Binder 是 Android 系统中用于跨进程通信的一种机制,它允许一个进程中的组件与另一个进程中的组件进行通信,从而实现进程间通信 (IPC)。Binder 机制是基于 Linux 内核提供的进程间通信机制 (IPC) 实现的。
在 Binder 机制中,每个进程都有一个 Binder 驱动程序,它负责管理该进程中的所有 Binder 对象。每个 Binder 对象都有一个唯一的标识符,称为 Binder 标识符 (Binder identity),它可以用于在进程之间传递 Binder 引用。Binder 机制允许在客户端进程和服务进程之间建立一个通信通道 (communication channel),客户端可以通过这个通道向服务端发送请求,服务端可以处理请求并返回结果。
Binder 机制中的主要组件包括以下几个部分:
Binder 驱动程序:负责管理 Binder 对象,以及为客户端进程和服务进程之间建立通信通道。
Binder 对象:具有唯一标识符的对象,用于在进程之间传递引用。
Binder 接口:定义了客户端可以调用的方法,以及服务端可以实现的方法。
Binder 代理 (Proxy):客户端进程中的对象,用于与服务端进程通信,并代表客户端调用服务端的方法。
Binder Stub:服务端进程中的对象,用于实现 Binder 接口,并处理客户端发送的请求。
使用 Binder 机制可以实现跨进程通信,例如在 Android 应用程序中,可以使用 AIDL (Android Interface Definition Language) 定义接口和方法,并使用 Binder 机制在客户端进程和服务端进程之间进行通信。这样可以使应用程序更加灵活和高效,例如可以将耗时的操作放在服务端处理,减少客户端的负担,提高应用程序的性能和响应速度。
AIDL(Android Interface Definition Language)是一种 IDL 语言,用于生成可以在 Android 设备上两个进程之间进行进程间通信(IPC)的代码。 通过 AIDL,可以在一个进程中获取另一个进程的数据和调用其暴露出来的方法,从而满足进程间通信的需求。通常,暴露方法给其他应用进行调用的应用称为服务端,调用其他应用的方法的应用称为客户端,客户端通过绑定服务端的 Service 来进行交互。
只有当你允许来自不同的客户端访问你的服务并且需要处理多线程问题时你才必须使用AIDL”,其他情况下你都可以选择其他方法,如使用 Messenger,也能跨进程通信。可见 AIDL 是处理多线程、多客户端并发访问的,而 Messenger 是单线程处理。
我们在android studio中创建aidl的方法如下:
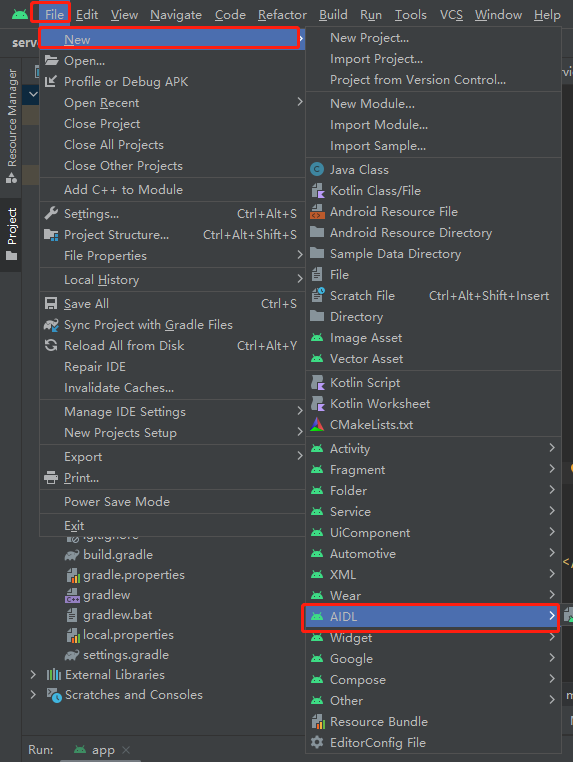
默认情况下,AIDL 支持下列数据类型:
八种基本数据类型:byte、char、short、int、long、float、double、boolean
String、CharSequence
List类型。List承载的数据必须是AIDL支持的类型,或者是其它声明的AIDL对象
Map类型。Map承载的数据必须是AIDL支持的类型,或者是其它声明的AIDL对象
定义三个java class,分别为MyService.java,MyBinder.Java,MainActivity.java
MyService.java的定义如下:
package com.example.binder;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Binder;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.util.Log;
public class MyService extends Service {
public MyService() {
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
MyBinder mBinder = new MyBinder();
return mBinder;
}
}package com.example.binder;
import android.os.Binder;
import android.util.Log;
public class MyBinder extends Binder {
final String TAG = "zhongjun_MyBinder";
public void sayHello() {
Log.d(TAG, "Hello from service!");
}
}package com.example.binder;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.ServiceConnection;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
final String TAG = "zhongjun_MainActivity";
private MyBinder binder;
private boolean bound = false;
Button myButton;
private ServiceConnection connection = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName componentName, IBinder iBinder) {
Log.d(TAG, "onServiceConnected");
bound = true;
binder = (MyBinder) iBinder;
binder.sayHello();
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName componentName) {
Log.d(TAG, "onServiceDisconnected");
bound = false;
}
};
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
Intent intent = new Intent(this, MyService.class);
myButton = findViewById(R.id.my_button);
myButton.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// 处理按钮点击事件
