今日光电



翻译自【OpenCV Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) for blur detection in images and video streams】,原文链接:
https://www.pyimagesearch.com/2020/06/15/opencv-fast-fourier-transform-fft-for-blur-detection-in-images-and-video-streams/
本文仅作学习分享。

(https://www.pyimagesearch.com/2015/09/07/blur-detection-with-opencv/)。
原始模糊检测方法:

图1:如何使用OpenCV和快速傅里叶变换(FFT)算法自动检测照片是否模糊?(图片来源:https://www.cs.unm.edu/~brayer/vision/fourier.html)
模糊检测,顾名思义,是检测图像是否模糊的算法。
模糊检测可能的应用包括:
图像质量的自动分级
帮助专业摄影师在100到1000张的照片拍摄过程中自动丢弃模糊/低质量的照片
将OCR应用于实时视频流,但仅对非模糊帧应用昂贵的OCR计算
这里的关键要点是,为在理想条件下捕获的图像编写计算机视觉代码总是比较容易的。
与其尝试处理质量非常差的图像的边缘情况,不如检测并丢弃质量差的图像(比如有明显模糊的图像)。
这种模糊检测程序既可以自动丢弃质量差的图像,也可以简单地告诉终端用户:”嘿,老兄,再试一次,让我们在这里捕捉一个更好的画面”。
请记住,计算机视觉应用程序应该是智能的,因此有了“人工智能”这个术语——有时候,“智能”可以只是检测输入数据的质量是否太差,而不是试图弄懂它。
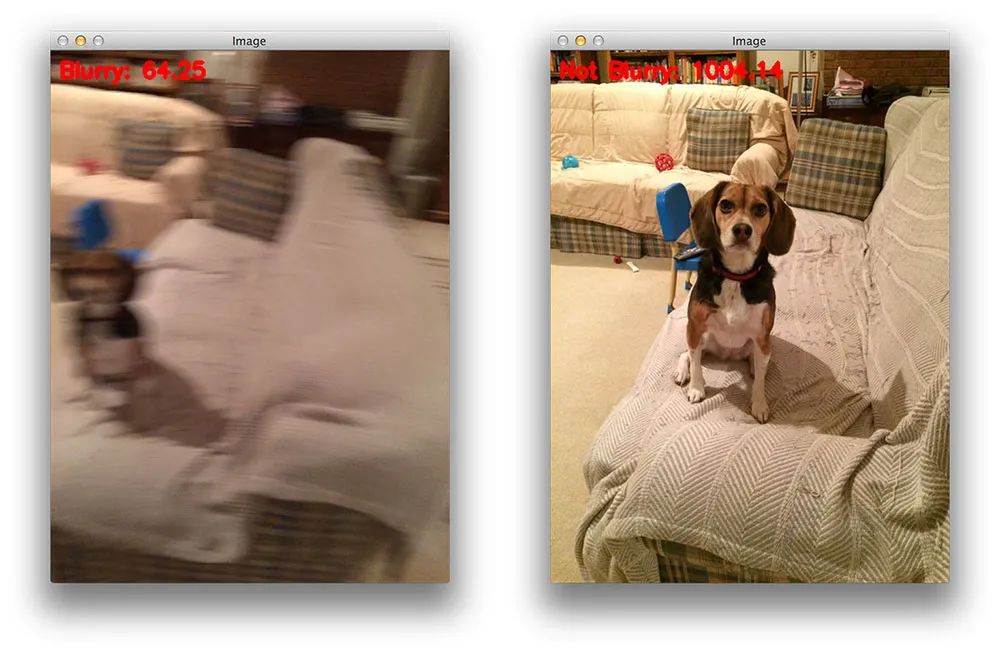

图2:在本教程中,我们将使用OpenCV和NumPy的组合在图像和视流中进行基于快速傅立叶变换(FFT)的模糊检测。
快速傅里叶变换是计算离散傅里叶变换的一种方便的数学算法。它用于将信号从一个域转换为另一个域。
https://homepages.inf.ed.ac.uk/rbf/HIPR2/fourier.htm
https://www.cc.gatech.edu/~afb/classes/CS4495-Fall2014/slides/CS4495-Frequency.pdf
首先使用本教程的“下载”部分下载源代码和示例图像。一旦你解压缩文件,你将有一个目录组织如下:
tree --dirsfirst.├── images│ ├── adrian_01.png│ ├── adrian_02.png│ ├── jemma.png│ └── resume.png├── pyimagesearch│ ├── __init__.py│ └── blur_detector.py├── blur_detector_image.py└── blur_detector_video.py2 directories, 8 files
http://www.cse.cuhk.edu.hk/leojia/all_final_papers/blur_detect_cvpr08.pdf
# import the necessary packagesimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport numpy as npdef detect_blur_fft(image, size=60, thresh=10, vis=False):# grab the dimensions of the image and use the dimensions to# derive the center (x, y)-coordinates(h, w) = image.shape(cX, cY) = (int(w / 2.0), int(h / 2.0))
我们的模糊检测器实现需要matplotlib和NumPy。我们将使用内建在NumPy中的快速傅里叶变换算法作为我们方法的基础;
