_mgr_t *mgr);
json_new_object和json_del_object等json_object *pjson_new_object(json_type_t type, json_mem_t *mem);
json_object *pjson_create_item(json_type_t type, void *value, json_mem_t *mem);
json_object *pjson_create_item_array(json_type_t item_type, void *values, int count, json_mem_t *mem);
static inline json_object *pjson_create_null(json_mem_t *mem);
static inline json_object *pjson_create_bool(bool value, json_mem_t *mem);
static inline json_object *pjson_create_int(int value, json_mem_t *mem);
static inline json_object *pjson_create_hex(unsigned int value, json_mem_t *mem);
#if JSON_LONG_LONG_SUPPORT
static inline json_object *pjson_create_lint(long long int value, json_mem_t *mem);
static inline json_object *pjson_create_lhex(unsigned long long int value, json_mem_t *mem);
#endif
static inline json_object *pjson_create_double(double value, json_mem_t *mem);
static inline json_object *pjson_create_string(json_string_t *value, json_mem_t *mem);
static inline json_object *pjson_create_array(json_mem_t *mem);
static inline json_object *pjson_create_object(json_mem_t *mem);
static inline json_object *pjson_create_bool_array(bool *values, int count, json_mem_t *mem);
static inline json_object *pjson_create_int_array(int *values, int count, json_mem_t *mem);
static inline json_object *pjson_create_hex_array(unsigned int *values, int count, json_mem_t *mem);
#if JSON_LONG_LONG_SUPPORT
static inline json_object *pjson_create_lint_array(long long int *values, int count, json_mem_t *mem);
static inline json_object *pjson_create_lhex_array(unsigned long long int *values, int count, json_mem_t *mem);
#endif
static inline json_object *pjson_create_double_array(double *values, int count, json_mem_t *mem);
static inline json_object *pjson_create_string_array(json_string_t *values, int count, json_mem_t *mem);
int pjson_string_strdup(json_string_t *src, json_string_t *dst, json_mem_mgr_t *mgr);
static inline int pjson_set_key(json_object *json, json_string_t *jkey, json_mem_t *mem);
static inline int pjson_set_string_value(json_object *json, json_string_t *jstr, json_mem_t *mem);
int pjson_replace_item_in_array(json_object *array, int seq, json_object *new_item);
int pjson_replace_item_in_object(json_object *object, json_object *new_item);
json_object *pjson_deepcopy(json_object *json, json_mem_t *mem);
int pjson_copy_item_to_array(json_object *array, json_object *item, json_mem_t *mem);
int pjson_copy_item_to_object(json_object *object, json_object *item, json_mem_t *mem);
json_object *pjson_add_new_item_to_array(json_object *array, json_type_t type, void *value, json_mem_t *mem);
json_object *pjson_add_new_item_to_object(json_object *object, json_type_t type, json_string_t *jkey, void *value, json_mem_t *mem);
static inline json_object *pjson_add_null_to_array(json_object *array, json_mem_t *mem);
static inline json_object *pjson_add_bool_to_array(json_object *array, bool value, json_mem_t *mem);
static inline json_object *pjson_add_int_to_array(json_object *array, int value, json_mem_t *mem);
static inline json_object *pjson_add_hex_to_array(json_object *array, unsigned int value, json_mem_t *mem);
#if JSON_LONG_LONG_SUPPORT
static inline json_object *pjson_add_lint_to_array(json_object *array, long long int value, json_mem_t *mem);
static inline json_object *pjson_add_lhex_to_array(json_object *array, unsigned long long int value, json_mem_t *mem);
#endif
static inline json_object *pjson_add_double_to_array(json_object *array, double value, json_mem_t *mem);
static inline json_object *pjson_add_string_to_array(json_object *array, json_string_t *value, json_mem_t *mem);
static inline json_object *pjson_add_array_to_array(json_object *array, json_mem_t *mem);
static inline json_object *pjson_add_object_to_array(json_object *array, json_mem_t *mem);
static inline json_object *pjson_add_null_to_object(json_object *object, json_string_t *jkey, json_mem_t *mem);
static inline json_object *pjson_add_bool_to_object(json_object *object, json_string_t *jkey, bool value, json_mem_t *mem);
static inline json_object *pjson_add_int_to_object(json_object *object, json_string_t *jkey, int value, json_mem_t *mem);
static inline json_object *pjson_add_hex_to_object(json_object *object, json_string_t *jkey, unsigned int value, json_mem_t *mem);
#if JSON_LONG_LONG_SUPPORT
static inline json_object *pjson_add_lint_to_object(json_object *object, json_string_t *jkey, long long int value, json_mem_t *mem);
static inline json_object *pjson_add_lhex_to_object(json_object *object, json_string_t *jkey, unsigned long long int value, json_mem_t *mem);
#endif
static inline json_object *pjson_add_double_to_object(json_object *object, json_string_t *jkey, double value, json_mem_t *mem);
static inline json_object *pjson_add_string_to_object(json_object *object, json_string_t *jkey, json_string_t *value, json_mem_t *mem);
static inline json_object *pjson_add_array_to_object(json_object *object, json_string_t *jkey, json_mem_t *mem);
static inline json_object *pjson_add_object_to_object(json_object *object, json_string_t *jkey, json_mem_t *mem);
typedef struct {
size_t str_len; // 打印到字符串时返回生成的字符串长度(strlen)
size_t plus_size; // 打印生成的字符串的realloc的增量大小 / write buffer的缓冲区大小
size_t item_size; // 每个json对象生成字符串的预估的平均长度
int item_total; // json对象节点的总数
bool format_flag; // 字符串是否进行格式化
const char *path; // 文件保存路径
} json_print_choice_t;
false: 压缩打印;true: 格式化打印char *json_print_common(json_object *json, json_print_choice_t *choice);
static inline char *json_print_format(json_object *json, int item_total, size_t *length);
static inline char *json_print_unformat(json_object *json, int item_total, size_t *length);
static inline char *json_fprint_format(json_object *json, int item_total, const char *path);
static inline char *json_fprint_unformat(json_object *json, int item_total, const char *path);
需要 json_memory_free释放返回的字符串不需要 json_memory_free释放返回的字符串typedef struct {
size_t mem_size; // 内存池每个内存块的大小
size_t read_size; // json读缓冲的初始大小
size_t str_len; // 要解析的字符串长度
bool reuse_flag; // 是否复用原始json字符串,原始json字符串会被修改
json_mem_t *mem; // 内存池管理结构
const char *path; // 要解析的json文件的路径
char *str; // 要解析的json字符串的指针
} json_parse_choice_t;
json_object *json_parse_common(json_parse_choice_t *choice);
static inline json_object *json_parse_str(char *str, size_t str_len);
static inline json_object *json_fast_parse_str(char *str, size_t str_len, json_mem_t *mem);
static inline json_object *json_reuse_parse_str(char *str, size_t str_len, json_mem_t *mem);
static inline json_object *json_parse_file(const char *path);
static inline json_object *json_fast_parse_file(const char *path, json_mem_t *mem);
json_del_object释放返回的管理结构pjson_memory_init初始化mem,用完后需要pjson_memory_free释放会修改传入的字符串,使用过程中不要释放原始的str , 速度最快,占用内存最少使用 SAX APIs 编译时需要设置 json.h 中的 JSON_SAX_APIS_SUPPORT 值为 1
typedef void* json_sax_print_hd;
json_sax_print_hd json_sax_print_start(json_print_choice_t *choice);
static inline json_sax_print_hd json_sax_print_format_start(int item_total);
static inline json_sax_print_hd json_sax_print_unformat_start(int item_total);
static inline json_sax_print_hd json_sax_fprint_format_start(int item_total, const char *path);
static inline json_sax_print_hd json_sax_fprint_unformat_start(int item_total, const char *path);
int json_sax_print_value(json_sax_print_hd handle, json_type_t type, json_string_t *jkey, const void *value);
static inline int json_sax_print_null(json_sax_print_hd handle, json_string_t *jkey);
static inline int json_sax_print_bool(json_sax_print_hd handle, json_string_t *jkey, bool value);
static inline int json_sax_print_int(json_sax_print_hd handle, json_string_t *jkey, int value);
static inline int json_sax_print_hex(json_sax_print_hd handle, json_string_t *jkey, unsigned int value);
#if JSON_LONG_LONG_SUPPORT
static inline int json_sax_print_lint(json_sax_print_hd handle, json_string_t *jkey, long long int value);
static inline int json_sax_print_lhex(json_sax_print_hd handle, json_string_t *jkey, unsigned long long int value);
#endif
static inline int json_sax_print_double(json_sax_print_hd handle, json_string_t *jkey, double value);
static inline int json_sax_print_string(json_sax_print_hd handle, json_string_t *jkey, json_string_t *value);
static inline int json_sax_print_array(json_sax_print_hd handle, json_string_t *jkey, json_sax_cmd_t value);
static inline int json_sax_print_object(json_sax_print_hd handle, json_string_t *jkey, json_sax_cmd_t value);
JSON_SAX_START 表示开始,一次值是 JSON_SAX_FINISH 表示完成json_saxstr_update 计算长度char *json_sax_print_finish(json_sax_print_hd handle, size_t *length);
需要 json_memory_free释放返回的字符串不需要 json_memory_free释放返回的字符串typedef enum {
JSON_SAX_PARSE_CONTINUE = 0,
JSON_SAX_PARSE_STOP
} json_sax_ret_t;
typedef struct {
int total;
int index;
json_string_t *array;
json_value_t value;
} json_sax_parser_t;
typedef json_sax_ret_t (*json_sax_cb_t)(json_sax_parser_t *parser);
typedef struct {
char *str;
const char *path;
size_t read_size;
json_sax_cb_t cb;
} json_sax_parse_choice_t;
JSON_SAX_PARSE_STOP 表示中断解析并返回类型+key 的层次结构,total表示当前分配了多少层次,index表示当前用了多少层次,即当前层为 array[index]json_parse_choice_t 说明int json_sax_parse_common(json_sax_parse_choice_t *choice);
static inline int json_sax_parse_str(char *str, size_t str_len, json_sax_cb_t cb);
static inline int json_sax_parse_file(const char *path, json_sax_cb_t cb);
本文来源网络,免费传达知识,版权归原作者所有。如涉及作品版权问题,请联系我进行删除。
《嵌入式Linux驱动大全》