一、标准库“引子”:
1、操作符"<<"的原生意义是按位左移,例如:
1<<2
它的意义是将整数1按位左移2位,即:
0000 0001 演变成 0000 0100
重载左移操作符,将变量或者常量左移到一个对象中
代码示例:
#include
const char endl = '\n';
class Console
{
public:
Console& operator <<(int i)
{
printf("%d\n",i);
return *this;
}
Console& operator << (char c)
{
printf("%c\n",c);
return *this;
}
Console& operator <<(const char* s)
{
printf("%s\n",s);
return *this;
}
Console& operator << (double d)
{
printf("%f\n",d);
return *this;
}
};
Console cout;
int main()
{
cout<<1 << endl;
cout<<"TXP"<
double a = 0.1;
double b = 0.2;
cout << a + b <
return 0;
}
运行结果:
root@txp-virtual-machine:/home/txp# ./a.out
1
TXP
0.300000
从上面我们可以看到,不直接使用printf函数去打印这个值,这个以前在书上,都是直接讲解把数值说送到输出流中去,但是你一开始学习cout函数(或者说你还没有接触到对象的时候,根本不明白这什么意思);如果进行了左移的重载之后,那么程序将产生神奇的变化,所以在 main() 中不用 printf() 和格式化字符串 '\n' 了,因为编译器会通过重载的机制会为我们选择究竟使用哪一个重载机制。
二、c++标准库:
1、标准库的特性:
C++标准库并不是C++语言的一部分
C++标准库是由类库和函数库组成的集合
C++标准库中定义的类和对象都位于std命名空间中
C++标准库的头文件都不带.h后缀,当然也兼容c语言里面的.h写法
C++标准库涵盖了C库的功能
2、C++编译环境的组成:
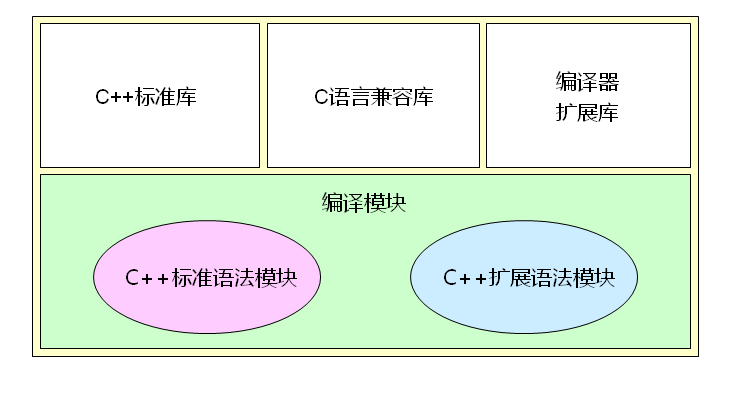
3、C++标准库预定义了很多常用的数据结构:
- -<set> -
- - -
- - -
- -
代码示例:
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;//所谓命名空间,是一种将程序库名称封装起来的方法,它就像在各个程序库中立起一道道围墙
int main()
{
printf("Hello world!\n");
char* p = (char*)malloc(16);
strcpy(p, "TXP");
double a = 3;
double b = 4;
double c = sqrt(a * a + b * b);
printf("c = %f\n", c);
free(p);
return 0;
}
输出结果:
root@txp-virtual-machine:/home/txp# ./a.out
Hello world!
c = 5.000000
注:关于命名空间的介绍,这里没有详细的去介绍,后面会重新做一个详细介绍。
4、cout和cin两个函数形象比喻:
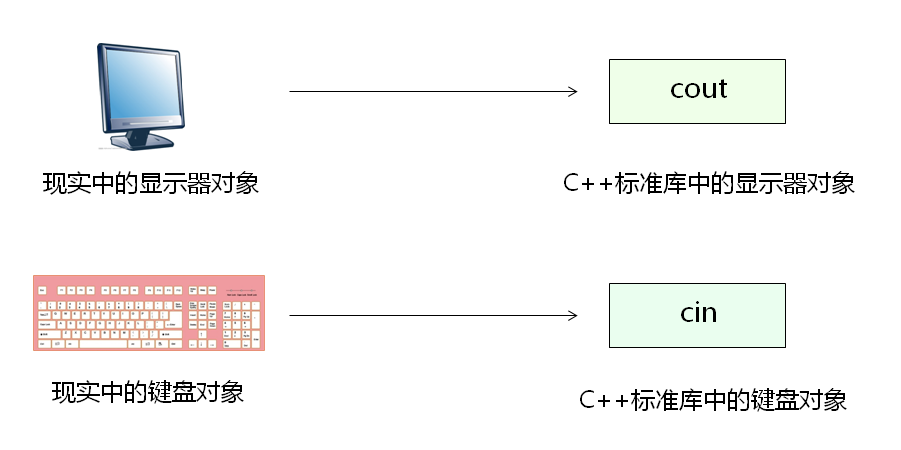
代码示例:
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
cout << "Hello world!" << endl;
double a = 0;
double b = 0;
cout << "Input a: ";
cin >> a;
cout << "Input b: ";
cin >> b;
double c = sqrt(a * a + b * b);
cout << "c = " << c << endl;
return 0;
}
结果输出:
root@txp-virtual-machine:/home/txp# ./a.out
Hello world!
Input a: 3
Input b: 5
c = 5.83095
当然这里关于cout和cin两个函数里面的细节也没有写明;不过如果接触过C++的朋友,现在看起来,现在这种写法,更加c++正统一点,之前的写法都是c写法,除了类的写法之外。
三、总结:
C++标准库是由类库和函数库组成的集合
C++标准库包含经典算法和数据结构的实现
C++标准库涵盖了C库的功能
C++标准库位于std命名空间中