整理一些 Linux 默认调度器 CFS 相关的东西。CFS、cgroup 等内核技术合力实现了进程的 CPU 资源限额(CPU 带宽控制),这是容器的基础之一。
1 概念及关系
1.3.1 CFS 存在的问题
1.3.2 CONFIG_CFS_BANDWIDTH
1.2.1 前提:CONFIG_CGROUPS
1.2.2 前提:CONFIG_CGROUP_SCHED
1.2.3 扩展:支持实时进程组(CONFIG_RT_GROUP_SCHED)
1.2.4 扩展:支持常规进程组(CONFIG_FAIR_GROUP_SCHED)
1.1 CFS:进程(task)的公平调度
1.2 CFS 扩展
1.3 常规进程组 CFS 再扩展:支持 CPU 带宽控制(限额)
1.4 CFS BANDWITH 近几年改进
1.5 小结:CFS 相关内核编译选项的关系
2 CFS 相关设计
CPU throttle 是怎么来的
上下文切换开销
新配置项
查看 k8s pod 的 CPU throttle 统计
更多设计细节
例子
2.3.1 实时进程调度策略
2.3.2 常规进程调度策略
2.3.3 常规进程 SCHED_NORMAL 和实时进程 SCHED_RR 调度策略的区别
2.3.4 查看或修改进程的调度属性
SCHED_FIFO
SCHED_RR
SCHED_NORMAL
SCHED_BATCH
SCHED_IDLE
2.2.1 vruntime
2.2.2 runqueue
2.2.3 基于时序的红黑树
2.1 设计目标和基本原理
2.2 核心概念
2.3 调度策略(scheduling policy)
2.4 调度类(scheduling class)
2.5 进程组调度器扩展(group scheduler extensions)
2.6 CFS 配置项
2.7 CPU 带宽控制设计(CONFIG_CFS_BANDWIDTH)
2.9 问题
3 内核实现
3.2.1 struct task_struct
3.2.2 struct task_group
3.2.3 struct sched_entity
3.2.4 struct cfs_rq
3.2.5 struct sched_class
3.1 CFS 第一版实现
3.2 核心数据结构
3.3 CFS CPU 带宽控制实现
4 使用
4.1 模拟 throttle 场景
4.2 k8s
参考资料
首先理清几个概念和它们之间的关系。
CFS(Completely Fair Scheduler)是 Linux 内置(也是目前默认)的一个内核调度器, 如名字所示,它实现了所谓的“完全公平”调度算法,将 CPU 资源均匀地分配给各进程( 在内核代码中称为“任务”,task)。 简单来说,如果一台机器有一个 CPU 多个(计算密集型)进程,那采用 CFS 调度器时,
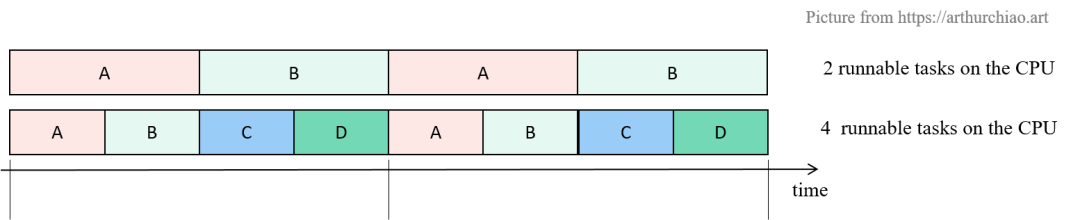
两个进程:每个进程会各占 50% CPU 时间;
四个进程:每个进程会各占 25% CPU 时间;
这个很好理解。接下来看第二个概念。
最初的 CFS 管理的是单个任务(进程)的调度,给每个进程分配公平的 CPU 时间。 但很多情况下,进程会组织成进程组(task group)的形式, 用户希望先对进程组分配 CPU 份额,再在每个进程组里面实现公平调度。
举个具体例子,多个用户使用同一台机器时,可能希望,
首先按 user 公平(也可以不公平)分配 CPU;
针对每个 user,再对其所有进程公平分配这个 user 的总 CPU 时间。
为此,CFS 引入了几项扩展,例如
实时任务的组调度(RT group)
常规进程的组调度(task group)
但实现这几个扩展是需要一些前提的。
CONFIG_CGROUPS要实现按进程组分配和管理 CPU 份额的功能,首先要能够控制(control) 进程组(task group)的资源限额, 这种技术在 Linux 内核中已经有了,叫控制组(control group),缩写是 cgroup。 (CONFIG_CGROUPS)。
cgroup 有两个版本,分别称为 cgroup v1 和 cgroup v2。这两个版本不兼容,现在默认都是用的 v1;
有了 cgroup,调度器就能通过 cgroup 伪文件系统来管理进程组占用的资源(我们这里关心的是CPU 资源)了;
更多信息见 Documentation/admin-guide/cgroup-v1/cgroups.rst。
CONFIG_CGROUP_SCHEDcgroup 是按资源类型(cpu/memory/device/hugetlb/…)来做资源限额的,每种资源 类型会有一种对应的控制器(controller),有独立的开关。 控制进程或进程组能使用的 CPU 时间,对应的开关是 CONFIG_CGROUP_SCHED。
至此,支持进程组级别资源控制的基础就具备了。接下来就是 CFS 扩展代码的实现, 添加对于 realtime/conventional task group 的支持。下面分别来看下。
CONFIG_RT_GROUP_SCHED)CONFIG_RT_GROUP_SCHED 支持对 real-time (SCHED_FIFO and SCHED_RR) 任务进行分组 CFS。
实时进程有严格的响应时间限制,不管机器的 load 有多高,都应该确保这些进程的响应实时性。 例子:内核中的 migration 进程,负责在不同 CPU 之间分发任务(进程负载均衡)。
