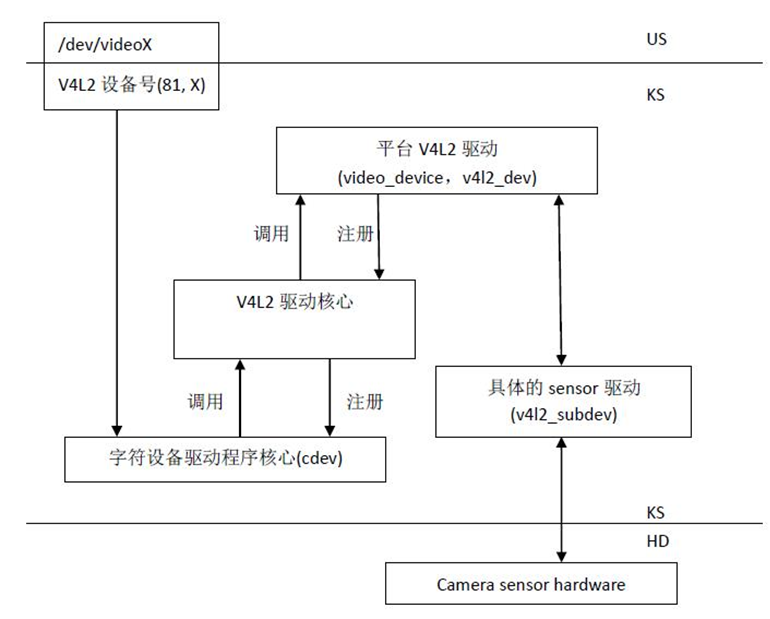
在应用层,我们可以在 /dev 目录发现 videoX的设备节点,应用程序打开设备节点进行数据捕获,显示视频画面。video0、video1、video2...这些设备节点是在核心层注册。
核心层(v4l2-dev.c)起承上启下的作用,它会为每一个驱动注册进来的设备设置一个统一的接口 v4l2_fops ,这些统一的接口最终将调用到驱动中的 video_device 的 fops 。
video_device
前面我们了解了一些Camera的基础知识《Camera基础知识》。接下来来看看Linux为Camera提供的驱动框架。
V4L2( Video for Linux Two),是一套Linux内核视频设备的驱动框架。该驱动框架为应用层提供一套统一的操作接口(一系列的ioctl)。V4L2在设计时,是要支持更广泛的设备,它们其中只有一部分在本质上是真正的视频设备,所以它不仅仅是为Camera设计。
网络图片
在应用层,我们可以在 /dev 目录发现 videoX的设备节点,应用程序打开设备节点进行数据捕获,显示视频画面。video0、video1、video2...这些设备节点是在核心层注册。
核心层(v4l2-dev.c)起承上启下的作用,它会为每一个驱动注册进来的设备设置一个统一的接口 v4l2_fops ,这些统一的接口最终将调用到驱动中的 video_device 的 fops 。
video_device
//表示一个视频设备struct video_device {struct media_entity entity;struct media_intf_devnode *intf_devnode;struct media_pipeline pipe;const struct v4l2_file_operations *fops; //文件操作接口(dev/videoX)u32 device_caps; //设备功能,用于v4l2_capabilities(应用层定义的结构体)struct device dev;struct cdev *cdev; //字符设备struct v4l2_device *v4l2_dev; //V4L2设备struct device *dev_parent;struct v4l2_ctrl_handler *ctrl_handler; //设备节点对应的控制句柄struct vb2_queue *queue;struct v4l2_prio_state *prio;char name[32]; //Video设备名称enum vfl_devnode_type vfl_type; //V4L设备类型enum vfl_devnode_direction vfl_dir; //V4L 接收者/发送者/m2mint minor; //子设备号,主设备为81u16 num;unsigned long flags;int index;spinlock_t fh_lock;struct list_head fh_list;int dev_debug;v4l2_std_id tvnorms;void (*release)(struct video_device *vdev); //video_device release()回调const struct v4l2_ioctl_ops *ioctl_ops; //IOCTL回调unsigned long valid_ioctls[BITS_TO_LONGS(BASE_VIDIOC_PRIVATE)];struct mutex *lock;};
v4l2_device
struct v4l2_device {struct device *dev;struct media_device *mdev;struct list_head subdevs; //用于追踪已注册的subdevspinlock_t lock;char name[V4L2_DEVICE_NAME_SIZE]; //设备名void (*notify)(struct v4l2_subdev *sd, unsigned int notification, void *arg);struct v4l2_ctrl_handler *ctrl_handler; //控制句柄struct v4l2_prio_state prio; //设备的优先状态struct kref ref; //引用void (*release)(struct v4l2_device *v4l2_dev);//引用计数为0后调用};
嵌入到video_device中,表示一个v4l2设备的实例。
v4l2_subdev
struct v4l2_subdev {struct media_entity entity;struct list_head list; //subdev列表struct module *owner;bool owner_v4l2_dev;u32 flags;struct v4l2_device *v4l2_dev; //依附的v4l2_deviceconst struct v4l2_subdev_ops *ops; //subdev操作函数const struct v4l2_subdev_internal_ops *internal_ops;struct v4l2_ctrl_handler *ctrl_handler; //控制句柄char name[V4L2_SUBDEV_NAME_SIZE]; //subdev名称u32 grp_id;void *dev_priv;void *host_priv;struct video_device *devnode;struct device *dev;struct fwnode_handle *fwnode;struct list_head async_list;struct v4l2_async_subdev *asd;struct v4l2_async_notifier *notifier;struct v4l2_async_notifier *subdev_notifier;struct v4l2_subdev_platform_data *pdata;//subdev平台数据};