第4行定义detect_blur_fft函数,接受四个参数:
图片image:我们对模糊检测输入图像
大小size:以图像中心点为中心的半径的大小,我们将使FFT偏移为零
阈值thresh:用于确定图像是否被认为是模糊的,将与震级的平均值(稍后详细说明)进行比较的一个值
标识符vis:一个布尔值,指示是否使用matplotlib可视化/绘制原始输入图像和大小图像
给定输入图像,首先获取它的尺寸(第7行)并计算中心(x, y)坐标(第8行)。
接下来,我们将使用NumPy的快速傅里叶变换(FFT)算法实现来计算离散傅里叶变换(DFT):
# compute the FFT to find the frequency transform, then shift# the zero frequency component (i.e., DC component located at# the top-left corner) to the center where it will be more# easy to analyzefft = np.fft.fft2(image)fftShift = np.fft.fftshift(fft)
# check to see if we are visualizing our outputif vis:# compute the magnitude spectrum of the transformmagnitude = 20 * np.log(np.abs(fftShift))# display the original input image(fig, ax) = plt.subplots(1, 2, )ax[0].imshow(image, cmap="gray")ax[0].set_title("Input")ax[0].set_xticks([])ax[0].set_yticks([])# display the magnitude imageax[1].imshow(magnitude, cmap="gray")ax[1].set_title("Magnitude Spectrum")ax[1].set_xticks([])ax[1].set_yticks([])# show our plotsplt.show()
# zero-out the center of the FFT shift (i.e., remove low# frequencies), apply the inverse shift such that the DC# component once again becomes the top-left, and then apply# the inverse FFTfftShift[cY - size:cY + size, cX - size:cX + size] = 0fftShift = np.fft.ifftshift(fftShift)recon = np.fft.ifft2(fftShift)
# compute the magnitude spectrum of the reconstructed image,# then compute the mean of the magnitude valuesmagnitude = 20 * np.log(np.abs(recon))mean = np.mean(magnitude)# the image will be considered "blurry" if the mean value of the# magnitudes is less than the threshold valuereturn (mean, mean <= thresh
现在我们的detect_blur_fft 辅助函数已经实现,让我们通过创建一个Python驱动程序脚本来使用它,该脚本从磁盘加载一个输入图像,然后对其应用FFT模糊检测。