$ ps -ef | grep migration
root 12 2 0 00:00:01 [migration/0]
CONFIG_FAIR_GROUP_SCHED)实时进程之外的进程就是所谓的常规进程,它们没有严格的响应时间限制, 当系统繁忙时,响应延迟就会增加。
在 cgroup 技术基础上上,再对 CFS 代码做一些增强,就能够支持进程组内的公平调度了。 这些增强代码是通过编译选项 CONFIG_FAIR_GROUP_SCHED 控制的。 支持对普通 CFS (SCHED_NORMAL, SCHED_BATCH) 任务进行分组。
至此,我们已经能对进程和进程组进行 CFS 调度。
CFS 自己也存在一些问题或限制:
某些情况下做不到真正的公平。
CFS 本质上是会把 CPU 用满的(work-conserving)。具体来说,如果一个 CPU 上 有两个任务,理论上应该各占用 50% 的 CPU;但如果其中一个任务有很多 sleep/wait 时间, CFS 就会把多余的时间给到第二个进程,导致第二个进程实际使用的时间超过一半。
优先级高的进程仍然可能获得更大的时间片。
内核中有两中调度类(scheduling class):SCHED_RT 和 SCHED_NORMAL,前者的优先级更大。 当一个 CPU 上有 RT 类型任务时,永远是它们先执行。优先级可以通过 nice(2) 控制。
无法设置 CPU 使用上限。
CFS 只关注 CPU 平均分配,并不保证 CPU 时间(上下限)。 换句话说,CPU share/quota 只有相对意义,share 大的一定比 share 小的能分到更多 CPU,仅此而已。 进程越多,每个进程分到的 CPU 时间越少。 CPU 限额(上限)对按 CPU 时间计费的场景非常关键,例如公有云。
图片来自 google paper [5]。注意:严格来说,这里的相对时间还只是在 SCHED_NORMAL 里的时间,不包括 SCHED_RT 进程占掉的 CPU 时间。
CONFIG_CFS_BANDWIDTH严格来说,Linux 中的调度单位是线程(thread),因此在调度上下文中并没有进程(process)的概念。
基于以上原因,Google 提出了 CFS CPU 带宽控制(CFS bandwidth control)方案,并合并到了主线内核。 这里的“CPU 带宽”指的就是 CPU 份额,或者说的更清楚点,CPU 比例。 SCHED_RT 中其实已经有这个功能,这里指的是 SCHED_NORMAL 支持这个功能。
这个功能的好处主要是给服务器,不是给桌面电脑。 好处:
能精确控制一个进程使用的 CPU 带宽上限;比如设置一个容器只能使用 0.2 CPU, 那它的总时间就不能超过这个比例,即使这个 CPU 非常空闲;
对容量规划非常有用(例如 OpenStack 调度 VM,k8s 调度 pod);
延迟更有保证;
burst 特性:允许借用前一个进程剩下的带宽。
总结一下前面提到的 CFS 相关功能,它们的配置选项或依赖关系如下:
CONFIG_CGROUPS # 1. 是否支持 cgroup,下面进一步区分 cpu/memory/hugetlb/...
|-CONFIG_MEMCG # 1.1 是否支持 memory cgroup
|-CONFIG_BLK_CGROUP # 1.2 是否支持 blkio cgroup
|-CONFIG_CGROUP_SCHED # 1.3 是否支持 cpu cgroup
| |-CONFIG_RT_GROUP_SCHED # 1.3.1 是否支持 realtime scheduler cpu cgroup
| |-CONFIG_FAIR_GROUP_SCHED # 1.3.2 是否支持 cfs for task cgroup
| |-CONFIG_CFS_BANDWIDTH # 1.3.2.1 是否支持 cfs cpu bandwidth
|
|-CONFIG_CGROUP_PIDS # 1.4 是否支持 pid cgroup
|-CONFIG_CPUSETS # 1.5 是否支持 cpuset cgroup
|-CONFIG_CGROUP_DEVICE # 1.6 是否支持 device cgroup
|-CONFIG_CGROUP_CPUACCT # 1.7 是否支持 cpu,acc cgroup
|-... # 1.8 是否支持 ... cgroup
这些宏定义(编译开关)的层次关系在 init/Kconfig 中可以看出来,在父一级开关为 yes 的条件下,才会有子一级的开关。 例如,要启用 CFS CPU 带宽控制功能,就必须要有: CONFIG_CGROUPS=y && CONFIG_CGROUP_SCHED=y && CONFIG_FAIR_GROUP_SCHED=y && CONFIG_CFS_BANDWIDTH=y 这是本文接下来将重点关注的部分(1 -> 1.3 -> 1.3.2 -> 1.3.2.1)。
各开关的详细解释:
// init/Kconfig
menuconfig CGROUPS
bool "Control Group support"
help
This option adds support for grouping sets of processes together, for
use with process control subsystems such as Cpusets, CFS, memory controls or device isolation.