依附在v4l2_device之下,并表示一个v4l2设备的子设备,一个v4l2_device下可以有多个sub_device。
v4l2_fh
struct v4l2_fh {struct list_head list; //文件句柄列表struct video_device *vdev; //依附的video_devicestruct v4l2_ctrl_handler *ctrl_handler;enum v4l2_priority prio; //文件句柄的优先级wait_queue_head_t wait;struct mutex subscribe_lock;struct list_head subscribed; //订阅的事件列表struct list_head available; //可用的事件unsigned int navailable; //可用的事件数u32 sequence;struct v4l2_m2m_ctx *m2m_ctx;};
用于追踪的文件句柄
v4l2_device和v4l2_subdev的关系:
subdev的设计目的是为了多路复用,就是用一个v4l2_device可以挂接多个v4l2_subdev。所谓的多路复用就是使用一个摄像头控制器来控制多个摄像头。比如手机上有前置和后置摄像头。
在V4L2驱动中,使用v4l2_device来表示摄像头控制器(ISP)。使用v4l2_subdev来表示具体的某一个摄像头(Sensor)。
v4l2_file_operations
//V4L2设备操作函数struct v4l2_file_operations {struct module *owner;ssize_t (*read) (struct file *, char __user *, size_t, loff_t *);ssize_t (*write) (struct file *, const char __user *, size_t, loff_t *);__poll_t (*poll) (struct file *, struct poll_table_struct *);long (*unlocked_ioctl) (struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long);long (*compat_ioctl32) (struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long);unsigned long (*get_unmapped_area) (struct file *, unsigned long, unsigned long, unsigned long, unsigned long);int (*mmap) (struct file *, struct vm_area_struct *);int (*open) (struct file *);int (*release) (struct file *);};
v4l2_ioctl_ops
//IOCTL操作函数struct v4l2_ioctl_ops {......int (*vidioc_overlay)(struct file *file, void *fh, unsigned int i);int (*vidioc_g_fbuf)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_framebuffer *a);int (*vidioc_s_fbuf)(struct file *file, void *fh, const struct v4l2_framebuffer *a);int (*vidioc_streamon)(struct file *file, void *fh, enum v4l2_buf_type i);int (*vidioc_streamoff)(struct file *file, void *fh, enum v4l2_buf_type i);......int (*vidioc_enum_framesizes)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_frmsizeenum *fsize);int (*vidioc_enum_frameintervals)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_frmivalenum *fival);int (*vidioc_s_dv_timings)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_dv_timings *timings);int (*vidioc_g_dv_timings)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_dv_timings *timings);int (*vidioc_query_dv_timings)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_dv_timings *timings);int (*vidioc_enum_dv_timings)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_enum_dv_timings *timings);int (*vidioc_dv_timings_cap)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_dv_timings_cap *cap);int (*vidioc_g_edid)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_edid *edid);int (*vidioc_s_edid)(struct file *file, void *fh, struct v4l2_edid *edid);int (*vidioc_subscribe_event)(struct v4l2_fh *fh, const struct v4l2_event_subscription *sub);int (*vidioc_unsubscribe_event)(struct v4l2_fh *fh, const struct v4l2_event_subscription *sub);long (*vidioc_default)(struct file *file, void *fh, bool valid_prio, unsigned int cmd, void *arg);};
v4l2_subdev_ops
//subdev操作函数struct v4l2_subdev_ops {const struct v4l2_subdev_core_ops *core; //subdev核心操作回调const struct v4l2_subdev_tuner_ops *tuner; //radio模式打开v4l设备时的操作回调const struct v4l2_subdev_audio_ops *audio; //音频相关设置回调const struct v4l2_subdev_video_ops *video; //video模式打开v4l设备时的操作回调const struct v4l2_subdev_vbi_ops *vbi; //通过vbi设备节点以video模式打开v4l设备时的操作回调const struct v4l2_subdev_ir_ops *ir; //IR(红外)设备操作函数const struct v4l2_subdev_sensor_ops *sensor; //sensor操作函数const struct v4l2_subdev_pad_ops *pad; //pad操作函数};
v4l2可以用于很多类型的设备,所以上面的回调只需根据实际设备的需要实现部分即可。
上面的v4l2_ioctl_ops中实现的部分ioctl最终会调用到v4l2_subdev_ops中的回调函数。
//注册/注销video_deviceint video_register_device(struct video_device *vdev, enum vfl_devnode_type type, int nr)void video_unregister_device(struct video_device *vdev)//分配/释放video_devicestruct video_device * __must_check video_device_alloc(void);void video_device_release(struct video_device *vdev)//注册/注销v4l2_deviceint v4l2_device_register(struct device *dev, struct v4l2_device *v4l2_dev)void v4l2_device_unregister(struct v4l2_device *v4l2_dev)//注册/注销v4l2_subdev(关联v4l2_device和v4l2_subdev)int v4l2_device_register_subdev(struct v4l2_device *v4l2_dev, struct v4l2_subdev *sd)void v4l2_device_unregister_subdev(struct v4l2_subdev *sd)//初始化v4l2_subdevvoid v4l2_subdev_init(struct v4l2_subdev *sd, const struct v4l2_subdev_ops *ops);/********************************I2C subdev*************************************///初始化v4l2_subdev, 该subdev是I2C设备void v4l2_i2c_subdev_init(struct v4l2_subdev *sd, struct i2c_client *client,const struct v4l2_subdev_ops *ops)/*******************************SPI subdev************************************************///初始化v4l2_subdev, 该subdev是SPI设备void v4l2_spi_subdev_init(struct v4l2_subdev *sd, struct spi_device *spi,const struct v4l2_subdev_ops *ops)
Linux版本:4.19
Sensor: OV13850
(1)装载和卸载函数
//DTS匹配表static const struct of_device_id ov13850_of_match[] = {{.compatible = "omnivision,ov13850-v4l2-i2c-subdev"},{},};MODULE_DEVICE_TABLE(i2c, ov13850_id);static struct i2c_driver ov13850_i2c_driver = {.driver = {.name = ov13850_DRIVER_NAME,.owner = THIS_MODULE,.of_match_table = ov13850_of_match},.probe = ov13850_probe,.remove = ov13850_remove,.id_table = ov13850_id,};module_i2c_driver(ov13850_i2c_driver);