# import the necessary packagesfrom pyimagesearch.blur_detector import detect_blur_fftimport numpy as npimport argparseimport imutilsimport cv2# construct the argument parser and parse the argumentsap = argparse.ArgumentParser()ap.add_argument("-i", "--image", type=str, required=True,help="path input image that we'll detect blur in")ap.add_argument("-t", "--thresh", type=int, default=20,help="threshold for our blur detector to fire")ap.add_argument("-v", "--vis", type=int, default=-1,help="whether or not we are visualizing intermediary steps")ap.add_argument("-d", "--test", type=int, default=-1,help="whether or not we should progressively blur the image")args = vars(ap.parse_args())
第2-6行进行导入,特别的是,我们需要导入我们在上一节中实现的detect_blur_fft函数。
从这里,我们解析四个命令行参数:
--image:用于模糊检测的输入图像的路径。
--thresh:我们的模糊检测器计算阈值。
--vis:我们的标志符,指示是否将输入图像的幅度值图像可视化。
--test:为了测试,我们可以逐步模糊输入图像,并对每个示例进行基于fft的模糊检测;此标志指示我们是否将执行此测试。
--image、--thresh和--vis参数分别对应于我们在上一节实现的detect_blur_fft函数的image、thresh和vis参数。
让我们继续,加载我们的输入图像,执行快速傅里叶变换模糊检测:
# load the input image from disk, resize it, and convert it to# grayscaleorig = cv2.imread(args["image"])orig = imutils.resize(orig, width=500)gray = cv2.cvtColor(orig, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)# apply our blur detector using the FFT(mean, blurry) = detect_blur_fft(gray, size=60,thresh=args["thresh"], vis=args["vis"] > 0)
# draw on the image, indicating whether or not it is blurryimage = np.dstack([gray] * 3)color = (0, 0, 255) if blurry else (0, 255, 0)text = "Blurry ({:.4f})" if blurry else "Not Blurry ({:.4f})"text = text.format(mean)cv2.putText(image, text, (10, 25), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.7,color, 2)print("[INFO] {}".format(text))# show the output