在熟悉了UART概念后,我们要学以致用,在Linux用起来来驱动起来蓝牙芯片!
我们直接借用man来看下,命令如下: man termios
#include <termios.h>
#include <unistd.h>open(“/dev/ttyUSB0”, O_RDWR|O_NOCTTY);
close(fd);Linux秉行一切皆文件的,所以打开关是用open,关闭串口使用close
struct termios
{
tcflag_t c_iflag; /* input flags */
tcflag_t c_oflag; /* output flags */
tcflag_t c_cflag; /* control flags */
tcflag_t c_lflag; /* local flags */
cc_t c_cc[NCCS]; /* control characters */
};下面我们来分别介绍下各个flag!
在输入值传给程序之前控制其处理的方式
负责控制输出字元的处理方式
用于控制终端设备的硬件设置
主要用来控制终端设备不同的特色
符号下标 (初始值) 和意义(即c_cc[]数组对应下标的数值对应含义,如c_cc[VMIN] = 3):
这些符号下标值是互不相同的,除了 VTIME,VMIN 的值可能分别与 VEOL,VEOF 相同。 (在 non-canonical 模式下,特殊字符的含义更改为延时含义MIN 表示应当被读入的最小字符数。TIME 是以十分之一秒为单位的计时器。如果同时设置了它们,read 将等待直到至少读入一个字符,一旦读入 MIN 个字符或者从上次读入字符开始经过了 TIME 时间就立即返回。如果只设置了 MIN,read 在读入 MIN 个字符之前不会返回。如果只设置了 TIME,read 将在至少读入一个字符,或者计时器超时的时候立即返回。如果都没有设置,read 将立即返回,只给出当前准备好的字符。)
MIN与TIME组合有以下四种:
/* 属性相关 */
int tcgetattr(int fd, struct termios *termios_p);
int tcsetattr(int fd, int optional_actions,
const struct termios *termios_p);
void cfmakeraw(struct termios *termios_p);
/* 控制相关 */
int tcsendbreak(int fd, int duration);
int tcdrain(int fd);
int tcflush(int fd, int queue_selector);
int tcflow(int fd, int action);
/* 速度相关 */
speed_t cfgetispeed(const struct termios *termios_p);
speed_t cfgetospeed(const struct termios *termios_p);
int cfsetispeed(struct termios *termios_p, speed_t speed);
int cfsetospeed(struct termios *termios_p, speed_t speed);| 函数名称 |
描述 |
| tcgetattr |
获取串口属性,填充到termios_p入参中 |
| tcsetattr |
根据termios_p的值改变串口属性 optional_actions (tcsetattr函数的第二个参数)指定了什么时候改变会起作用: |
| cfmakeraw |
把串口属性设置位初始状态,比如以下值: termios_p->c_iflag &= ~(IGNBRK | BRKINT | PARMRK | ISTRIP | INLCR | IGNCR | ICRNL | IXON); termios_p->c_oflag &= ~OPOST; termios_p->c_lflag &= ~(ECHO | ECHONL | ICANON | ISIG | IEXTEN); termios_p->c_cflag &= ~(CSIZE | PARENB); termios_p->c_cflag |= CS8; |
| cfgetispeed |
获取input的串口波特率 |
| cfgetospeed |
获取output的串口波特率 |
| cfsetispeed |
设置input的串口波特率 |
| cfsetospeed |
获取output的串口波特率 |
| tcsendbreak |
|
| tcdrain |
等待所有写入fd中的数据输出 |
| tcflush |
清空串口BUFFER中的数据函数 常用的有三个值, TCIFLUSH清除正收到的数据,且不会读取出来; TCOFLUSH清除正写入的数据,且不会发送至终端; TCIOFLUSH清除所有正在发生的I/O数据; |
| tcflow |
挂起 fd 引用的对象上的数据传输或接收,取决于 action 的值 TCOOFF 挂起输出 |
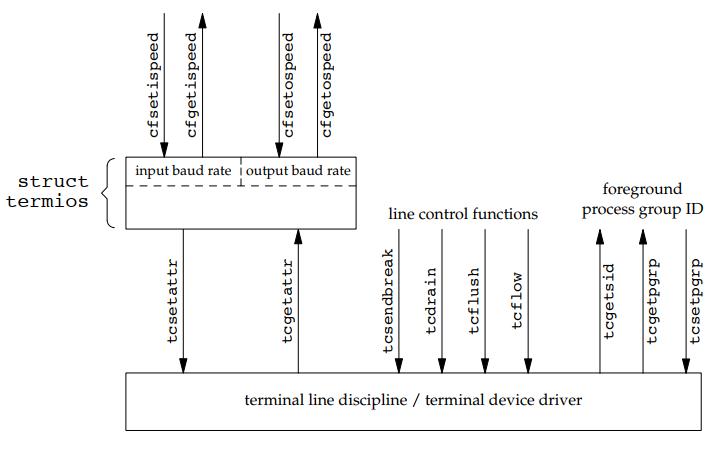
框图如下:
我们写一个sample,用H4 transport来发送一个HCI RESET然后读回来值:
#include <termios.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#define UART_MAX_SIZE 256
int uart_fd;
uint8_t uart_buffer[UART_MAX_SIZE] = {0};
void usage()
{
printf("---------------------------------\n");
printf(" ./uart_test port_name \n");
printf("example: ./uart_test /dev/ttyUSB0\n");
printf("---------------------------------\n");
}
#define MAX_COL 16
#define SHOW_LINE_SIZE 16
void bt_hex_dump(uint8_t *data,uint32_t len)
{
uint32_t line;
uint32_t curline = 0;
uint32_t curcol = 0;
char showline[SHOW_LINE_SIZE];
uint32_t data_pos = 0;
if(len % MAX_COL)
{
line = len/MAX_COL 1;
}
else
{
line = len/MAX_COL;
}
for(curline = 0; curline < line; curline )
{
sprintf(showline,"xh:",curline*MAX_COL);
printf("%s",showline);
for(curcol = 0; curcol < MAX_COL; curcol )
{
if(data_pos < len)
{
printf("x ",data[data_pos]);
data_pos ;
continue;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
printf("\n");
}
}
void alarm_send_command()
{
uint8_t hci_reset[] = {0x01,0x03,0x0c,0x00};
printf("send HCI command\n");
write(uart_fd,hci_reset,sizeof(hci_reset));
alarm(1);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
struct termios toptions;
usage();
if(argc != 2)
{
printf("Usage error\n");
return 0;
}
uart_fd = open(argv[1], O_RDWR | O_NOCTTY);
printf("uart_fd %d\n",uart_fd);
if (tcgetattr(uart_fd, &toptions) < 0)
{
printf("ERROR:Couldn't get term attributes\n");
return -1;
}
cfmakeraw(&toptions);
// 8N1
toptions.c_cflag &= ~CSTOPB;
toptions.c_cflag |= CS8;
toptions.c_cflag |= CREAD | CLOCAL | CRTSCTS;
toptions.c_iflag &= ~(IXON | IXOFF | IXANY);
toptions.c_cflag &= ~PARENB;
toptions.c_cc[VMIN] = 1;
toptions.c_cc[VTIME] = 0;
if(tcsetattr(uart_fd, TCSANOW, &toptions) < 0)
{
printf("ERROR:Couldn't set term attributes\n");
return -1;
}
if (tcgetattr(uart_fd, &toptions) < 0)
{
printf("ERROR:Couldn't get term attributes\n");
return -1;
}
cfsetospeed(&toptions, B115200);
cfsetispeed(&toptions, B115200);
if( tcsetattr(uart_fd, TCSANOW, &toptions) < 0)
{
printf("ERROR:Couldn't set term attributes\n");
return -1;
}
signal(SIGALRM, alarm_send_command);
alarm(1);
while(1)
{
int read_result = read(uart_fd,uart_buffer,UART_MAX_SIZE);
bt_hex_dump(uart_buffer,read_result);
memset(uart_buffer,0,UART_MAX_SIZE);
}
}整个程序实现的效果很简单,就是打开串口(8N1 流控),设置波特率,然后1s发送一次hci reset,然后读取数据uart数据