OV13850是使用I2C接口进行控制,所以使用i2c_driver进行注册。
(2)probe()
static int ov13850_probe(struct i2c_client *client,const struct i2c_device_id *id){dev_info(&client->dev, "probing...\n");ov13850_filltimings(&ov13850_custom_config); //填充时序信息v4l2_i2c_subdev_init(&ov13850.sd, client, &ov13850_camera_module_ops); //初始化v4l2_subdevov13850.sd.flags |= V4L2_SUBDEV_FL_HAS_DEVNODE;ov13850.custom = ov13850_custom_config;mutex_init(&ov13850.lock);dev_info(&client->dev, "probing successful\n");return 0;}
上面主要是根据全局变量ov13850_custom_config中的信息填充时序信息。然后初始化v4l2_subdev, ov13850是I2C接口,所以使用v4l2_i2c_subdev_init 进行初始化。v4l2_i2c_subdev_init就是对v4l2_subdev_init的封装。
//v4l2_subdev_opsstatic struct v4l2_subdev_ops ov13850_camera_module_ops = {.core = &ov13850_camera_module_core_ops, //核心操作.video = &ov13850_camera_module_video_ops, //video操作.pad = &ov13850_camera_module_pad_ops};static struct ov_camera_module_custom_config ov13850_custom_config = {.start_streaming = ov13850_start_streaming, //sensor开始输出数据流.stop_streaming = ov13850_stop_streaming, //sensor停止输出数据流.s_ctrl = ov13850_s_ctrl,.s_ext_ctrls = ov13850_s_ext_ctrls, //sensor控制(设置自动曝光控制).g_ctrl = ov13850_g_ctrl,.g_timings = ov13850_g_timings, //获取sensor时序.check_camera_id = ov13850_check_camera_id, //读取Sensor ID.s_vts = ov13850_auto_adjust_fps, //自动调节刷新率.set_flip = ov13850_set_flip, //设置sensor镜像.configs = ov13850_onelane_configs, //单lane的配置信息(分辨率,刷新率等).num_configs = ARRAY_SIZE(ov13850_onelane_configs),.configs = ov13850_configs, //多lane的配置信息.num_configs = ARRAY_SIZE(ov13850_configs),.power_up_delays_ms = {5, 20, 0},/**0: Exposure time valid fileds; 曝光时间*1: Exposure gain valid fileds; 曝光增益*(2 fileds == 1 frames)*/.exposure_valid_frame = {4, 4}};
上面设置的回调基本都是去设置寄存器。
(3)打开数据流
static int ov13850_start_streaming(struct ov_camera_module *cam_mod){int ret = 0;ov_camera_module_pr_debug(cam_mod,"active config=%s\n", cam_mod->active_config->name);ret = ov13850_g_VTS(cam_mod, &cam_mod->vts_min);if (IS_ERR_VALUE(ret))goto err;mutex_lock(&cam_mod->lock);ret = ov_camera_module_write_reg(cam_mod, 0x0100, 1); //写0x0100寄存器, 选择streaming模式 0:standby 1:streamingmutex_unlock(&cam_mod->lock);if (IS_ERR_VALUE(ret))goto err;msleep(25);return 0;err:ov_camera_module_pr_err(cam_mod, "failed with error (%d)\n",ret);return ret;}
主要就是操作寄存器,开启数据流传输。其他的一些操作函数也基本类似。
我们从上面的内容中可以看出,sensor端的驱动没有特别复杂,主要是一些参数和控制相关的内容。sensor主要是生产数据,而数据的处理主要交给ISP。
end
一口Linux
关注,回复【1024】海量Linux资料赠送
精彩文章合集
文章推荐