imagecv2.imshow("Output", image)cv2.waitKey(0)
# check to see if are going to test our FFT blurriness detector using# various sizes of a Gaussian kernelif args["test"] > 0:# loop over various blur radiifor radius in range(1, 30, 2):# clone the original grayscale imageimage = gray.copy()# check to see if the kernel radius is greater than zeroif radius > 0:# blur the input image by the supplied radius using a# Gaussian kernelimage = cv2.GaussianBlur(image, (radius, radius), 0)# apply our blur detector using the FFT(mean, blurry) = detect_blur_fft(image, size=60,thresh=args["thresh"], vis=args["vis"] > 0)# draw on the image, indicating whether or not it is# blurryimage = np.dstack([image] * 3)color = (0, 0, 255) if blurry else (0, 255, 0)text = "Blurry ({:.4f})" if blurry else "Not Blurry ({:.4f})"text = text.format(mean)cv2.putText(image, text, (10, 25), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,0.7, color, 2)print("[INFO] Kernel: {}, Result: {}".format(radius, text))# show the imagecv2.imshow("Test Image", image)cv2.waitKey(0)
$ python blur_detector_image.py --image images/adrian_01.png[INFO] Not Blurry (42.4630)

图3:结合快速傅里叶变换(FFT)算法,使用Python和OpenCV来确定照片是否模糊
这里你可以看到我在锡安国家公园的地铁徒步旅行的输入图像-图像被正确地标记为不模糊。
让我们试试另一张图片,这是我家的狗,Jemma:
$ python blur_detector_image.py --image images/jemma.png[INFO] Blurry (12.4738)
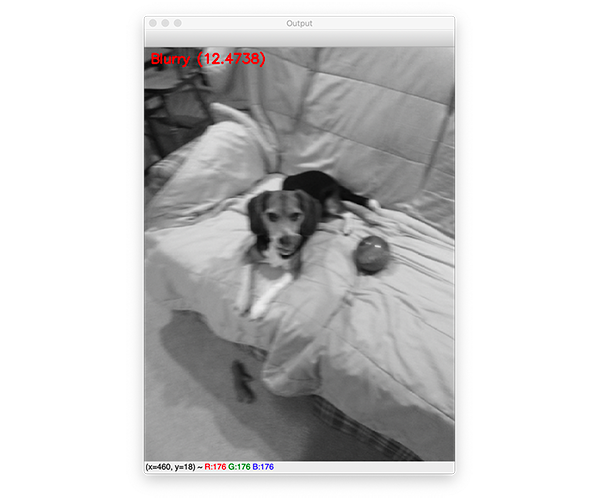
图4:基于Python、OpenCV和NumPy的快速傅里叶变换(FFT)模糊检测算法已经自动判定Janie的这张图像模糊。
这幅图像有明显的模糊,因此被标记为模糊。
$ python blur_detector_image.py --image images/adrian_02.png --test 1[INFO] Not Blurry (32.0934)[INFO] Kernel: 1, Result: Not Blurry (32.0934)[INFO] Kernel: 3, Result: Not Blurry (25.1770)[INFO] Kernel: 5, Result: Not Blurry (20.5668)[INFO] Kernel: 7, Result: Blurry (13.4830)[INFO] Kernel: 9, Result: Blurry (7.8893)[INFO] Kernel: 11, Result: Blurry (0.6506)[INFO] Kernel: 13, Result: Blurry (-5.3609)[INFO] Kernel: 15, Result: Blurry (-11.4612)[INFO] Kernel: 17, Result: Blurry (-17.0109)[INFO] Kernel: 19, Result: Blurry (-19.6464)[INFO] Kernel: 21, Result: Blurry (-20.4758)[INFO] Kernel: 23, Result: Blurry (-20.7365)[INFO] Kernel: 25, Result: Blurry (-20.9362)[INFO] Kernel: 27, Result: Blurry (-21.1911)[INFO] Kernel: 29, Result: Blurry (-21.3853)

图5:使用Python模糊检测器脚本的——测试例程,我们应用了一系列有意的模糊以及快速傅里叶变换(FFT)方法来确定图像是否模糊。这个测试例程非常有用,因为它允许您调优模糊阈值参数。
$ python blur_detector_image.py --image images/resume.png --thresh 27 --test 1 --vis 1[INFO] Not Blurry (34.6735)[INFO] Kernel: 1, Result: Not Blurry (34.6735)[INFO] Kernel: 3, Result: Not Blurry (29.2539)[INFO] Kernel: 5, Result: Blurry (26.2893)[INFO] Kernel: 7, Result: Blurry (21.7390)[INFO] Kernel: 9, Result: Blurry (18.3632)[INFO] Kernel: 11, Result: Blurry (12.7235)[INFO] Kernel: 13, Result: Blurry (9.1489)[INFO] Kernel: 15, Result: Blurry (2.3377)[INFO] Kernel: 17, Result: Blurry (-2.6372)[INFO] Kernel: 19, Result: Blurry (-9.1908)[INFO] Kernel: 21, Result: Blurry (-15.9808)[INFO] Kernel: 23, Result: Blurry (-20.6240)[INFO] Kernel: 25, Result: Blurry (-29.7478)[INFO] Kernel: 27, Result: Blurry (-29.0728)[INFO] Kernel: 29, Result: Blurry (-37.7561)
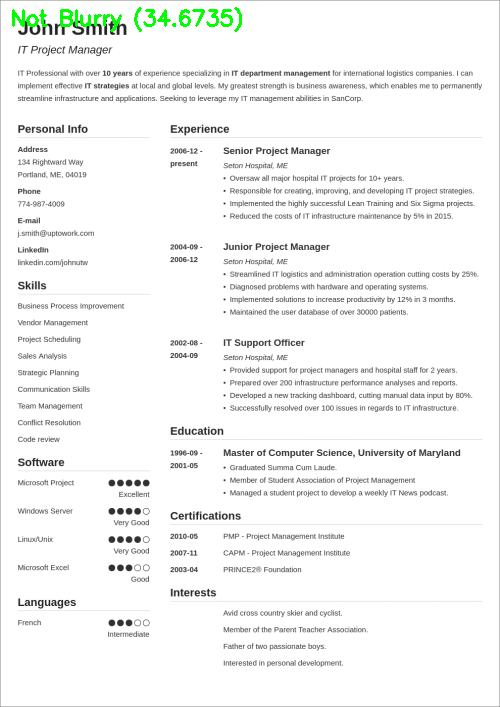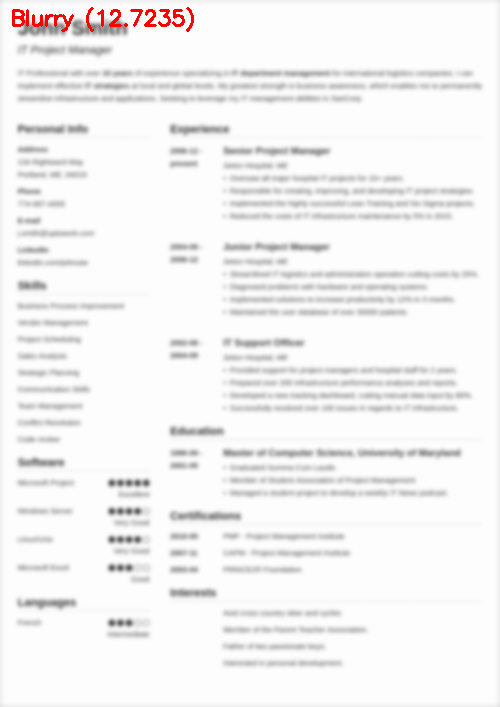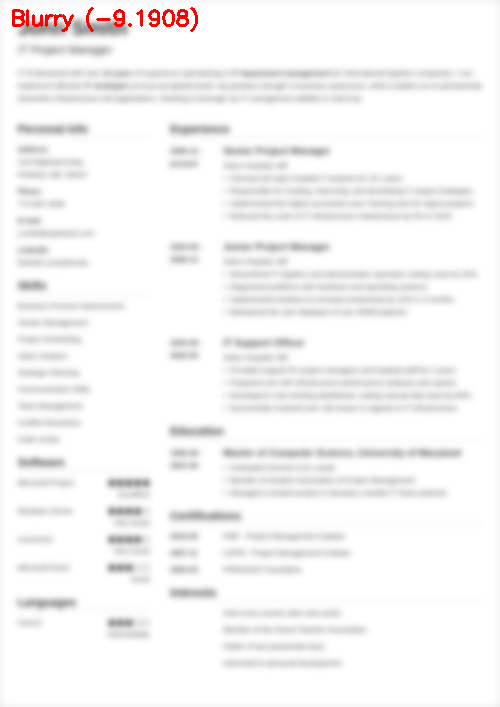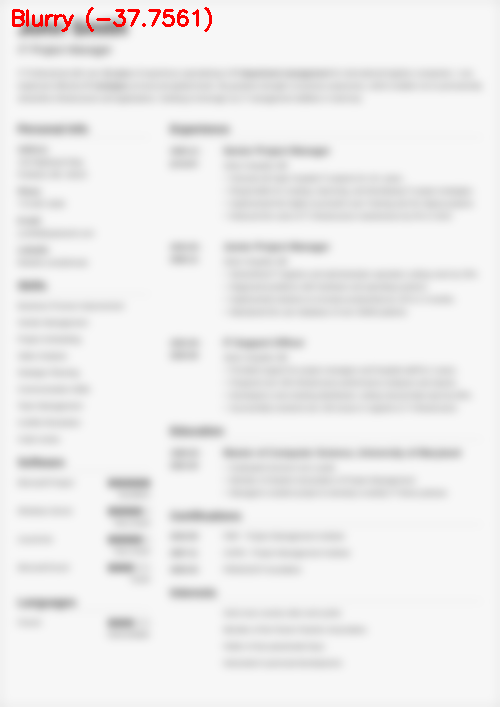
图6:OpenCV快速傅里叶变换(FFT)用于图像和视视频中的模糊检测,可以判断简历等文档是否模糊。
在这里,您可以看到我们的图像很快变得模糊和不可读,正如输出所示,我们的OpenCV FFT模糊检测器正确地将这些图像标记为模糊。
下面是一个可视化的快速傅里叶变换幅度值,图像变得越来越模糊:
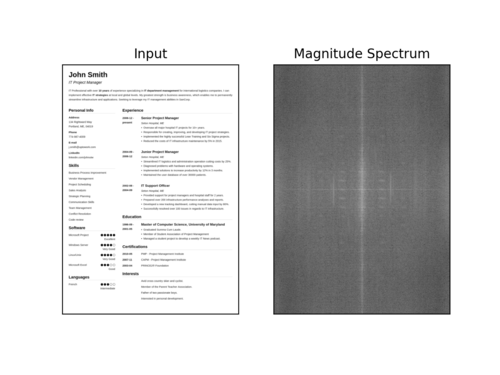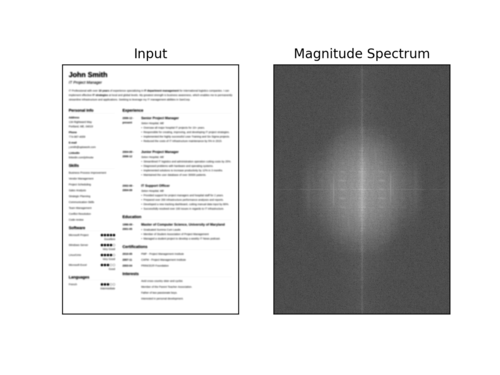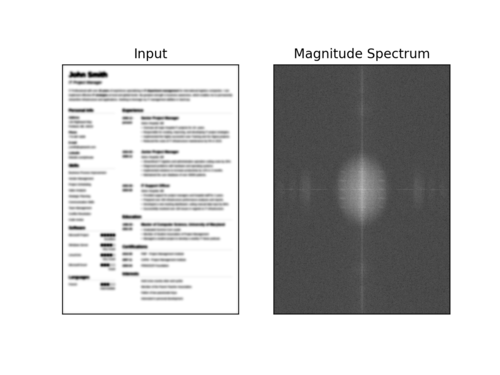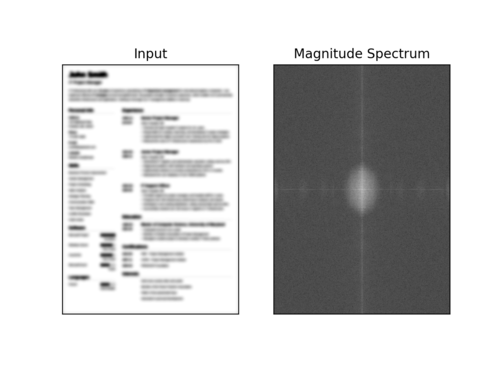