Log.d(TAG, "click button ");
bindService(intent, connection, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
}
});
}
}ServiceConnection 是 Android 应用程序中用于连接和管理服务的接口。它允许客户端应用程序与服务进行通信并获取服务提供的数据或执行服务提供的操作。
ServiceConnection 接口中定义了两个方法:onServiceConnected() 和 onServiceDisconnected()。onServiceConnected() 方法在客户端应用程序成功绑定到服务时调用,该方法提供了一个 IBinder 对象,该对象可以用于与服务进行通信。onServiceDisconnected() 方法在客户端应用程序与服务断开连接时调用。
使用 ServiceConnection,客户端应用程序可以绑定到一个服务并发送请求,服务可以在收到请求后执行相应的操作并返回结果。客户端应用程序还可以使用 ServiceConnection 监听服务的连接状态,并在服务连接断开时采取相应的措施,例如重新绑定服务或提示用户。
总之,ServiceConnection 是 Android 应用程序中用于连接和管理服务的重要接口,它允许客户端应用程序与服务进行通信并控制服务的连接状态。在开发 Android 应用程序时,开发人员通常需要实现 ServiceConnection 接口来管理应用程序与服务之间的通信和连接。
Intent intent = new Intent(this, MyService.class);
这行代码是创建一个 Intent 对象,用于启动或绑定 MyService 类中定义的服务。
第一个参数 this 是当前上下文对象,用于标识 Intent 的来源。在这个例子中,this 可能是一个 Activity 或者一个 Service。
第二个参数 MyService.class 是服务的类名。它告诉系统要启动或绑定哪个服务。
创建 Intent 对象后,可以使用 startService() 方法启动服务,或使用 bindService() 方法绑定服务。如果希望服务在后台持续运行并执行某些操作,通常会使用 startService() 方法启动服务。如果希望与服务进行交互并执行某些操作,通常会使用 bindService() 方法绑定服务。
例如,如果要启动 MyService,可以使用以下代码:
Intent intent = new Intent(this, MyService.class);
startService(intent);如果要绑定到 MyService,并获取服务提供的数据或执行服务提供的操作,可以使用以下代码:
Intent intent = new Intent(this, MyService.class);
bindService(intent, mServiceConnection, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);其中,mServiceConnection 是一个 ServiceConnection 对象,用于管理服务的连接状态。BIND_AUTO_CREATE 参数表示如果服务不存在,则会自动创建一个。
AndroidManifest.xml为
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools">
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:dataExtractionRules="@xml/data_extraction_rules"
android:fullBackupContent="@xml/backup_rules"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:theme="@style/Theme.Binder"
tools:targetApi="31">
<service
android:name=".MyService"
android:enabled="true"
android:exported="true" />
<activity
android:name=".MainActivity"
android:exported="true">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
</application>
</manifest>一共有两个类MainActivity.java,Myservice.java跟一个aidl文件MyAidlInterface.aidl
MainActivity.java
package com.example.aidl_signal;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.ServiceConnection;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.os.RemoteException;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
final String TAG = "zhongjun_MainActivity";
Button myButton;
private ServiceConnection mServiceConnection = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName componentName, IBinder iBinder) {
MyAidlInterface mMyAidlInterface = MyAidlInterface.Stub.asInterface(iBinder);
try{
int result = mMyAidlInterface.add(1, 2);
Log.d(TAG, "mMyAidlInterface.add:" result);
}catch (RemoteException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "RemoteException: " e.getMessage());
}
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName componentName) {