See
- Documentation/scheduler/sched-design-CFS.rst (CFS)
- Documentation/admin-guide/cgroup-v1/ (features for grouping, isolation and resource control)
if CGROUPS
config MEMCG
bool "Memory controller"
select PAGE_COUNTER
help
Provides control over the memory footprint of tasks in a cgroup.
config BLK_CGROUP
bool "IO controller"
depends on BLOCK
help
Generic block IO controller cgroup interface. This is the common
cgroup interface which should be used by various IO controlling policies.
Currently, CFQ IO scheduler uses it to recognize task groups and
control disk bandwidth allocation (proportional time slice allocation)
to such task groups. It is also used by bio throttling logic in
block layer to implement upper limit in IO rates on a device.
This option only enables generic Block IO controller infrastructure.
One needs to also enable actual IO controlling logic/policy. For
enabling proportional weight division of disk bandwidth in CFQ, set
CONFIG_BFQ_GROUP_IOSCHED=y; for enabling throttling policy, set
CONFIG_BLK_DEV_THROTTLING=y.
See Documentation/admin-guide/cgroup-v1/blkio-controller.rst for more information.
menuconfig CGROUP_SCHED
bool "CPU controller"
help
This feature lets CPU scheduler recognize task groups and control CPU
bandwidth allocation to such task groups. It uses cgroups to group tasks.
if CGROUP_SCHED
config FAIR_GROUP_SCHED
bool "Group scheduling for SCHED_OTHER"
depends on CGROUP_SCHED
default CGROUP_SCHED
config CFS_BANDWIDTH
bool "CPU bandwidth provisioning for FAIR_GROUP_SCHED"
depends on FAIR_GROUP_SCHED
help
This option allows users to define CPU bandwidth rates (limits) for
tasks running within the fair group scheduler. Groups with no limit
set are considered to be unconstrained and will run with no restriction.
See Documentation/scheduler/sched-bwc.rst for more information.
config RT_GROUP_SCHED
bool "Group scheduling for SCHED_RR/FIFO"
depends on CGROUP_SCHED
help
This feature lets you explicitly allocate real CPU bandwidth
to task groups. If enabled, it will also make it impossible to
schedule realtime tasks for non-root users until you allocate realtime bandwidth for them.
See Documentation/scheduler/sched-rt-group.rst for more information.
endif #CGROUP_SCHED
config CGROUP_PIDS
bool "PIDs controller"
config CPUSETS
bool "Cpuset controller"
help
This option will let you create and manage CPUSETs which
allow dynamically partitioning a system into sets of CPUs and
Memory Nodes and assigning tasks to run only within those sets.
This is primarily useful on large SMP or NUMA systems.
config CGROUP_DEVICE
bool "Device controller"
help
Provides a cgroup controller implementing whitelists for
devices which a process in the cgroup can mknod or open.
config CGROUP_CPUACCT
bool "Simple CPU accounting controller"
help
Provides a simple controller for monitoring the total CPU consumed by the tasks in a cgroup.
endif # CGROUPS
CFS 早在 2007 年就合并到 Linux 内核(2.6.23) [1],取代了之前调度器中的 SCHED_OTHER 实现。 CFS 80% 的设计都可以总结为一句话:将真实 CPU 建模为一个“理想、精确的多任务 CPU”。 “理想多任务 CPU” 掌控 100% 物理资源,能精确地以相同速度并行执行多个进程, 每个任务的速度都是 1/nr_running。
内核为每个 CPU 维护了一个可运行进程的队列(runqueue); CFS 有一个可配置的调度周期 sched_latency;接下来的基本调度过程:
CFS 根据当前可运行进程的数量 N,计算得到每个进程应该执行的时间 sched_latency/N;
依次取出进程执行以上计算出的时间;
如果 runqueue 有变化,再重新计算可执行时间。
vruntime在真实 CPU 上,任意时间只能运行一个任务;为了实现“公平”,CFS 引入了 “virtual runtime”(虚拟运行时间)的概念。
vruntime 表示进程真正在 CPU 上执行的时间,不包括任何形式的等待时间;
注意机器一般都是多核的,因此 vruntime 是在多个 CPU 上执行时间的累加。
runqueue刚才其实已经提到了,是每个 CPU 上的可运行进程队列,之前就已经存在,并不是 CFS 引入的。
哪个进程 vruntime 最小,说明累计执行时间最少,从“公平”的角度来说,就需要执行它。
CFS 用红黑树来组织这些进程(描述 runqueue),用 vruntime 做 key, 所以这是一个基于时序的红黑树(time-ordered rbtree), 所有 runnable 的进程都是用 p->se.vruntime 作为 key 来排序的。
CFS 每次取出最左边的进程(红黑树特性),执行完成后插入越来越右边,这样每个任务都有机会成为最左边的节点, 在一段确定是时间内总得得到 CPU 资源。
实际上 CFS 还维护了 min/max vruntime,
min vruntime 用途:新进程或重新回到 ready 状态的进程,用 vruntime=min_vruntime 来初始化,放到最左边;这对防止进程饥饿非常关键;
max vruntime 用途:限额?