图7:当图像变得越来越模糊时,我们可以看到幅度谱可视化的变化。本教程使用OpenCV和NumPy在图像和视流中执行快速傅里叶变换(FFT)模糊检测。
# import the necessary packagesfrom imutils.video import VideoStreamfrom pyimagesearch.blur_detector import detect_blur_fftimport argparseimport imutilsimport timeimport cv2# construct the argument parser and parse the argumentsap = argparse.ArgumentParser()ap.add_argument("-t", "--thresh", type=int, default=10,help="threshold for our blur detector to fire")args = vars(ap.parse_args())
# initialize the video stream and allow the camera sensor to warm upprint("[INFO] starting video stream...")vs = VideoStream(src=0).start()time.sleep(2.0)# loop over the frames from the video streamwhile True:# grab the frame from the threaded video stream and resize it# to have a maximum width of 400 pixelsframe = vs.read()frame = imutils.resize(frame, width=500)# convert the frame to grayscale and detect blur in itgray = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)(mean, blurry) = detect_blur_fft(gray, size=60,thresh=args["thresh"], vis=False)
# draw on the frame, indicating whether or not it is blurrycolor = (0, 0, 255) if blurry else (0, 255, 0)text = "Blurry ({:.4f})" if blurry else "Not Blurry ({:.4f})"text = text.format(mean)cv2.putText(frame, text, (10, 25), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,0.7, color, 2)# show the output framecv2.imshow("Frame", frame)key = cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF# if the `q` key was pressed, break from the loopif key == ord("q"):break# do a bit of cleanupcv2.destroyAllWindows()vs.stop()
$ python blur_detector_video.py[INFO] starting video stream...

申明:感谢原创作者的辛勤付出。本号转载的文章均会在文中注明,若遇到版权问题请联系我们处理。

----与智者为伍 为创新赋能----

联系邮箱:uestcwxd@126.com
QQ:493826566