}
};
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
Intent intent = new Intent(this, MyService.class);
myButton = findViewById(R.id.my_button);
myButton.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// 处理按钮点击事件
Log.d(TAG, "click button ");
bindService(intent, mServiceConnection, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
}
});
}
}Myservice.java
package com.example.aidl_signal;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.IBinder;
public class MyService extends Service {
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return new MyServiceImpl();
}
private class MyServiceImpl extends MyAidlInterface.Stub{
// 这是一个示例方法
public int add(int a, int b) {
return a b;
}
}
}MyAidlInterface.aidl
// MyAidlInterface.aidl
package com.example.aidl_signal;
// Declare any non-default types here with import statements
interface MyAidlInterface {
int add(int a, int b);
}AndroidManifest.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools">
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:dataExtractionRules="@xml/data_extraction_rules"
android:fullBackupContent="@xml/backup_rules"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:theme="@style/Theme.Aidl_signal"
tools:targetApi="31">
<service
android:name=".MyService"
android:enabled="true"
android:exported="true"></service>
<activity
android:name=".MainActivity"
android:exported="true">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
</application>
</manifest>跟前面的本质区别就是几行代码
MyAidlInterface mMyAidlInterface = MyAidlInterface.Stub.asInterface(iBinder);
这行代码是将 IBinder 对象转换为 MyAidlInterface 接口的实例对象。
在 Android 应用程序中,跨进程通信 (IPC) 常常使用 AIDL (Android Interface Definition Language) 来定义接口和方法。当客户端绑定到一个服务时,服务返回一个 IBinder 对象,客户端可以使用它来调用服务中的方法。但是,IBinder 对象并不能直接调用服务中的方法,因为客户端和服务在不同的进程中。因此,需要将 IBinder 对象转换为接口实例对象,以便客户端可以使用接口调用服务中的方法。
在这个例子中,MyAidlInterface 是一个 AIDL 接口,它定义了客户端可以调用的方法。Stub 是 MyAidlInterface 的内部类,它实现了 MyAidlInterface 接口,并提供了 asInterface() 静态方法,用于将 IBinder 对象转换为接口实例对象。
当客户端绑定到服务时,服务返回的 IBinder 对象可以在客户端的 ServiceConnection 实现中获取。然后,客户端可以使用 Stub.asInterface() 方法将 IBinder 对象转换为接口实例对象,以便客户端可以使用接口调用服务中的方法
一共有一个MyService.java,一个MyInterface.aidl,一个AndroidManifest.xml文件
MyService.java
package com.example.server;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.os.RemoteException;
public class MyService extends Service {
private IBinder mBinder = new MyBinder();
public MyService() {
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return mBinder;
}
private class MyBinder extends MyInterface.Stub {
@Override
public int add(int a, int b) throws RemoteException {
return a b;
}
}
}MyInterface.aidl
// MyInterface.aidl
package com.example.server;
// Declare any non-default types here with import statements
interface MyInterface {
/**
* Demonstrates some basic types that you can use as parameters
* and return values in AIDL.