查询复杂度:
O(1)插入复杂度O(logN)
可运行的进程都放到了一个 runqueue(运行队列)的数据结构中,调度器根据调度策略从里面取出进程放到 CPU 上执行。 有两种调度策略:SCHED_RR 和 SCHED_FIFO。
SCHED_FIFO很简单,先进先出。
进程在下面的条件下会放弃 CPU:
进程在等待,例如 IO 操作。当进程再回到 ready 状态时,它会被放到 runqueue 队尾。
进程通过 sched_yield yield(主动让出) CPU。进程立即进入 runqueue 队尾。
SCHED_RR在这种调度策略中,runqueue 中的每个进程轮流获得时间片(quantum)。
调度策略:影响的是 runqueue 如何工作,每个进程能获得多少执行时间。
CFS 实现了三种调度策略:
SCHED_NORMAL历史上叫 SCHED_OTHER,适用于普通任务的调度。
SCHED_BATCH适合批量任务。不像普通任务那样容易被抢占,因此每个任务运行的时间可以更长,缓存效率更高,但交互性变差。
SCHED_IDLEThis is even weaker than nice 19, but its not a true idle timer scheduler in order to avoid to get into priority inversion problems which would deadlock the machine.
SCHED_NORMAL 和实时进程 SCHED_RR 调度策略的区别二者都是按进程公平分配 CPU,计算好每个进程的执行时间(时长都一样),然后依次取出进程执行, 听起来有点像,但不一样:
| SCHED_RR | SCHED_NORMAL | |
|---|---|---|
| 调度的进程类型 | 实时进程 | 普通进程 |
| 时间片 | 静态,不依赖系统中的进程数量 | 动态,根据系统中进程的数量会发生变化 |
| 下一个进程的选择 | 从 runqueue 中按 RR 选下一个 | 从红黑树中选 vruntime 最小的一个 |
chrt 可查看或修改进程的调度属性:
$ chrt --help
Show or change the real-time scheduling attributes of a process.
...
查看调度属性:
$ chrt -p 219027
pid 219027's current scheduling policy: SCHED_OTHER
pid 219027's current scheduling priority: 0
CFS 引入了 “Scheduling Class” 概念,将调度策略封装到一个调度类型,使得 CFS 调度器核心代码不用处理调度策略细节。
这些调度类组成一个可扩展的调度模块层级(an extensible hierarchy of scheduler modules)。
CONFIG_FAIR_GROUP_SCHED 启用后,会为每个 task group 在对应的 cgroup 目录中创建一个名为 cpu.shares 的文件。
CFS 的时间粒度是 ns,并不依赖任何 jiffies 或 HZ 信息。 有一个可调优的配置,(需要在编译内核时打开 CONFIG_SCHED_DEBUG):
kernel < 5.15: /proc/sys/kernel/sched_min_granularity_ns
kernel >= 5.15: /sys/kernel/debug/sched/min_granularity_ns
可以通过调整这个参数来让调度器从 “desktop”(低延迟)到“server”(高并发)workloads。 默认配置适合的是 desktop workloads。
下面是个例子,创建进程组,通过 cgroup 文件系统设置 CPU shares,
# 1. 挂载 cgroup 文件系统
$ mount -t tmpfs cgroup_root /sys/fs/cgroup
$ mkdir /sys/fs/cgroup/cpu # 创建 cpu 目录,用于控制 cpu 资源份额
$ mount -t cgroup -ocpu none /sys/fs/cgroup/cpu
$ cd /sys/fs/cgroup/cpu
# 2. 创建进程组对应的 cgroup 目录
$ mkdir multimedia # create "multimedia" group of tasks
$ mkdir browser # create "browser" group of tasks
# 3. 设置进程组的 CPU 份额: multimedia 可以比 browser 多用一倍
$ echo 2048 > multimedia/cpu.shares
$ echo 1024 > browser/cpu.shares
# 4. 启动浏览器进程 firefox 并放到 "browser" 进程组
$ firefox &
$ echo > browser/tasks
# 启动多媒体进程 gmplayer 并放到 "multimedia" 进程组
$ gmplayer &
$ echo > multimedia/tasks
CONFIG_CFS_BANDWIDTH)给 cpu cgroup 引入了两个新配置项:
cpu.cfs_period_us: 周期(period),每个周期单独计算,周期结束之后状态(quota 等)清零;默认 100ms
cpu.cfs_quota_us: 在一个周期里的份额(quota),默认 5ms。
最大 1s,最小 1ms:
const u64 max_cfs_quota_period = 1 * NSEC_PER_SEC; /* 1s */
const u64 min_cfs_quota_period = 1 * NSEC_PER_MSEC; /* 1ms */
此外还有一个统计输出:
cpu.stat:输出 throttling statistics
后来还引入了一个优化项:
cpu.cfs_burst_us: the maximum accumulated run-time。上一个进程没用完的份额,可以给下一个 CPU 用。
默认值:
cpu.cfs_period_us=100ms
cpu.cfs_quota_us=-1
cpu.cfs_burst_us=0 # 5.15+
在一个 k8s node 上查看某个 pod 的 CPU throttle 统计:
$ cat /sys/fs/cgroup/cpu/kubepods/pod/cpu.stat
nr_periods 1312889
nr_throttled 100714
throttled_time 22081774986248
The skeleton of our approach is as follows:
We maintain a global pool (per-tg) pool of unassigned quota. Within it we track the bandwidth period, quota per period, and runtime remaining in the current period. As bandwidth is used within a period it is decremented from runtime. Runtime is currently synchronized using a spinlock, in the current implementation there’s no reason this couldn’t be done using atomic ops instead however the spinlock allows for a little more flexibility in experimentation with other schemes.
When a cfs_rq participating in a bandwidth constrained task_group executes it acquires time in sysctl_sched_cfs_bandwidth_slice (default currently 10ms) size chunks from the global pool, this synchronizes under rq->lock and is part of the update_curr path.
Throttled entities are dequeued, we protect against their re-introduction to the scheduling hierarchy via checking for a, per cfs_rq, throttled bit.
After received a slice, sched_entities in cfs_rq would start running, and keep applying after every slice is used up. If there are no more slices, which means the cfs_rq used up all the allowable quota in this period, it will be throttled, at the meanwhile tasks couldn’t run anymore. The throttling statistics could be checked with Cgroup cpu.stat. After this period, global quota pool will be refreshed and cfs_rq get out of throttled state, tasks continue running.
多核情况下:可以在一个核上运行很长时间,也可以在多个核上运行很短时间。 后一种情况会导致进程在很短的时间内用完了全部 quota,在调度周期内剩下的时间里,只能等待。这就是 throttle(关闭阀门,节流)。
典型场景:多核,多线程(例如线程池)进程。
过载情况下,每个进程能分到的时间片很短,例如 1ms,导致大部分 CPU 开销都花在了上下文切换上。
上下文切换做的事情:
保存当前进程或线程的状态;
恢复下一个进程或线程的状态;
执行后一个进程。
如果一个时间片是 6ms,切换占 1ms,那我们还有5ms 可以执行; 如果 1.5ms,那只有 0.5ms 可以执行。
为了避免这个问题,引入 min_granularity;反过来,这也会影响 sched_latency 的选取。
SCHED_FIFO/_RR are implemented in sched/rt.c and are as specified by POSIX.
sched/rt.c implements SCHED_FIFO and SCHED_RR semantics. It uses 100 runqueues (for all 100 RT priority levels, instead of 140 in the previous scheduler) and it needs no expired array.
见 [1],代码不太多。想快速了解整体实现的可以浏览一下。
接下来的部分都是参考 5.10 代码。
介绍几个核心的数据结构。
struct task_struct每个进程的结构体表示是 struct task,
// include/linux/sched.h
struct task_struct {
struct thread_info thread_info;
volatile long state; /* -1 unrunnable, 0 runnable, >0 stopped: */
void *stack;
refcount_t usage;
unsigned int flags; /* Per task flags (PF_*), defined further below: */
unsigned int ptrace;
int on_cpu;
struct __call_single_node wake_entry;
unsigned int cpu; /* Current CPU: */
unsigned int wakee_flips;
unsigned long wakee_flip_decay_ts;
struct task_struct *last_wakee;
int recent_used_cpu;
int wake_cpu;
int on_rq;
int prio;
int static_prio;
int normal_prio;
const struct sched_class *sched_class;
struct sched_entity se; // schedule entity, including vruntime
#ifdef CONFIG_CGROUP_SCHED
struct task_group *sched_task_group;
#endif
...
};
其中有个调度相关的字段是 struct sched_entity se。可以是一个进程、一个进程组或一个用户。
struct task_group同理,进程组中也有一个 struct sched_entity se 字段:
// https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v5.10/kernel/sched/sched.h#L383
/* Task group related information */
struct task_group {
struct cgroup_subsys_state css;
#ifdef CONFIG_FAIR_GROUP_SCHED
struct sched_entity **se; /* schedulable entities of this group on each CPU */
struct cfs_rq **cfs_rq; /* runqueue "owned" by this group on each CPU */
unsigned long shares;
atomic_long_t load_avg ____cacheline_aligned;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_RT_GROUP_SCHED
struct sched_rt_entity **rt_se;
struct rt_rq **rt_rq;
struct rt_bandwidth rt_bandwidth;
#endif
struct rcu_head rcu;
struct list_head list;
struct task_group *parent;
struct list_head siblings;
struct list_head children;
#ifdef CONFIG_SCHED_AUTOGROUP
struct autogroup *autogroup;
#endif
struct cfs_bandwidth cfs_bandwidth;
#ifdef CONFIG_UCLAMP_TASK_GROUP
/* The two decimal precision [%] value requested from user-space */
unsigned int uclamp_pct[UCLAMP_CNT];
/* Clamp values requested for a task group */
struct uclamp_se uclamp_req[UCLAMP_CNT];
/* Effective clamp values used for a task group */
struct uclamp_se uclamp[UCLAMP_CNT];
#endif
};
struct sched_entityscheduling entities 通过一个红黑树组织到一起,根据 vruntime 排序,通过 cfs_rq 来管理.
所以 virtual runtime(vruntime)就定义在这个结构体里面,单位是 ns,
// https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v5.10/include/linux/sched.h#L451
struct sched_entity {
struct load_weight load; // For load-balancing
struct rb_node run_node;
struct list_head group_node;
unsigned int on_rq;
u64 exec_start;
u64 sum_exec_runtime;
u64 vruntime; // unit: ns
u64 prev_sum_exec_runtime;
u64 nr_migrations;
struct sched_statistics statistics;
#ifdef CONFIG_FAIR_GROUP_SCHED
int depth;
struct sched_entity *parent;
struct cfs_rq *cfs_rq; // rq on which this entity is (to be) queued
struct cfs_rq *my_q; // rq "owned" by this entity/group
unsigned long runnable_weight; /* cached value of my_q->h_nr_running */
#endif
// Per entity load average tracking.
// Put into separate cache line so it does not collide with read-mostly values above.
struct sched_avg avg;
};
有了这个字段,就能精确地通过时间戳来保证一个任务应该获得的 “expected CPU time”。
前面已经提到,CFS 就是基于 p->se.vruntime 来选择(调度)进程的,逻辑非常简单: 永远选择 p->se.vruntime 最小(说明这个进程到目前为止累积执行的时间最少)的进程来运行。 CFS 会不断尝试均衡各进程的 CPU 时间,尽量接近“理想多任务 CPU”。
struct cfs_rq// https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v5.10/kernel/sched/sched.h#L518
/* CFS-related fields in a runqueue (rq) */
struct cfs_rq {
struct load_weight load;
unsigned int nr_running;
unsigned int h_nr_running; /* SCHED_{NORMAL,BATCH,IDLE} */
unsigned int idle_h_nr_running; /* SCHED_IDLE */
u64 exec_clock;
u64 min_vruntime;
u64 min_vruntime_copy;
struct rb_root_cached tasks_timeline; // rbtree
/*
* 'curr' points to currently running entity on this cfs_rq.
* It is set to NULL otherwise (i.e when none are currently running).
*/
struct sched_entity *curr;
struct sched_entity *next;
struct sched_entity *last;
struct sched_entity *skip;
/*
* CFS load tracking
*/
struct sched_avg avg;
#ifndef CONFIG_64BIT
u64 load_last_update_time_copy;
#endif
struct {
raw_spinlock_t lock ____cacheline_aligned;
int nr;
unsigned long load_avg;
unsigned long util_avg;
unsigned long runnable_avg;
} removed;
#ifdef CONFIG_FAIR_GROUP_SCHED
unsigned long tg_load_avg_contrib;
long propagate;
long prop_runnable_sum;
/*
* h_load = weight * f(tg)
*
* Where f(tg) is the recursive weight fraction assigned to
* this group.
*/
unsigned long h_load;
u64 last_h_load_update;
struct sched_entity *h_load_next;
#endif /* CONFIG_FAIR_GROUP_SCHED */
#ifdef CONFIG_FAIR_GROUP_SCHED
// the main per-CPU runqueue structure, which cfs_rq would attached to
struct rq *rq; /* CPU runqueue to which this cfs_rq is attached */
/*
* leaf cfs_rqs are those that hold tasks (lowest schedulable entity in
* a hierarchy). Non-leaf lrqs hold other higher schedulable entities
* (like users, containers etc.)
*
* leaf_cfs_rq_list ties together list of leaf cfs_rq's in a CPU.
* This list is used during load balance.
*/
int on_list;
struct list_head leaf_cfs_rq_list;
struct task_group *tg; /* group that "owns" this runqueue */
#ifdef CONFIG_CFS_BANDWIDTH
int runtime_enabled;
s64 runtime_remaining;
u64 throttled_clock;
u64 throttled_clock_task;
u64 throttled_clock_task_time;
int throttled;
int throttle_count;
struct list_head throttled_list;
#endif /* CONFIG_CFS_BANDWIDTH */
#endif /* CONFIG_FAIR_GROUP_SCHED */
};
其中的 CFS 红黑树:
// include/linux/rbtree.h
// Leftmost-cached rbtrees.
struct rb_root_cached {
struct rb_root rb_root;
struct rb_node *rb_leftmost;
};
在 cfs_rq 中声明了这个 rbtree 变量:
CFS 维护了 rq->cfs.min_vruntime 值,这是一个单调递增值,跟踪 runqueue 所有进程中最小的 vruntime。
系统完成的总 work 量用 min_vruntime 表示,新激活的进程,会用这个值来初始化,放到 rbtree 尽量最左边;
runqueue 中的总 running 进程数量用 rq->cfs.load 表示,是 runqueue 中所有进程的 weights 总和;
总结一下 CFS 的工作原理:
runs a task a bit, 当进程被调度(或 scheduler tick 到来时),更新这个进程的 CPU usage: 这个进程使用的物理 CPU 时间会累加到 p->se.vruntime;
当 p->se.vruntime (加上一个很小的”granularity” distance,以避免过度调度进程,trash the cache)大到已经不是最左侧节点时, 新的最左侧节点就会被选中,当前进程被强占(current task is preempted)。
struct sched_classScheduling class 是通过 struct sched_class 实现的,
// kernel/sched/sched.h
struct sched_class {
int uclamp_enabled;
void (*enqueue_task) (struct rq *rq, struct task_struct *p, int flags);
void (*dequeue_task) (struct rq *rq, struct task_struct *p, int flags);
void (*yield_task) (struct rq *rq);
bool (*yield_to_task)(struct rq *rq, struct task_struct *p);
void (*check_preempt_curr)(struct rq *rq, struct task_struct *p, int flags);
struct task_struct *(*pick_next_task)(struct rq *rq);
void (*put_prev_task)(struct rq *rq, struct task_struct *p);
void (*set_next_task)(struct rq *rq, struct task_struct *p, bool first);
int (*balance)(struct rq *rq, struct task_struct *prev, struct rq_flags *rf);
int (*select_task_rq)(struct task_struct *p, int task_cpu, int sd_flag, int flags);
void (*migrate_task_rq)(struct task_struct *p, int new_cpu);
void (*task_woken)(struct rq *this_rq, struct task_struct *task);
void (*set_cpus_allowed)(struct task_struct *p, const struct cpumask *newmask);
void (*rq_online)(struct rq *rq);
void (*rq_offline)(struct rq *rq);
void (*task_tick)(struct rq *rq, struct task_struct *p, int queued);
void (*task_fork)(struct task_struct *p);
void (*task_dead)(struct task_struct *p);
/*
* The switched_from() call is allowed to drop rq->lock, therefore we
* cannot assume the switched_from/switched_to pair is serliazed by
* rq->lock. They are however serialized by p->pi_lock.
*/
void (*switched_from)(struct rq *this_rq, struct task_struct *task);
void (*switched_to) (struct rq *this_rq, struct task_struct *task);
void (*prio_changed) (struct rq *this_rq, struct task_struct *task, int oldprio);
unsigned int (*get_rr_interval)(struct rq *rq, struct task_struct *task);
void (*update_curr)(struct rq *rq);
#define TASK_SET_GROUP 0
#define TASK_MOVE_GROUP 1
#ifdef CONFIG_FAIR_GROUP_SCHED
void (*task_change_group)(struct task_struct *p, int type);
#endif
} __aligned(STRUCT_ALIGNMENT); /* STRUCT_ALIGN(), vmlinux.lds.h */
初始化:
// kernel/sched/fair.c
/*
* All the scheduling class methods:
*/
const struct sched_class fair_sched_class
__section("__fair_sched_class") = {
.enqueue_task = enqueue_task_fair,
.dequeue_task = dequeue_task_fair,
.yield_task = yield_task_fair,
.yield_to_task = yield_to_task_fair,
.check_preempt_curr = check_preempt_wakeup,
.pick_next_task = __pick_next_task_fair,
.put_prev_task = put_prev_task_fair,
.set_next_task = set_next_task_fair,
#ifdef CONFIG_SMP
.balance = balance_fair,
.select_task_rq = select_task_rq_fair,
.migrate_task_rq = migrate_task_rq_fair,
.rq_online = rq_online_fair,
.rq_offline = rq_offline_fair,
.task_dead = task_dead_fair,
.set_cpus_allowed = set_cpus_allowed_common,
#endif
.task_tick = task_tick_fair,
.task_fork = task_fork_fair,
.prio_changed = prio_changed_fair,
.switched_from = switched_from_fair,
.switched_to = switched_to_fair,
.get_rr_interval = get_rr_interval_fair,
.update_curr = update_curr_fair,
#ifdef CONFIG_FAIR_GROUP_SCHED
.task_change_group = task_change_group_fair,
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_UCLAMP_TASK
.uclamp_enabled = 1,
#endif
};
内核文档:CFS bandwidth control。
$ cat /proc/sys/kernel/sched_cfs_bandwidth_slice_us
5000
$ sysctl -a | grep cfs_
kernel.sched_cfs_bandwidth_slice_us = 5000
第一版实现: https://github.com/torvalds/linux/commit/ab84d31e15502fb626169ba2663381e34bf965b2
sched: Introduce primitives to account for CFS bandwidth tracking
In this patch we introduce the notion of CFS bandwidth, partitioned into
globally unassigned bandwidth, and locally claimed bandwidth.
- The global bandwidth is per task_group, it represents a pool of unclaimed
bandwidth that cfs_rqs can allocate from.
- The local bandwidth is tracked per-cfs_rq, this represents allotments from
the global pool bandwidth assigned to a specific cpu.
Bandwidth is managed via cgroupfs, adding two new interfaces to the cpu subsystem:
- cpu.cfs_period_us : the bandwidth period in usecs
- cpu.cfs_quota_us : the cpu bandwidth (in usecs) that this tg will be allowed
to consume over period above.
cpu.cfs_period_us: 周期(period),每个周期单独计算,周期结束之后状态(quota 等)清零;默认 100ms
cpu.cfs_quota_us: 在一个周期里的份额(quota),默认 5ms。
最大 1s,最小 1ms:
const u64 max_cfs_quota_period = 1 * NSEC_PER_SEC; /* 1s */
const u64 min_cfs_quota_period = 1 * NSEC_PER_MSEC; /* 1ms */
static int tg_set_cfs_bandwidth(struct task_group *tg, u64 period, u64 quota)
{
int i;
struct cfs_bandwidth *cfs_b = tg_cfs_bandwidth(tg);
static DEFINE_MUTEX(mutex);
if (tg == &root_task_group)
return -EINVAL;
/*
* Ensure we have at some amount of bandwidth every period. This is
* to prevent reaching a state of large arrears when throttled via
* entity_tick() resulting in prolonged exit starvation.
*/
if (quota < min_cfs_quota_period || period < min_cfs_quota_period)
return -EINVAL;
/*
* Likewise, bound things on the otherside by preventing insane quota
* periods. This also allows us to normalize in computing quota
* feasibility.
*/
if (period > max_cfs_quota_period)
return -EINVAL;
mutex_lock(&mutex);
raw_spin_lock_irq(&cfs_b->lock);
cfs_b->period = ns_to_ktime(period);
cfs_b->quota = quota;
raw_spin_unlock_irq(&cfs_b->lock);
for_each_possible_cpu(i) {
struct cfs_rq *cfs_rq = tg->cfs_rq[i];
struct rq *rq = rq_of(cfs_rq);
raw_spin_lock_irq(&rq->lock);
cfs_rq->runtime_enabled = quota != RUNTIME_INF;
cfs_rq->runtime_remaining = 0;
raw_spin_unlock_irq(&rq->lock);
}
mutex_unlock(&mutex);
return 0;
}
用 Overly aggressive CFS 中的程序测试 CFS CPU throttle:
package main
import (
"crypto/sha512"
"flag"
"log"
"syscall"
"time"
)
func main() {
sleep := flag.Duration("sleep", time.Second, "sleep between iterations")
interations := flag.Int("iterations", 100, "number of iterations")
flag.Parse()
time.Sleep(time.Second)
b := time.Now()
for i := 0; i < *interations; i++ {
s := time.Now()
burn(time.Millisecond * 5)
e := time.Now().Sub(s)
log.Printf("[%d] burn took %dms, real time so far: %dms, cpu time so far: %dms", i, ms(e), ms(time.Since(b)), ms(usage()))
time.Sleep(*sleep)
}
}
func ms(duration time.Duration) int {
return int(duration.Nanoseconds() / 1000 / 1000)
}
func burn(duration time.Duration) {
s := time.Now()
for {
sum := sha512.New()
sum.Write([]byte("banana"))
sum.Sum([]byte{})
if time.Since(s) > duration {
break
}
}
}
func usage() time.Duration {
r := syscall.Rusage{}
syscall.Getrusage(syscall.RUSAGE_SELF, &r)
return time.Duration(r.Stime.Nano() + r.Utime.Nano())
}
程序每个 iteration 会执行 5ms,然后 sleep 一段时间。
用 docker container 来执行,避免污染本机配置。
period=100ms,quota=5m,sleep=10ms 情况下,不会产生 throttle:
$ dk run --rm -it -v $(pwd):$(pwd) -w $(pwd) golang:1.19.4 go run cfs.go -iterations 20 -sleep 10ms
2023/02/05 09:50:35 [0] burn took 5ms, real time so far: 5ms, cpu time so far: 7ms
2023/02/05 09:50:35 [1] burn took 5ms, real time so far: 20ms, cpu time so far: 12ms
2023/02/05 09:50:35 [2] burn took 5ms, real time so far: 37ms, cpu time so far: 17ms
...
2023/02/05 09:50:35 [18] burn took 5ms, real time so far: 338ms, cpu time so far: 102ms
2023/02/05 09:50:35 [19] burn took 5ms, real time so far: 355ms, cpu time so far: 108ms
period=100ms,quota=25m,sleep=10ms 情况下,会产生 throttle:
$ dk run --rm -it --cpu-quota 25000 --cpu-period 100000 -v $(pwd):$(pwd) -w $(pwd) golang:1.19.4 go run cfs.go -iterations 20 -sleep 10ms
2023/02/05 09:48:38 [0] burn took 5ms, real time so far: 5ms, cpu time so far: 6ms
2023/02/05 09:48:38 [1] burn took 11ms, real time so far: 35ms, cpu time so far: 19ms
2023/02/05 09:48:38 [2] burn took 5ms, real time so far: 51ms, cpu time so far: 24ms
2023/02/05 09:48:38 [3] burn took 20ms, real time so far: 83ms, cpu time so far: 28ms
2023/02/05 09:48:38 [4] burn took 5ms, real time so far: 100ms, cpu time so far: 33ms
2023/02/05 09:48:38 [5] burn took 5ms, real time so far: 115ms, cpu time so far: 38ms
2023/02/05 09:48:38 [6] burn took 5ms, real time so far: 131ms, cpu time so far: 43ms
2023/02/05 09:48:38 [7] burn took 5ms, real time so far: 147ms, cpu time so far: 49ms
2023/02/05 09:48:38 [8] burn took 24ms, real time so far: 182ms, cpu time so far: 51ms
2023/02/05 09:48:38 [9] burn took 5ms, real time so far: 197ms, cpu time so far: 56ms
...
研究这些东西是为了更好理解一些容器问题。
TODO。
CFS 第一版实现, kernel/sched_fair.c,kernel v2.6.23, 2007
CFS scheduler design (kernel 5.10), kernel doc, 2023
The burstable CFS bandwidth controller, lwn.net, 2021
CFS bandwidth control, lwn.net, 2011
CPU bandwidth control for CFS, google, 2009
CPU bandwidth control warmup, 2021
Overly aggressive CFS, 2018
Process Scheduling In Linux, 2021