*/
int add(int a, int b);
}AndroidManifest.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools">
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:dataExtractionRules="@xml/data_extraction_rules"
android:fullBackupContent="@xml/backup_rules"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:theme="@style/Theme.Server"
tools:targetApi="31">
<service
android:name=".MyService"
android:enabled="true"
android:exported="true">
<intent-filter>
<!--添加了一个唯一的action,供客户端隐式启动service-->
<action android:name="com.example.server.MyService"/>
</intent-filter></service>
</application>
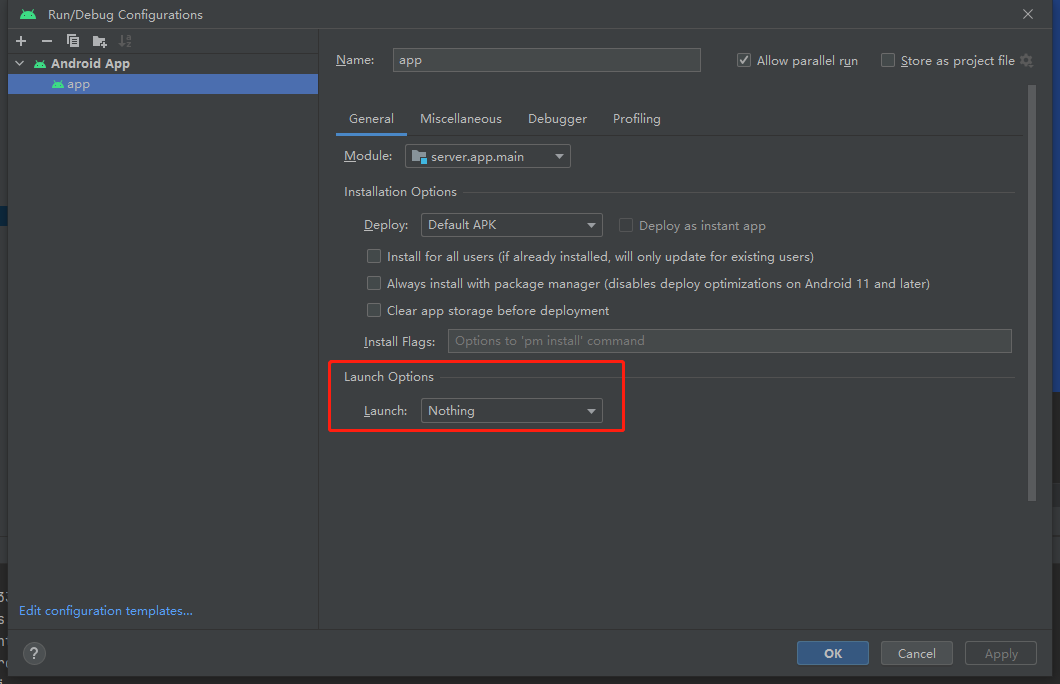
</manifest>需要注意的是server没有activity,只有service,所以我们在配置工程的时候配置没有activity启动
客户端只有MainActivity
package com.example.client;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.ServiceConnection;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.os.RemoteException;
import android.util.Log;
import com.example.server.MyInterface;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
final String TAG = "zhongjun_MainActivity";
private MyInterface mMyService;
private ServiceConnection mConnection = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName className, IBinder service) {
Log.d(TAG, "onServiceConnected");
mMyService = MyInterface.Stub.asInterface(service);
try {
int result = mMyService.add(1, 2);
Log.d(TAG, "mMyService.add:" result);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName className) {
Log.d(TAG, "onServiceDisconnected");
}
};
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
Log.d(TAG, "onCreate");
Intent intent = new Intent("com.example.server.MyService");
intent.setPackage("com.example.server");
bindService(intent, mConnection, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
}
}另外,还需要把server端的aidl copy过来
copy路径为server\app\src\main整个aidl文件夹 放到client\app\src\main下面,工程显示如下: